The Dencun upgrade, originally scheduled for October 2023, has been continually postponed due to various reasons. According to the latest updates, the Dencun upgrade is now set to take place on March 13, 2024. In preparation for this, the Ethereum client Geth released version v1.13.12 on February 9, laying the groundwork for the Ethereum mainnet’s Dencun hard fork (Danksharding).
This upgrade marks a pivotal moment for Ethereum, aiming to further scale its capacity and increase the transaction throughput of the network. It also signifies the beginning of a new phase in the development of Ethereum’s data storage and retrieval capabilities.
Following the completion of the upgrade, the gas fees required for digital asset transactions on Ethereum Layer 2 networks will see a significant reduction, potentially up to 14 times lower. This performance enhancement resulting from the upgrade promises substantial benefits for Ethereum’s long-term development.
What is the Dencun Upgrade?
The Dencun upgrade represents the next phase of upgrades for Ethereum following the Shanghai upgrade. Named after the city where the Ethereum developers’ conference is held, the Dencun upgrade incorporates several critical Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) aimed at addressing the blockchain trilemma and enhancing performance and user experience.
Key EIPs included in the Cancun upgrade:
EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding) paves the way for a complete implementation of Danksharding, a significant step forward in Ethereum’s scalability journey.
EIP-1153 aims to save on-chain data storage costs and make more efficient use of block space.
EIP-4788 aims to strengthen the architecture of cross-chain bridges and staking pools, enhancing security and functionality.
EIP-5656 proposes subtle yet significant modifications to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to improve performance.
EIP-6780 advocates for deprecating the SELFDESTRUCT function, eliminating the ability to terminate smart contracts through this code.
These EIPs collectively contribute to a broader vision for a more scalable, cost-effective, and robust Ethereum network.
The Core of the Dencun upgrade — EIP-4844
The introduction of EIP-4844 (also known as Proto-Danksharding) holds the promise of improving transaction processing speed and volume, particularly beneficial for Layer 2 solutions built on the Ethereum main blockchain.
Scalability is the primary goal of Ethereum’s expansion efforts, aiming to increase data processing capacity and speed. Currently, Ethereum has two main approaches in this direction: Layer 2 rollup solutions and mainnet sharding solutions. The complete sharding solution involves three steps, with EIP-4844 being the first step.
Sharding is the most promising solution for L1 scaling in public chains. Previous Ethereum sharding 1.0 solutions have been abandoned due to data synchronization and MEV issues. Danksharding introduces a new sharding solution, focusing on achieving “centralized block production + decentralized verification + censorship resistance”, turning Ethereum into a settlement layer and data availability layer, leaving room for improvement in L2 computing performance.
Danksharding focuses on scalability around Layer 2 Rollup. This new sharding solution can solve scalability issues while minimizing the burden on nodes and ensuring decentralization and security.
EIP-4844 introduces new transaction types, known as Blob-carrying transactions. EIP-4844 can be seen as adding another separate data layer (actually a consensus layer) to Ethereum, which can increase data availability capacity and reduce costs.
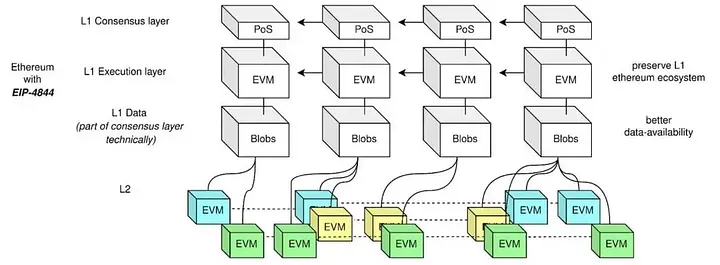
Potential Opportunities in Ethereum Layer 2
01 Optimistic Rollup
Currently, Arbitrum and Optimism are leading the Optimistic Rollup sector, but EIP-4844 may provide more opportunities for smaller Optimistic Rollup solutions such as Metis, Boba, Blast, and Manta.
In early 2024, the locked-in value of encrypted assets on the Arbitrum One mainnet chain exceeded $10 billion, with approximately 50% of the TVL market share, maintaining its position as the leader among many Layer 2 projects.
Arbitrum One has nearly 700 ecological projects recorded on its network, many of which have great potential, such as EMC, a project focused on AI DePIN, which has gained considerable attention recently, combining AI with DePIN and RWA concepts, and is expected to develop rapidly in the AI era.
From the perspective of TVL, Op Mainnet is the second-largest network in the current Layer 2 market, second only to Arbitrum.
Base is a Layer 2 built by Coinbase based on OP Stack. As of February 1st, the TVL was $723 million, and the number of ETH stored across chains has reached 320,000.
02 ZK Rollup
With technological updates, the ZK sector is expected to receive more attention. Current star projects in the ZK sector include ZkSync, Starknet, Polygon zkEVM, Linea, and Scroll.
03 Storage
EIP-4844 will benefit L1 storage extension networks. L1 storage extension networks are essentially the same as existing L2 solutions, both of which are solutions to improve L1 performance and scalability.
EthStorage, as the first Layer 2 solution with storage extension as its core, aims to reuse the security of the Ethereum mainnet, regularly submitting storage proofs from the EthStorage Layer 2 network to Ethereum L1, greatly expanding Ethereum storage at a lower cost.
In addition, projects such as Arweave, Filecoin, Celestia, Avail, EigenDA, NearDA, Covalent, Storj, BNB Greenfield, etc., in the Ethereum data availability layer (DA layer) and storage layout are also worth paying attention to.
04 RaaS
In the RaaS sector, customized RaaS is most likely to succeed. The rise of RaaS depends heavily on ecosystem construction, and mature RaaS must be able to meet the customized rollup needs of all projects. Therefore, in the end, multiple RaaS may occupy the market. Therefore, the RaaS will see a full competitive pattern based on ZK multi-layer networks and OP ecosystem construction.
After EIP-4844, various services related to Rollup will expand the market to a certain extent, and the implementation of EIP-4844 will further reduce the cost of L2 Rollup, and the difference in cost and efficiency brought by RaaS will be further reduced. In the future, RaaS can be customized to achieve privacy functions on the basis of Rollup and even Rollup of rollup.
The noteworthy ones include OP Stack, Polygon CDK, ZK Stack, Caldera, Conduit, Lumoz, and AltLayer, among others.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the Ethereum Dencun upgrade on March 13 is an important step forward for the Ethereum network, focusing on enhancing scalability, security, and availability, providing a transformative solution to Ethereum’s blockchain trilemma.
As a precursor to the Dencun upgrade, EIP-4844 opens a new chapter in Ethereum L1 sharding, reducing transmission costs between L1 and L2, achieving lower gas fees, higher TPS, and directly benefiting the Rollup ecosystem and Layer 2. Ethereum’s competitiveness will be further enhanced, and we look forward to a more prosperous ecosystem and killer applications in the future.

