In this article, we will be breaking down what the Arbitrum network brings to Ethereum to make it much more scalable, offering users a lot more performant ecosystem for investing in Ethereum. At this time, Arbitrum stands at the top of the best layer 2 networks ranking for Ethereum and has garnered significant amounts of attention and interest from the Ethereum community calling it the future of scaling for the Ethereum blockchain. In this blog post, we will be diving into what it is and how it has accomplished all of this.
Disclaimer: Nothing I mention here should be considered financial advice. Investments like Cryptocurrency pose significant market risks and the readers are advised to do their own research before performing any transactions. The writer is not responsible for any sort of damage or problems caused.
Introduction

The core problem of the Ethereum network is that it is not very scalable. While it has improved now, with their latest Dencun Upgrade and the Merge Upgrade prior to it, the Ethereum network still struggles to process a lot of transactions if they occur at the same time and considering how important it is for transactions to go through instantly and to increase the number of transactions per second the Ethereum network can handle, the L2 layer scaling solutions [covered in my blog posts] have popped up out of which Arbitrum is one of the best choices which boosts the performance of the network and is said to be able to handle 40k transactions per second which is a lot more than what the standalone Ethereum network [also known as an L1 network] can handle.
Arbitrum is a Layer 2 scaling solution designed to address the challenges of slow and expensive transactions on the Ethereum blockchain. It operates by offloading as much work and data storage as possible from Ethereum's mainnet (Layer 1) to a Layer 2 network, thereby reducing network congestion and transaction costs. This approach is facilitated through the use of Optimistic Rollups [covered in my blog posts], a technology that allows for the processing of transactions off-chain while still maintaining the security and decentralization of the Ethereum network.
By implementing Optimistic Rollups, Arbitrum enables faster and cheaper transactions by processing them off-chain and only submitting the final state to the Ethereum mainnet. This method significantly reduces the load on the Ethereum network, allowing for a higher throughput of transactions without compromising on security or decentralization. Arbitrum's compatibility with Ethereum Virtual Machines (EVMs) also facilitates the deployment of decentralized applications (dApps) on its network with minimal code modifications, making it an attractive option for developers looking to leverage the benefits of Layer 2 scaling.
Arbitrum's approach to scaling is part of a broader ecosystem of Layer 2 solutions designed to enhance the scalability, speed, and efficiency of the Ethereum blockchain. These solutions, including Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups, aim to address the blockchain trilemma, which posits that blockchain networks must choose between scalability, security, and decentralization. By focusing on scalability and efficiency, Arbitrum and other Layer 2 solutions contribute to the overall health and sustainability of the Ethereum ecosystem, enabling it to support a wider range of applications and users without sacrificing its core principles of security and decentralization.
How Does the Arbitrum Network Work?
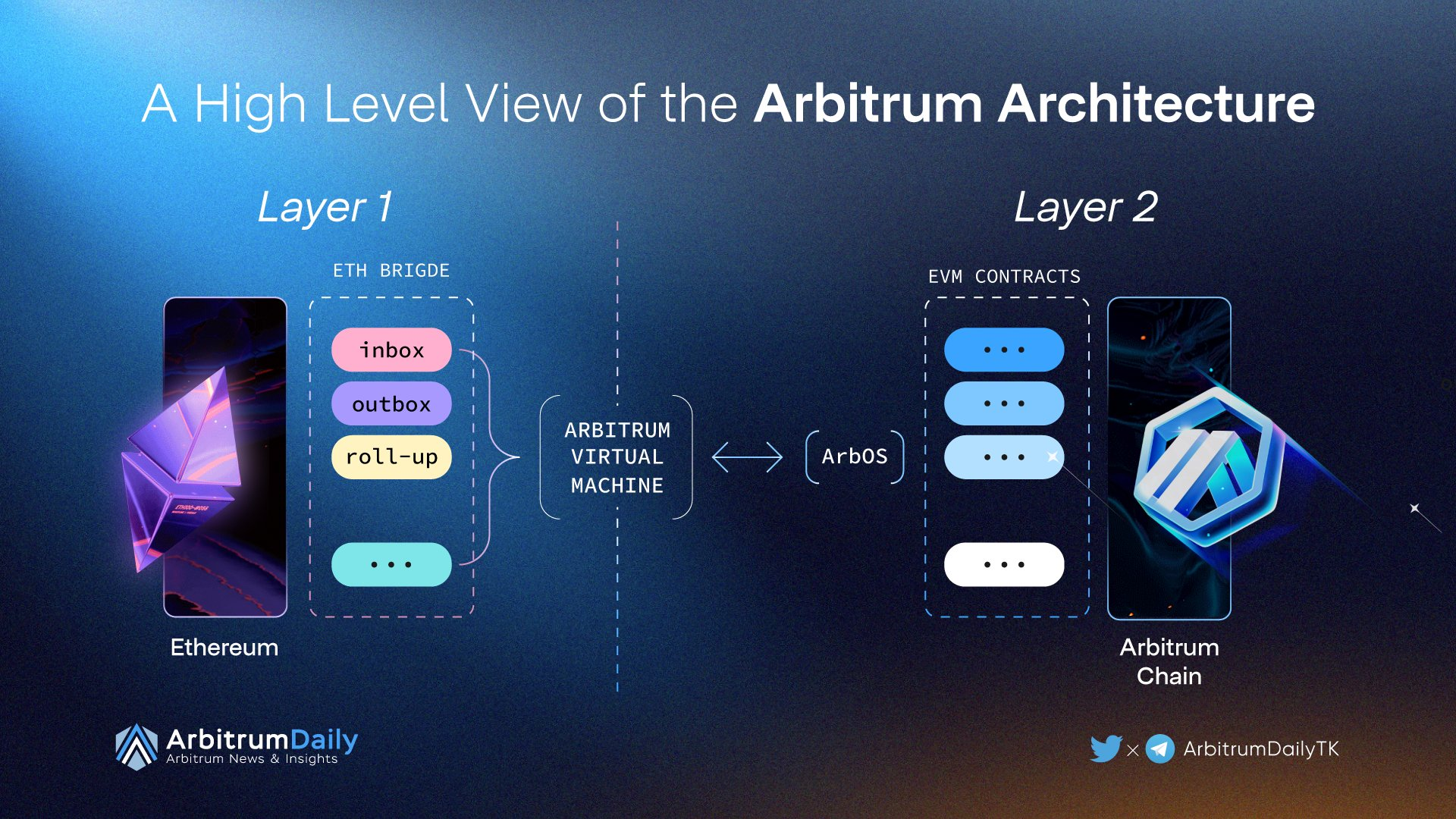
Arbitrum is a Layer 2 scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain that uses Optimistic Rollups to enhance scalability, reduce transaction fees, and improve overall network performance. Here's a clear understanding of how Arbitrum works:
-
User Transactions: Users initiate transactions on the Arbitrum network. These transactions are initially processed off-chain, which means they are not directly recorded on the Ethereum mainnet (Layer 1).
-
Batching Transactions: The transactions are collected by a batcher node, typically the sequencer. Once enough transactions are gathered, they are submitted to an Ethereum smart contract on the mainnet as a batch.
-
Processing Transactions: A validator node reads these transactions from the smart contract and processes them on a local copy of the Layer 2 (L2) state. This process is done off-chain, which significantly reduces the load on the Ethereum mainnet.
-
Updating L2 State: After processing, the validator generates a new L2 state locally and posts this new state root into another Ethereum smart contract. This step updates the L2 state on the mainnet, reflecting the outcomes of the transactions.
-
Verification by Other Validators: The Other validators on the network process the same transactions on their local copies of the L2 state. They compare their resultant L2 state root with the one posted to the mainnet. If there's a discrepancy, a challenge is initiated.
-
Challenges and Resolution: Now, coming back to the challenge initiation, it is in general performed If a validator's state root differs from the one posted to the mainnet. The challenger and the validator who posted the original state root take turns proving the correct state root. This process continues until the contested part of execution is only one instruction long. In the event of a discrepancy, a multi-round fraud-proof is initiated. The challenger and the validator who posted the original state root take turns proving the correct state root. This process continues until the contested part of execution is only one instruction long. At this point, a one-step proof is executed, and the block whose state matches the one-step proof wins the challenge. The losing block's stake is slashed.
-
Finalization: Once the challenge is resolved, the new L2 state is finalized. This process ensures that only valid transactions are added to the L2 chain, maintaining the integrity and security of the network.
-
Benefits: By processing transactions off-chain and only posting the final state to the Ethereum mainnet, Arbitrum significantly increases the network's throughput and reduces transaction costs. This approach allows for many more transactions to be processed, thereby lowering gas costs and improving the overall scalability of the Ethereum network.
-
Interactive Proving: Arbitrum's use of interactive proving for challenges offers several advantages, such as no limits on contract size, which are not present in other rollup implementations. This feature enhances the network's flexibility and efficiency.
-
Validator Nodes and Staking: The Validators must stake a certain amount of ETH to submit new L2 state data to the rollup. This staking system penalizes validators that submit invalid state data, ensuring the integrity of the L2 chain.
-
Native OS and EVM: The Arbitrum network uses its virtual machine (AVM) and operating system (ArbOS) to manage and track the resources of smart contracts used during execution. The AVM is designed to support compatibility with EVM-compiled smart contracts and includes features like CodePoints to facilitate the execution of challenges.
In summary, Arbitrum's Optimistic Rollup works by processing transactions off-chain, updating the L2 state, and verifying the state through challenges and resolutions. This process, combined with the use of interactive proving, AVM, and ArbOS, enhances the scalability and efficiency of the Ethereum network.
Arbitrum vs Other L2 Scaling Solutions

Arbitrum stands out as the best Layer 2 scaling solution overall right now due to its unique combination of features that address the core challenges of Ethereum's scalability, security, and developer experience. Here's why Arbitrum is considered the best Layer 2 solution and how it compares to other solutions like Optimism and ZK-rollups:
Why Arbitrum is the Best Layer 2 Scaling Solution
-
Optimistic Rollups: Arbitrum utilizes Optimistic Rollups, a technology that allows for the processing of transactions off-chain while maintaining the security and decentralization of the Ethereum network. This approach significantly reduces the load on the Ethereum mainnet, enabling higher transaction throughput and lower fees.
-
Multi-round Fraud Proofs: Unlike Optimism, which uses a single-round fraud-proof system, Arbitrum employs multi-round fraud proofs. This method not only enhances security but also optimizes transaction processing, potentially offering users savings on gas fees.
-
Ecosystem and Developer Experience: Arbitrum has established itself as a leading platform in the DeFi space, with a large share across DeFi applications. This ecosystem support and compatibility with Ethereum's Virtual Machine (EVM) make it easier for developers to migrate their dApps to Arbitrum, enhancing the overall developer experience.
-
Interactive Proving: Arbitrum's interactive proving mechanism for challenges offers several advantages, such as no limits on contract size, which are not present in other rollup implementations. This feature enhances the network's flexibility and efficiency.
Comparison with Other Layer 2 Solutions
-
Optimistic Rollups: While Optimism also uses Optimistic Rollups, it simplifies the transaction validation process with a single-round fraud-proof system. This approach might lead to faster transaction finality but could incur higher gas fees on the Ethereum main chain. Arbitrum's multi-round fraud proofs aim to balance speed, cost, and security more effectively.
-
ZK-Rollups: ZK-rollups, like those used by Polygon, offer arguably better security and potentially even lower fees due to their use of zero-knowledge proofs. However, they have different infrastructural complexities and ecosystem support compared to Arbitrum. Arbitrum's compatibility with Ethereum's EVM and its established ecosystem make it a more accessible choice for developers and users.
Unique Features of Arbitrum
-
Established Ecosystem: Arbitrum benefits from a more established ecosystem of dApps and complex smart contracts, which can be a significant advantage for developers looking to deploy their applications on a platform with a proven track record.
-
Optimistic Rollups: Arbitrum's use of Optimistic Rollups allows it to process transactions off-chain while still maintaining the security and decentralization of the Ethereum network. This approach significantly reduces the load on the Ethereum mainnet, enabling higher transaction throughput and lower fees.
-
Interactive Proving: Arbitrum's interactive proving mechanism for challenges offers several advantages, such as no limits on contract size, which are not present in other rollup implementations. This feature enhances the network's flexibility and efficiency.
In summary, Arbitrum's combination of Optimistic Rollups, multi-round fraud proofs, established ecosystem, and interactive proving mechanism make it the best Layer 2 scaling solution overall. Its approach balances speed, cost, and security, offering a compelling platform for developers and users alike.
Arbitrum Ecosystem

The Arbitrum ecosystem is a dynamic and rapidly growing Layer 2 scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain, offering a range of products and services designed to enhance scalability, reduce transaction fees, and improve overall network performance. Here's an in-depth look at the major components of the Arbitrum ecosystem, including Arbitrum One, Nitro, Nova, the Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM), and ArbOS.
Arbitrum One
Arbitrum One is the official mainnet of the Arbitrum ecosystem, launched on August 31st, 2021. It powers the entire ecosystem and processes transactions on the Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM), an extension compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This compatibility ensures that developers can deploy their Ethereum-based applications on Arbitrum with minimal modifications, facilitating a smooth transition for existing projects and attracting new developers to the platform.
Arbitrum Nitro
Arbitrum Nitro is a major technical upgrade to the underlying technology of Arbitrum One. Introduced on August 31st, 2022, Nitro aims to make the ecosystem faster, more EVM-compatible, and cheaper. It achieves these goals by introducing interactive proofs that run over the WebAssembly (WASM) code used by Arbitrum. This upgrade allows developers to use standardized EVM-compatible languages and run unmodified EVM contracts, significantly expanding the development scope and attracting more developers to the platform.
Arbitrum Nova
Arbitrum Nova is a new chain within the Arbitrum ecosystem that focuses on reducing individual transaction costs by minimizing data storage on the Ethereum blockchain. Unlike Arbitrum One, which stores full transaction data on Ethereum, Nova uses Ethereum to store only data signatures from third-party storage providers like Infura and Google Cloud. This approach makes Nova more centralized but significantly reduces transaction fees and increases scalability, making it particularly useful for applications with high transaction volumes but low individual transaction values, such as games and social dApps.
Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) and ArbOS
The Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) is a key component of the Arbitrum ecosystem, designed to be compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This compatibility ensures that developers can deploy their Ethereum-based applications on Arbitrum with minimal modifications, facilitating a smooth transition for existing projects and attracting new developers to the platform. The AVM includes features like CodePoints to facilitate the execution of challenges, enhancing the network's flexibility and efficiency.
ArbOS, or Arbitrum Operating System, is the operating system for the Arbitrum network. It manages and tracks the resources of smart contracts used during execution, ensuring the integrity and security of the Layer 2 chain. ArbOS is designed to support the efficient execution of transactions and challenges, further enhancing the scalability and efficiency of the Arbitrum network.
Arbitrum Token ($ARB)
The Arbitrum token is an ERC-20-compatible governance token for the Arbitrum blockchain. It serves multiple purposes including transferring value, investing, and voting on governance decisions. The ARB token has become a significant part of the Arbitrum ecosystem, with anticipated airdrops in 2023 targeting active users who meet specific criteria.
In summary, the Arbitrum ecosystem, including its major products like Arbitrum One, Nitro, and Nova, along with the Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) and ArbOS, plays a crucial role in enhancing the scalability, security, and efficiency of the Ethereum network. The introduction of Nitro and Nova further expands the ecosystem's capabilities, catering to a wide range of applications and use cases, from traditional Ethereum dApps to high-volume, low-value transactions.
Deep-dive Into The Key Components of the Arbitrum Ecosystem

1. Arbitrum Nitro
Arbitrum Nitro represents a significant upgrade to the Arbitrum ecosystem, introducing advanced features and optimizations that enhance scalability, efficiency, and compatibility with the Ethereum network. Here's a detailed breakdown of its architecture and the rationale behind its design:
Core Features and Optimizations
-
Advanced Calldata Compression: Nitro significantly reduces transaction costs by minimizing the amount of data posted to the Ethereum mainnet (Layer 1). This is achieved through advanced calldata compression techniques, which reduce the size of transaction data.
-
Separate Contexts for Common Execution and Fault Proving: Nitro introduces separate contexts for the execution of transactions and the proving of faults. This separation improves the performance of Layer 1 nodes, leading to lower fees and faster transaction processing.
-
Ethereum L1 Gas Compatibility: Nitro ensures that the gas costs on Arbitrum are perfectly aligned with those on the Ethereum mainnet. This compatibility makes it easier for developers to estimate costs and manage resources effectively.
-
Additional L1 Interoperability: Nitro enhances the synchronization with Layer 1 block numbers and provides full support for all Ethereum Layer 1 precompiles. This interoperability ensures that dApps on Arbitrum can interact seamlessly with the Ethereum mainnet.
-
Safe Retryables: Nitro addresses a common failure mode in rollup protocols where a retryable ticket fails to get created. This feature eliminates such failures, improving the reliability of the system.
Arbitrum Nitro Virtual Machine (VM) Architecture
Arbitrum Nitro's VM architecture is a multi-VM model, where each VM has its state and runs independently from others. This design ensures that the execution of one VM does not impact others, allowing for efficient batching of many steps of computation together. Each VM is executed as a sequence of assertions, which are claims about the execution of several steps within the VM.
Optimized Data Structures
Nitro introduces improvements in data storage and structure, including the use of Sequencers and a Reduced Ordered State Tree (ROST). SRBlocks hold the inputs of user transactions but not the transaction outputs, significantly reducing the amount of data required to be stored on-chain. ROST is a more compact and efficient data structure for representing the state of VMs, leading to substantial reductions in gas costs for block submission and increases in the speed at which validators can process blocks.
To conclude, Arbitrum Nitro presents a compelling approach to scaling Ethereum by maintaining security and decentralization. Its sophisticated architecture and thoughtful optimizations bring immense promise to the evolution of Layer 2 solutions. As developers, understanding the intricacies of Arbitrum Nitro can open up new possibilities and paradigms in building efficient and scalable DApps on the Ethereum network
2. Arbitrum One
Arbitrum One is a Layer 2 (L2) optimistic rollup chain that significantly enhances the scalability, efficiency, and security of the Ethereum network. It achieves this through a unique architecture and technology stack, which includes several key components and mechanisms. Here's a detailed breakdown of its architecture and how it contributes to the Arbitrum ecosystem:
Core Components of Arbitrum One
-
Optimistic Rollup Protocol: At the heart of Arbitrum One is the implementation of the Optimistic Rollup protocol. This protocol allows for the processing of transactions off-chain while maintaining the security and decentralization of the Ethereum network. It does so by batching transactions and posting their outcomes to the Ethereum mainnet (Layer 1), significantly reducing the load on the mainnet and enabling higher throughput and lower fees.
-
Nitro Technology Stack: Arbitrum One utilizes the Nitro technology stack, which is designed to provide advanced features and optimizations. This includes calldata compression, separate contexts for common execution and fault proving, and Ethereum L1 gas compatibility. The "Geth-at-the-core" architecture of Nitro ensures that Arbitrum One can offer a high degree of compatibility with Ethereum's infrastructure and tooling, making it easier for developers to build and deploy their dApps on the network.
-
Validator and Challenger System: Arbitrum One employs a system where validators and challengers continuously split the disputed part of a transaction in a binary fashion off-chain until the dispute is narrowed down to a specific part. This multi-round interactive design allows for efficient dispute resolution on the Ethereum mainnet at a low cost, ensuring the integrity and security of the network.
-
Arbitrum One Block Explorer: The Arbitrum One Block Explorer is an open-source web tool that synchronizes with the Arbitrum One network, allowing users to view information about blocks, transactions, and addresses on the network. This tool is crucial for transparency and user engagement, enabling users to interact with the network and verify transactions.
Architecture
Arbitrum One's architecture is indeed complex and sophisticated, designed to enhance the scalability, efficiency, and security of the Ethereum network. Here's a detailed breakdown of its architecture:
Optimistic Rollup Protocol
At the core of Arbitrum One is the implementation of the Optimistic Rollup protocol. This protocol allows for the processing of transactions off-chain while maintaining the security and decentralization of the Ethereum network. It achieves this by batching transactions and posting their outcomes to the Ethereum mainnet (Layer 1), significantly reducing the load on the mainnet and enabling higher throughput and lower fees.
Nitro Technology Stack
Arbitrum One utilizes the Nitro technology stack, which is designed to provide advanced features and optimizations. This includes:
-
Calldata Compression: Reduces the size of transaction data, making it more efficient to process and store.
-
Separate Contexts for Common Execution and Fault Proving: This separation allows for more efficient processing of transactions and challenges, improving the overall performance of the network.
-
Ethereum L1 Gas Compatibility: Ensures that the gas costs on Arbitrum One are compatible with those on the Ethereum mainnet, making it easier for developers to estimate costs and manage resources.
Validator and Challenger System
Arbitrum One employs a system where validators and challengers continuously split the disputed part of a transaction in a binary fashion off-chain until the dispute is narrowed down to a specific part. This multi-round interactive design allows for efficient dispute resolution on the Ethereum mainnet at a low cost, ensuring the integrity and security of the network.
To conclude, Arbitrum One stands as a pivotal Layer 2 (L2) solution for the Ethereum ecosystem, offering a robust and secure platform for developers to build high-performance decentralized applications (dApps) with significantly reduced transaction costs and Ethereum-grade security guarantees. Its architecture, underpinned by the Nitro technology stack, ensures compatibility with Ethereum's infrastructure, making it a seamless choice for developers looking to leverage the scalability and efficiency of Layer 2 solutions without compromising on the security and decentralization of the Ethereum network.
3. Arbitrum Nova
Arbitrum Nova introduces a novel approach to scaling the Ethereum network, focusing on decentralized social and gaming applications (dApps) with a unique architecture that emphasizes performance, affordability, and a minimal trust assumption. Here's a detailed breakdown of its architecture and the rationale behind its design:
AnyTrust Protocol
Arbitrum Nova implements the AnyTrust protocol, a mostly trustless approach that introduces an additional trust assumption in the form of a Data Availability Committee (DAC). This committee is responsible for expediting the process of storing, batching, and posting Layer 2 (L2) transaction data to Ethereum's Layer 1 (L1). This design allows Arbitrum Nova to be used in scenarios that demand performance and affordability, while Arbitrum One remains optimal for scenarios that demand Ethereum's pure trustlessness.
Data Availability Committee (DAC)
The DAC plays a crucial role in Arbitrum Nova's architecture. It ensures data availability for end users by signing Data Availability Certificates (DACs) for batches of transactions. These certificates are then stored on a smart contract on the Ethereum chain, significantly reducing the amount of data stored on Ethereum compared to Arbitrum One, where the entire transaction data is stored. This approach not only lowers transaction costs but also accelerates the process of making transactions available on the Ethereum mainnet.
Minimal Trust Assumption
Arbitrum Nova assumes that at least two members of the DAC committee are honest and will provide the necessary data. This minimal trust assumption is a key feature of the AnyTrust protocol, allowing for efficient and secure transaction processing without the need for full trustlessness. It balances the need for security with the practical requirements of scalability and performance.
Nitro Technology
Arbitrum Nova utilizes Nitro technology, which allows for the execution of fraud proofs by running EVM code on top of WebAssembly (WASM). This integration ensures compatibility with Ethereum's smart contracts and enables the execution of complex operations efficiently. However, it's important to note that there's a risk of funds being lost if there are mistakes in the Nitro and WASM one-step prover process.
EVM Compatibility
Arbitrum Nova supports EVM-compatible smart contracts, making it easier for developers to deploy their existing Ethereum dApps on the network. This compatibility is achieved through the Nitro technology stack, which facilitates the execution of EVM code on top of WASM, enhancing the platform's flexibility and developer-friendliness.
To conclude, Arbitrum Nova represents a significant advancement in the Arbitrum ecosystem, offering a high-performance, mostly trustless solution for decentralized social and gaming applications. Its unique architecture, leveraging the AnyTrust protocol and a Data Availability Committee, addresses the scalability and performance challenges of the Ethereum network. By assuming minimal trust in the DAC committee and utilizing Nitro technology for efficient execution, Arbitrum Nova provides a compelling option for developers looking to build and deploy dApps that require high throughput and low transaction costs.
4.ArbOS
ArbOS is the operating system that powers the Arbitrum blockchain. It is specifically designed to execute smart contracts and process transactions on the second layer (L2) network. ArbOS works in conjunction with the Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) to provide a seamless and compatible environment for developers to deploy and run their decentralized applications (dApps).
Layered Architecture
ArbOS follows a layered architecture, which helps in organizing and separating different components of the operating system. The layered architecture allows for modularity, scalability, and ease of maintenance. While specific details about the architecture of ArbOS are not readily available, we can draw insights from general software architecture principles.
In a layered architecture, different layers handle specific responsibilities. These layers can include the data layer, domain layer, business logic layer, and presentation layer. The data layer is responsible for interacting with external APIs and managing data storage. The domain layer transforms the data received from the data layer into a format suitable for processing. The business logic layer manages the state of the data, often using frameworks like flutter_bloc, and the presentation layer renders the user interface components based on the state.
Compatibility with Ethereum
ArbOS is designed to be fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This compatibility allows developers to leverage their existing knowledge of Ethereum development tools, languages, and frameworks when building applications on Arbitrum. Developers can write smart contracts in popular languages such as Vyper, Solidity, Flint, YUL+, and LLLL, and deploy them on the Arbitrum network without significant modifications.
Transaction Processing and Scalability
ArbOS, in combination with the Arbitrum Nitro Stack, addresses the scalability challenges faced by the Ethereum network. The Arbitrum Rollup variant of the Nitro Stack aggregates multiple transactions into a single batch and submits cryptographic proof to the Ethereum mainnet. This approach significantly reduces transaction costs and improves throughput, allowing for a higher number of transactions to be processed in a given time frame.
Security and Trust
ArbOS aims to maintain the security standards of the Ethereum network while providing scalability. It achieves this by leveraging the security of the Ethereum mainnet through the use of cryptographic proofs. The security of the Arbitrum network is further enhanced by the consensus mechanisms and cryptographic protocols implemented in the underlying technology stack.
Conclusion
ArbOS is the operating system that powers the Arbitrum blockchain. It follows a layered architecture, providing modularity and scalability. ArbOS is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing developers to leverage existing Ethereum tools and languages. It addresses scalability challenges through transaction aggregation and cryptographic proofs. The security of ArbOS is maintained by leveraging the security of the Ethereum mainnet and implementing robust consensus mechanisms and cryptographic protocols.
5. Arbitrum Virtual Machine [AVM]
The Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) is a custom virtual machine that serves as the execution environment for smart contracts on the Arbitrum blockchain. It is designed to be fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing developers to write and deploy Ethereum-compatible smart contracts on the Arbitrum network with ease.
Compatibility with Ethereum
The AVM is designed to be compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine at the bytecode level. This means that developers can write smart contracts using popular Ethereum programming languages such as Solidity and Vyper and deploy them on the Arbitrum network without significant modifications. The AVM ensures that Ethereum-compatible smart contracts are automatically translated to run on the Arbitrum network.
Multi-Language Support
One of the key features of the AVM is its support for multiple programming languages. Developers can write smart contracts in languages like Rust, C, and C++ in addition to the traditional Ethereum languages. This allows developers to leverage their existing knowledge and skills in these languages, making it easier to build on the Arbitrum network without the need to learn a new programming language like Solidity or Vyper.
Scalability and Efficiency
The AVM, in combination with the Arbitrum protocol, addresses the scalability limitations of the Ethereum network. By utilizing optimistic roll-up technology, Arbitrum achieves high throughput and low transaction fees. The AVM allows for the aggregation of multiple transactions into a single batch, which is then processed off-chain. Once the batch is verified and validated, a cryptographic proof is submitted to the Ethereum mainnet, ensuring the security and integrity of the transactions. This approach significantly improves scalability and reduces transaction costs compared to the Ethereum network.
Security and Trust
The AVM incorporates various security measures to ensure the integrity and trustworthiness of smart contract execution. It utilizes a challenge-based protocol to identify and penalize dishonest parties that attempt to manipulate the behavior of a smart contract. Validators and miners on the Arbitrum network verify the digital signatures and confirm that parties have agreed on the behavior of a smart contract. In case of disagreement, honest parties can advance the state of the virtual machine on-chain, ensuring that the system remains secure and reliable.
Thus, The Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) is a custom virtual machine that serves as the execution environment for smart contracts on the Arbitrum blockchain. It is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and supports multiple programming languages, including Rust, C, and C++. The AVM, in combination with the Arbitrum protocol, addresses scalability challenges by utilizing optimistic roll-up technology and cryptographic proofs. It incorporates security measures to ensure the integrity and trustworthiness of smart contract execution.
Security and Governance of Arbitrum

Arbitrum, a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, has implemented various security measures to ensure the safety and integrity of its protocol. One notable security feature is the use of hardware wallets. Hardware wallets provide an added layer of protection by storing private keys offline, making it difficult for malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to funds or manipulate transactions. By utilizing hardware wallets, Arbitrum enhances the security of user assets and reduces the risk of potential vulnerabilities associated with software-based wallets.
Security Measures
Arbitrum has implemented robust security measures to safeguard the integrity and safety of its protocol. One significant security feature is the utilization of hardware wallets. Hardware wallets store private keys offline, providing an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access and potential vulnerabilities associated with software-based wallets. By employing hardware wallets, Arbitrum enhances the security of user assets and minimizes the risk of malicious activities.
Governance Model: The Arbitrum DAO
The governance model of Arbitrum is based on a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) known as the Arbitrum DAO. This DAO, built on the Ethereum blockchain, serves as a community-driven governance mechanism for the Arbitrum network. The Arbitrum DAO allows $ARB token holders to actively participate in proposing and voting on changes to the organization and the technologies it governs.
Role of $ARB Token in Governance
The $ARB token, an ERC-20 governance token, plays a vital role in the governance process of Arbitrum. Token holders can utilize their $ARB tokens to vote on proposals within the Arbitrum DAO. The voting power of each token holder is proportional to the amount of $ARB they hold or represent, ensuring a democratic decision-making process where decisions reflect the collective voice of the token holders.
Functions and Powers of the Arbitrum DAO
The governance scope of the Arbitrum DAO covers various aspects of the Arbitrum ecosystem. This includes:
-
Protocol Upgrades: The DAO has the authority to propose and approve upgrades to the Arbitrum protocol. These upgrades can enhance functionality, improve security, or introduce new features to the network.
-
Funds Allocation: The DAO decides how funds within the Arbitrum ecosystem are allocated. This includes the distribution of resources for development, research, marketing, and other initiatives that support the growth and sustainability of the network.
-
Technical Changes: The DAO can propose and vote on technical changes to the Arbitrum infrastructure, ensuring that the network remains adaptable to evolving needs and challenges.
The Security Council
The Arbitrum DAO delegates certain powers to the Security Council, a team responsible for addressing critical risks associated with the Arbitrum protocol and ecosystem. The Security Council's powers are granted by the DAO and are exercised in the best interests of the DAO and the broader Arbitrum community. This delegation allows for efficient risk management and timely response to potential security threats.
Token Distribution and Airdrop
To foster a decentralized governance structure, the $ARB governance token was initially distributed through an airdrop to a diverse set of stakeholders in the Arbitrum ecosystem. This distribution aimed to ensure broad ownership and geographical diversity among token holders, enabling a more inclusive and representative governance process.
In conclusion, Arbitrum implements stringent security measures, such as the use of hardware wallets, to protect user assets. The governance model revolves around the Arbitrum DAO, where $ARB token holders actively participate in proposing and voting on changes. The $ARB token plays a critical role in the governance process, allowing token holders to shape the direction and evolution of the Arbitrum network. The delegation of powers to the Security Council enhances risk management and ensures the security of the ecosystem.
Tokenomics of the $ARB Token

The $ARB token, the native token of the Arbitrum ecosystem, has the following tokenomics:
Initial Supply: The initial supply of the $ARB token is set at 10 billion tokens.
Inflation Rate: The $ARB token has a maximum yearly inflation rate of 2%. This ensures a gradual increase in the token supply over time.
Token Distribution: The distribution of the $ARB token is as follows :
-
Investors receive 17.53% of the token supply.
-
DAOs in the Arbitrum ecosystem receive 1.13% of the token supply.
-
Individual wallets receive 11.62% of the token supply.
-
DAO Treasury receives 42.78% of the token supply.
-
Team, future team, and advisors receive 26.94% of the token supply.
Utility of $ARB Token
Beyond transferring value, the $ARB token has utility within the Arbitrum ecosystem, including:
Voting Rights: $ARB token holders can participate in the governance process of the Arbitrum network. They can submit their votes on proposals within the Arbitrum DAO, influencing decisions related to protocol upgrades, funds allocation, and technical changes.
Governance Participation: Holding $ARB tokens grants individuals a seat at the governance table, allowing them to actively shape the direction and evolution of the Arbitrum ecosystem.
It's worth noting that the Arbitrum DAO, as a self-executing governance model, conducts all voting on-chain without the need for intermediaries. This ensures a transparent and decentralized decision-making process.
In conclusion, the $ARB token has a defined tokenomics structure, including an initial supply of 10 billion tokens, a maximum yearly inflation rate of 2%, and a distribution among various stakeholders. Beyond transferring value, the $ARB token provides voting rights and governance participation within the Arbitrum ecosystem, allowing token holders to actively shape the future of the network.
Conclusion

Importance of Arbitrum in Solving Ethereum's Scaling Problem
Arbitrum is a Layer 2 scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain that addresses the scalability challenges faced by the network. It aims to increase transaction throughput, reduce transaction costs, and improve overall efficiency. Here are some key points highlighting the importance of Arbitrum in solving Ethereum's scaling problem:
1. Scalability, Decentralization, and Security: Arbitrum aims to solve the blockchain trilemma by providing scalability, decentralization, and security. It achieves this through rollups, a type of Layer 2 solution. Rollups like Arbitrum allow for increased transactional throughput while preserving the fundamental properties of blockchain technology.
2. Compatibility with Ethereum: Arbitrum is designed to be compatible with Ethereum, allowing developers to leverage Ethereum's security while benefiting from the scalability provided by Arbitrum. This compatibility ensures a seamless transition for existing Ethereum applications to the Arbitrum ecosystem.
3. Lower Network Congestion and Transaction Costs: Arbitrum offloads much of the work and data storage from Ethereum's mainnet or Layer 1 (L1), resulting in lower network congestion and transaction costs. By delegating complex computational tasks to the second chain, Arbitrum reduces congestion on the main network and improves the overall user experience.
4. Adoption by DeFi Projects: Arbitrum has gained significant adoption within the decentralized finance (DeFi) space. Projects like Sushiswap and Aave utilize Arbitrum to offer efficient swaps with lower gas fees. This adoption demonstrates the practical benefits of using Arbitrum for DeFi applications, enhancing the accessibility and affordability of decentralized finance.
Impact on the Blockchain Ecosystem
Arbitrum's emergence as a prominent Layer 2 solution has had a significant impact on the blockchain ecosystem. Here are a few key points highlighting its impact:
1. Improved Transaction Speed and Cost-Effectiveness: The Arbitrum Ecosystem offers significant improvements in transaction speed and cost-effectiveness. By reducing network congestion and transaction costs, Arbitrum enhances the overall efficiency of the Ethereum blockchain, making it more accessible to a wider range of users and applications.
2. Attracting Diverse Range of Projects: Since its launch, Arbitrum has attracted a diverse range of projects, including decentralized applications (dApps) and decentralized finance protocols. The growing ecosystem of projects utilizing Arbitrum demonstrates its appeal and potential to address the scalability challenges faced by the Ethereum network.
3. Decentralized Governance: The Arbitrum DAO plays a crucial role in the governance of the Arbitrum protocol. It allows individuals across the ecosystem to participate in governance decisions, including protocol upgrades, funds allocation, and the election of a Security Council. This decentralized governance model ensures that the community has a voice in shaping the future of the Arbitrum ecosystem.
Future Outlook for Arbitrum
Arbitrum has shown promising potential as a Layer 2 scaling solution within the Ethereum ecosystem. Its compatibility with Ethereum, focus on scalability, and adoption by various projects position it as a key player in addressing Ethereum's scaling challenges. While facing competition from other Layer 2 solutions like Polygon and Optimism, Arbitrum's unique features, such as the Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM), set it apart and could prove advantageous in the evolving landscape of blockchain technology.
As the ecosystem continues to grow and evolve, Arbitrum is expected to play a significant role in enabling faster, more cost-effective, and scalable transactions on the Ethereum network.