How can raw dark web data be turned into actionable cybersecurity plans? Learn essential monitoring locations, the path from data to intelligence, and key tools.
This article is also published on my Medium page.
In previous articles, we discussed techniques for monitoring and scraping data from the dark web. We also reviewed the legal ramifications and Department of Justice guidelines to ensure that these activities remain within the law. Building on that foundation, this article delves into transforming the raw data collected from the dark web into actionable intelligence.
Dark Web Monitoring: Marketplaces, Forums, & Chat Rooms
Effective monitoring of the dark web demands a targeted approach, honing in on specific sites, channels, and forums that are critical to cybersecurity. Let’s dive deeper into these essential areas, providing a nuanced perspective along with real-world examples of what exactly to keep an eye on.
Marketplaces
The dark web’s marketplaces are infamous for their vast array of illicit offerings, from narcotics to stolen data. Keeping a vigilant eye on these hubs is crucial for gathering intelligence about the types of data being targeted and understanding the current trends in buying and selling prices. Example: Vigilance on platforms like 2Easy or OMG!OMG! Market is key; look for mentions of your organization’s domain or employee details, which could signal potential data breaches.
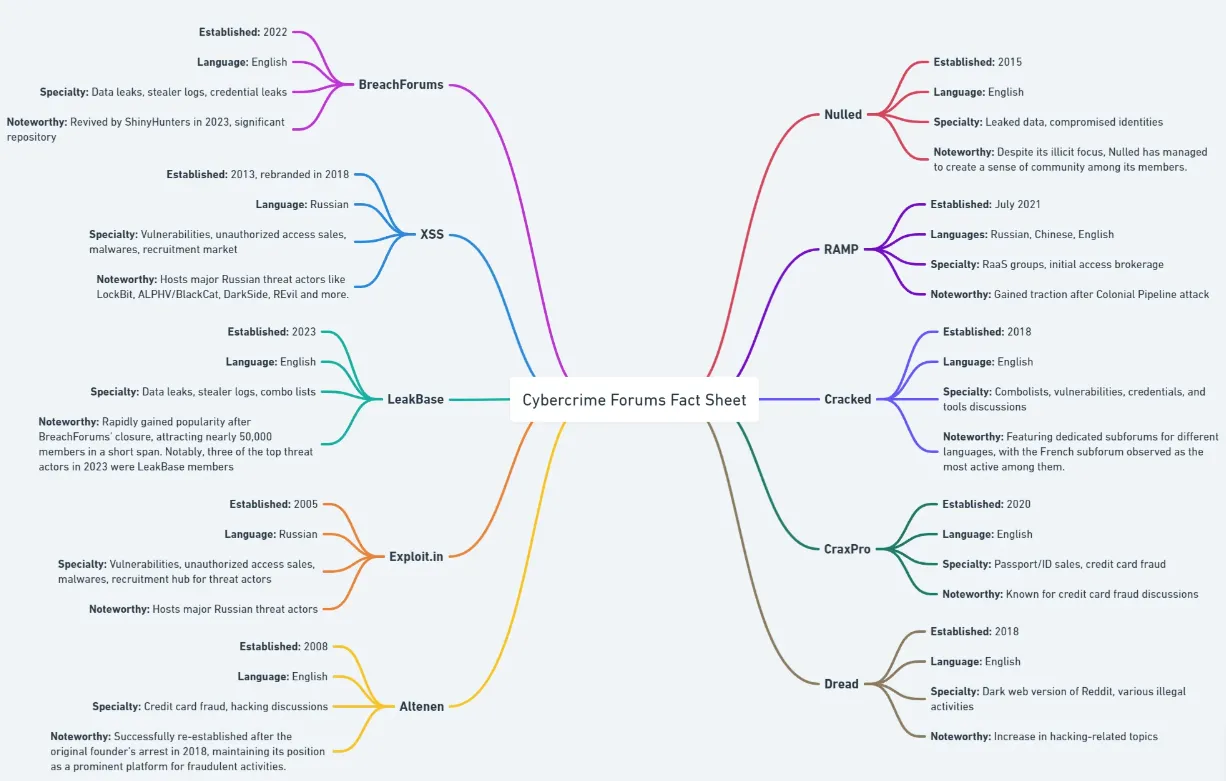
Forums
Regarded as hotbeds for cybercriminal activity, forums are where tactics, vulnerabilities, and exploits are openly discussed and shared. Example: Engaging in forums such as XSS and BreachForums can provide insights into the latest security threats and vulnerabilities that may affect your systems, informing you of necessary updates and patches.
Chat Rooms
Platforms like Telegram and Discord serve as rapid communication tools for cybercriminals, facilitating the exchange of information and coordination of activities. These venues are critical for understanding the dynamics of current and emerging cyber threats. Example: By monitoring specific channels known for distributing hacking tools and stolen credentials and setting up alerts for specific keywords related to your organization, you can proactively detect and respond to threats.
By sharpening the focus of your monitoring strategies and paying close attention to these pivotal areas, your organization can effectively thwart and mitigate the myriad threats that originate from the dark web, thereby maintaining a proactive defense posture against cyber threats.
Raw Dark Web Data to Actionable Intelligence: A Guide
Extracting actionable intelligence from raw data is a critical process that requires several key steps. Each step builds upon the previous to refine the data and enhance its value, culminating in intelligence that can significantly influence decision-making.
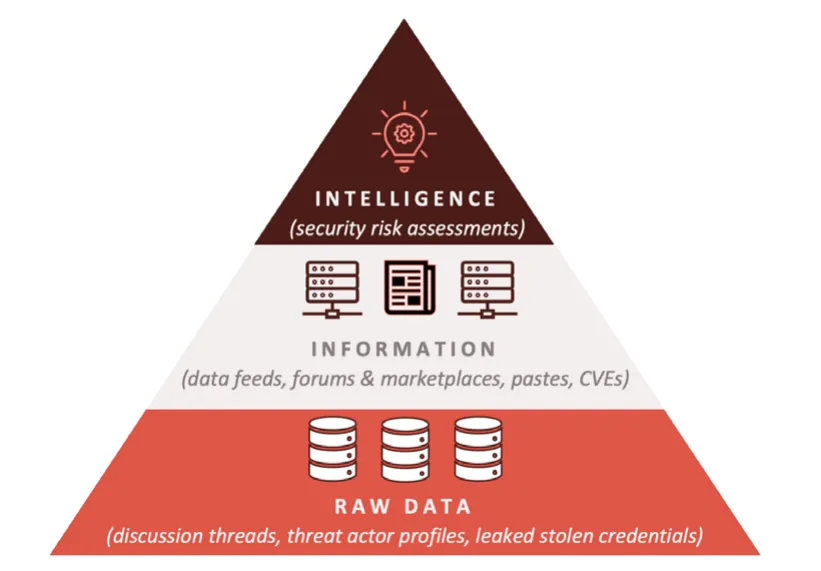
Data, Information, Intelligence: Key Differences
-
Data: These are the raw facts and figures collected without any context. For instance, consider a list of leaked email addresses and passwords found on a dark web forum.
-
Information: This is when data is processed and organized to add meaning and context, such as categorizing leaked data by company domains to identify affected organizations.
-
Intelligence: This stage involves analyzing the contextual information to aid decision-making. It could determine the impact of a data leak on organizational security or pinpoint the likely source of the breach.
Dark Web Intelligence: Collection, Analysis, Action
-
Collection: Utilizing both automated tools and human intelligence, data is gathered from various dark web sources, including forums, marketplaces, and chat rooms. For example, an automated scraping tool might collect posts from a dark web marketplace that mentions a new exploit for popular software.
-
Processing: The collected data is organized into a structured format to facilitate analysis, often categorizing it by type, source, and content. An example here could be cataloging data from the marketplace to distinguish between different types of exploits, associated software, and posting dates.
-
Analysis: This step involves evaluating the organized information to identify patterns, trends, and actionable insights. This process turns the processed information into intelligence by contextualizing and assessing its implications. For instance, an analysis might reveal that an exploit is newly developed, targets a widespread vulnerability not yet covered by mainstream security patches, and is gaining traction among cybercriminals.
-
Dissemination: The final step is sharing the developed intelligence with stakeholders to enable informed decisions. This might include detailed reports, briefs for decision-makers, or real-time alerts. For example, a cybersecurity team might prepare a detailed report on a new exploit, including mitigation strategies and urgent patch recommendations, and then circulate it to IT departments and company leadership to initiate rapid response measures.
The Recorded Future Intelligence Graph. Source: Recorded Future on YouTube.
By leveraging threat intelligence, you not only fight threat actors and data breaches but also equip your security teams to anticipate and preempt them. This approach ensures that every piece of data, once contextualized and analyzed, transforms into a powerful tool for strengthening your cybersecurity posture. It illustrates the importance of understanding the attacker, their motivation, capabilities, and behavior, and keeping an eye out for potential Indicators of Compromise (IoC).
Challenges in Dark Web Monitoring
Navigating the complexities of dark web monitoring is fraught with significant challenges. Each operation layer presents unique hurdles that can obstruct the path to obtaining actionable intelligence.
Dynamic Nature
Challenge: Dark web sites’ ephemeral nature poses a significant hurdle; they frequently shut down and re-emerge under different names and URLs to evade detection by law enforcement and cybersecurity teams. Example: A dark web marketplace dealing in stolen data may be accessible via one URL today and then vanish, only to reappear under a different URL the following week.
Access Restrictions
Challenge: Many dark web spaces operate like exclusive clubs, where entry is granted only to those with established reputations or specific referrals from current members. Example: Entry into a prestigious hacking forum might require new members to obtain endorsements from well-known participants or demonstrate their technical prowess, which helps keep undercover agents and potential informants at bay.
Persona Cultivation
Challenge: Successfully infiltrating these closed communities often necessitates creating and maintaining a credible online persona. This process involves not only aligning with the community’s norms and objectives but also navigating a minefield of legal and ethical considerations, demanding a considerable investment of time and careful strategy. Example: Establishing trust within a cybercriminal network may involve sharing advanced hacking techniques or even participating in cyber-attacks. These activities straddle the delicate line between intelligence gathering and ethical transgressions. For detailed guidance on how to navigate these legal complexities while researching the dark web, refer to my article, “A Boring (But Essential) Article Every Cybersecurity Pro Must Read: DOJ on Dark Web Law.” This will help ensure that you remain within legal boundaries.
Outsourcing Dark Web Monitoring: Expert Services
Given these formidable challenges, many organizations opt to leverage specialized third-party services like Flare, DarkOwl, or Flashpoint. These providers are adept at dark web monitoring and intelligence and equipped with the necessary tools and expertise to adeptly navigate these murky waters. They skillfully manage the risks associated with persona cultivation, watch the ever-changing landscape of the dark web, and navigate access restrictions with relative ease. By outsourcing these tasks, organizations can tap into vital intelligence without exposing themselves to the operational risks and ethical dilemmas often accompanying direct engagement in dark web operations.
Dark Web Intelligence: Your Cybersecurity Advantage
Extracting actionable intelligence from the dark web’s shadows is no easy task. It demands a unique mix of technical expertise, unwavering ethical awareness, and strategic vision. As we’ve explored in this guide, monitoring key areas such as marketplaces, forums, chat rooms, and even social media platforms provides a comprehensive view of potential threats. The meticulous process of turning data into intelligence — through collection, processing, analysis, and dissemination — enables organizations to respond to emerging threats proactively rather than react to breaches post-incident.
However, the inherent challenges of dark web monitoring — from the dynamic nature of its platforms to the difficulties in persona cultivation — pose significant barriers. These obstacles underscore that it is worth considering third-party services like Flare, DarkOwl, or Flashpoint, which specialize in the nuances of dark web operations. By outsourcing these tasks, organizations not only safeguard themselves against the direct risks associated with dark web engagement but also enhance their capability to derive meaningful insights from the chaos of cyber underworld activities.
Whether you decide to develop and maintain your own dark web monitoring tools or opt for the expertise of a third-party service, navigating the complexities of the dark web is crucial to modern cybersecurity strategies. It’s a terrain filled with hazards and opportunities; mastering it can turn potential threats into actionable intelligence. Advanced tools and refined analysis are indispensable, yet the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats demands continual adaptation and vigilance. In this digital age, securing our systems isn’t just about shielding against attacks — it’s about turning the dark web from a battlefield of risks into a mine of invaluable insights.
Explore Next
Discover how blockchain is transforming industries on the Blockchain Insights Hub. Follow me on Twitter for real-time updates on the intersection of blockchain and cybersecurity. Subscribe now to get my exclusive report on the top blockchain security threats of 2024. Dive deeper into my blockchain insights on Medium.