Introduction
-
A thesis on why the ‘Data Economy’ and attracting data projects to a blockchain should be second in priority after Decentralized Finance.
-
Today, energy is the backbone of the global economy, intertwining everything we use and produce in our daily lives, from industrially produced commodities and mobility to cooking our food. However, with advancements in solar and battery, the marginal cost of energy production is literally a near-zero cost phenomenon. Consequently, I believe Data(Data Assets) will replace Energy as the backbone of the global economy.
-
Returning to the comparison between blockchains and nation-states, access to affordable and reliable energy plays a crucial role in a nation's competitiveness. When energy costs approach near zero, access to data will then become a nation's competitive advantage. Hence, a nation-like blockchain's access to data will be its MOAT.
-
This thesis emphasizes why blockchains should prioritize the Data Economy for on-chain activity and can even serve as a foundational research platform for blockchains that are strongly considering tapping into the data economy
Prerequisites: Basic understanding of web3
Table of contents
-
First Principles - What’s Blockchain & Data
-
Why Blockchain + Data?
-
Access, reliability & traceability
-
Value creation
-
With the emergence of IoT & AI, Consumers evolving into prosumers
-
Data Dilemma
-
-
Trends to note, and accordingly align strategic priorities
-
Data Privacy
-
Expansion of Data-Driven revenue streams: Collection, sharing, & analyses
-
Data Security
-
Data Synchronicity
-
Data Ownership & Portability
-
Data Governance, DAOs as Data Trusts
-
-
What interesting projects do we see in the space?
-
Data Marketplaces - Data DeFi
-
New business lines with existing data
-
Data DAO/Unions
-
Data Tokens
-
Data Wallets
-
Marketing & Advertising in a cookieless world
-
Privacy projects
-
Composable & Reusable Data
-
Blockchain-ready sensor technologies
-
Public-Private Data Partnerships
-
-
The road to perpetually sustainable crypto economic activity
-
Architecture
-
Stack
-
The data economy will be deployed in(chains)
-
Priority framework for a blockchain
-
-
Conclusion
- How should Blockchains Strategize
What’s Blockchain & Data?
What is data? - Data is a collection of discrete values that convey information. It describes attributes like quantity, quality, facts, statistics, etc that may be further interpreted. Data is the smallest factual unit of information. When such information is processed, analyzed, and connected with other pieces of information we get data-driven insights or intelligence. Hence, Data can be regarded as the atom of decision-making. It is used in scientific research, finance, and almost every form of human organization.
What is a blockchain? - A blockchain is a database or ledger that is distributed among the nodes of a p2p computer network. As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in a digital format. Data stored in blockchains is tamper resistant, has better accuracy, and is peer-reviewed. It facilitates the exchange of data, aka “transactions”. Blockchain leverage protocols, a set of rules that govern the blockchain network, it is a set of economic incentivization mechanisms that in turn manifest and accrue $Value . They are a set of guidelines that facilitate & incentivize information exchange in a secure, fast, simple, p2p & trustless way.
Why blockchain & data?
It's no secret that Blockchain and Data Science go hand-in-hand. Blockchain technology aims to create a secure and decentralized system for managing data, while ‘Data Science’ focuses on analyzing and understanding data. A great way to illustrate the relationship between blockchains and data is to think of a token (any ERC standard) as a wrapper for various types of data, ranging from a picture to a Netflix show or even a LinkedIn subscription. In the case of NFTs, every data item becomes non-fungible, assigned a unique ID, stored on the blockchain, governed by protocols, and valued through cryptocurrencies.
When modern data management and blockchains are combined, the possibilities are truly endless.
Access, reliability & traceability
Access to reliable data is a powerful tool that can be used to solve complex problems, such as predicting cancer years in advance. Unfortunately, less than 1% of the world's data is currently analyzed, and there are challenges with reliability and accuracy. While we have great AI models, they require vast amounts of reliable data to be more effective.
Presently, data is often collected and stored in isolated servers controlled by the platforms that gather it. This creates issues regarding data reliability and challenges in verifying its origin for data consumers. However, blockchain technology offers solutions to these problems by leveraging traceability, peer-to-peer (p2p) components, consensus mechanisms, incentivization, and tokenization features.
By utilizing a blockchain, real-world data can be recorded more effectively while ensuring its reliability. The consensus mechanism and immutability of the blockchain eliminate the need for trust in a central entity or middleman to validate the authenticity of the data.
Value Creation
Data is often referred to as the new oil, and the combination of blockchains and data allows us to extract the maximum value from this valuable resource. Thought leaders like Shermin Voshmgir envision blockchain networks as data-driven economies. As modern society increasingly spends time in the digital realm, recording more interactions with data on a public blockchain, rather than on existing isolated systems like SaaS platforms and two-sided marketplaces, we can create the internet of value. This serves as the foundational infrastructure for a globalized digital economy, promoting a free market and democratic structure.
Tokenomics, which involves cryptocurrency mechanisms, further enhances the value creation of data. Currently, value creation is primarily seen in two-sided marketplaces. For example, on LinkedIn, we pay for a sales navigator because it provides a data repository of the business ecosystem. Similarly, b2c brands pay for marketing on Instagram because it offers a data repository of user behavior patterns, which brands utilize for targeted advertisements.
However, blockchains and cryptocurrencies have the potential to transform data into its own asset class—a paid resource accessible to everyone and a sellable commodity producible by anyone.
To delve deeper into how startups can establish durable data moats, I recommend reading: 'How Can Startups Establish Durable Data Moats?'"
Emergence of IoT & AI. Consumer evolves into a Prosumer
Key trends to note: The emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) suggests that the data we capture and transfer through sensors, without human intervention, is poised to scale exponentially. This indicates that the role of data in our daily lives is set to become increasingly significant with each passing day

At the beginning of the 21st century, with the rise of tech platforms, millions of consumers became prosumers, producing their own information goods such as videos on YouTube, news blogs, and ebooks. This revolution disrupted traditional industries like television, news, and publishing, as the cost of information goods plummeted close to zero. With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), this trend has the potential to extend from information goods to physical goods(IoT-integrated 3D printing). While the exact manifestation is still uncertain, the trajectory is clear. Consider a smart inhaler equipped with sensors: any new startup that effectively leverages the data collected by its inhaler can drastically reduce its purchase cost, empower consumers to become prosumers, and challenge traditional brands in the manufacturing of such devices.
READ: The Zero Marginal Cost Society by Jeremy Rifkin
The opportunity to extract actionable insights from data using AI/ML will revolutionize various industries, including transportation, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail, and many more. AI training models not only demand vast amounts of data but also require a clear audit trail to ensure data quality.
Data Dilemma
On one hand, during the peak of the Covid-19 pandemic, extensive data capture, sharing, and analysis have proven to accelerate healthcare innovations, improve disease surveillance, and enable more informed public health decisions. On the other hand, instances of data misuse, such as the Cambridge Analytica scandal, highlight privacy breaches and demonstrate how data can be exploited, infringing upon individuals' freedom of choice. The use of data raises numerous questions, sparks contrary opinions, offers promising solutions, and evokes both utopian and dystopian visions. Data privacy, protection, and ownership have gained significant attention from corporations, regulators, governments, and consumers, aiming to prevent data concentration in the hands of a few entities.
While blockchain technology may not provide all the answers or an ideal solution, coupling modern data management with blockchain features—from encryption, smart contracts, and decentralization, to tokenization, secure wallets, and more—can lead us to a crucial milestone that ensures fairness for all stakeholders involved in the data value chain.
Trends to note, and accordingly align strategic priorities
Data Privacy
Blockchains are predominantly public in nature, requiring individuals or businesses to expose their wallet details (public address) when interacting and participating in protocols, such as receiving airdrops. This means that anyone can view the entire financial history and holdings associated with a public address. However, this shouldn't be the case. There is a growing need for innovation to enhance consumer protection, strengthen security, and safeguard people's privacy.
Web2 has conditioned people to trade their data and privacy for free and convenient internet services. Web3, powered with privacy, offers an alternative approach. In this new model, individuals can regain control over their data and selectively disclose personal information at their discretion. Privacy-enhancing solutions like zero-knowledge (ZK) and identity (ID) solutions add a crucial privacy layer to blockchain networks.
Expansion of Data-Driven revenue streams: Collection, sharing, & analyses
Enterprises that capitalized on the platform wave of the last decade have successfully built innovative business models around the data they collected, offering valuable services to users across the value chain. Examples include Google, Amazon, LinkedIn, and others. Enterprises that missed this trend, found themselves lagging behind in comparison.
Fortunately, the upcoming data landscape is wide open for competition and presents an opportunity to reclaim the edge. The emergence of sensors, digital-first customers, and smart devices presents a new opportunity for both established and emerging enterprises to diversify their revenue streams through data and gain a competitive edge. Eg- Ford harnessing and creating value of automobile or driver data
Many platforms, such as Bloomberg and Forbes, face challenges in converting freemium users into premium users. By developing a better understanding of ethical data collection and combining it with web3 circular economy monetization techniques (such as marketplace tokens or DAO networked businesses), these platforms can sustain and evolve, enjoying improved revenue benefits.
Data Security
With the advent of 5G technology, traditional platforms become more vulnerable to hacking. Centralized servers and databases pose a significant risk as they represent key single points of failure. In a distributed and decentralized ecosystem, data can be safeguarded more effectively, as it becomes exponentially more difficult to steal or manipulate data across multiple nodes.
Read: [Blockchains for better security]
Another intriguing approach to data security is token-controlled access and private vaults. While specific blockchain features like encryption and hashing are currently utilized, whether the data is attested to a blockchain remains a business secret. It's important to note that this is an example of permissioned blockchain features without crypto economics, at least as of today.
Read: [Visa Payment Tokenization]
Please note that while blockchain addresses temporary cybersecurity challenges, it also introduces a new set of crypto-economic security challenges that are constantly under debate, discussion, and resolution.
Data Synchronicity
Primarily an ERP use case, tailored for app-specific, sovereign blockchains. The lack of real-time data synchronization has resulted in a significant amount of administrative communication. This includes email exchanges, document transfers, and phone calls among various stakeholders. Let's consider the example of the marine insurance value chain, which typically involves the following steps:
-
A ship owner approaches a broker.
-
The broker engages an insurer.
-
The insurer takes on the risk and seeks another broker.
-
The broker finds a re-insurer to share the risk.
-
The re-insurer approaches another broker to find a retrocession insurer.
Insuring a vessel in the marine business often requires around 100 document transactions and involves approximately 50 different stakeholders throughout the value chain. Unfortunately, there is a lack of transparency in this process, leading to information loss. Furthermore, significant value leaks occur due to intermediaries in the value chain, who take a portion of the premium as it traverses through multiple entities. Transactional costs alone can account for up to 40% of the premium. This antiquated and inefficient system has left insurers' customers dissatisfied.
Blockchain technology, with its inherent tamper-proof data synchronization capabilities, has emerged as an early application to address these challenges. However, enterprise-level use cases like this have historically struggled to gain traction. This can be attributed to enterprises' reluctance to relinquish their walled gardens and their resistance to adopting public blockchain solutions. Herein lies the opportunity: by solving such use cases on a public blockchain with crypto-economic incentive mechanisms, an uncharted territory can be explored.
Data Ownership & Portability
When you go online to any application today, you'll find it running on a few different components: code, data (which includes all the information that populates the websites you see, such as user data and application data), and value mechanisms that enable business models. A significant portion of any online application, product, or service is driven by data. Platforms like Wikipedia, YouTube, Facebook, Airbnb, and Google are all built around information sourced from individual users. However, despite their contributions, the vast majority of internet users own less than 1% of the data they generate. This could be higher if not for the overhead costs of cloud infrastructure.
Enabling social networks to operate in a peer-to-peer (p2p) architecture, promoting community building and ownership, will fuel the next wave of value creation. User ownership serves as a powerful motivator for users to contribute to products in meaningful ways, whether through ideas, computing resources, code, or community building. The concept of user ownership lies at the core of the success of Bitcoin and Ethereum, as the first user-owned and operated networks at scale.
With the advent of interoperability, users can now move from one platform to another and take their data with them. For example, I can write this article on Mirror.xyz, store the data on a public blockchain like Arweave (owned by me), and publish it on another platform like Farcaster for distribution.
Data Governance - DAOs as Data Trusts
Trusts, which have long existed in property rights law, are legal structures that separate the legal ownership and control of the property from its equitable ownership and benefits. Data trusts apply a similar structure to data assets, appointing an independent body (such as a DAO) as a fiduciary or steward of the data asset on behalf of the data owner. These trusts aggregate data and unlock its value in a fair and transparent manner.
Data governance involves establishing decision rights and an accountability framework to ensure responsible behavior in the valuation, creation, consumption, and control of data and analytics. Traditional data governance frameworks often face challenges, including a lack of incentives and enforceability.
To address these challenges and create a standardized, effective data governance system, there is a need to shift toward incentive models. This is where blockchain technology plays a crucial role. The blockchain serves as a natural data governance platform, offering unique capabilities that can revolutionize existing practices. For example, I can be incentivized to wear a smartwatch and supply standardized health data. When this data is tokenized on the blockchain, it provides an audit trail that allows for traceability and ensures that it is not misused.
By leveraging blockchain's characteristics such as transparency, immutability, and decentralized control, data governance can be significantly improved. Blockchain provides a trustless environment where data integrity is assured, and decision-making processes are more transparent and auditable.
For further insights, I recommend reading about bottom-up data trusts and their role in disrupting the 'one size fits all' approach to data governance.
What are some interesting types of projects we see in the space?
Data Marketplaces - Data DeFi
A data marketplace is like an Amazon but for data sets, utilizing the decentralized finance (DeFi) architecture. It leverages data tokens to create a seamless connection between data providers, services, and consumers with DeFi - allowing the data ecosystem to be integrated into various financial products and services powered DeFi. On one end of the spectrum, there are consumers such as analytics, AI, and ML companies that require data sets to enhance their products, and they can also monetize their existing algorithms, analytics, and dashboards. On the other end, we have data providers, which can range from individual car drivers to average users of Google Chrome or enterprise companies hosting vast amounts of untapped data. These data providers can sell their data in a p2p marketplace and capitalize on this valuable resource.
In the traditional non-Web3 world, notable data marketplace projects include Snowflake Data Marketplace, European Data Union, and Data.gov. Within the Web3 ecosystem, we have innovative platforms like Acentrick, Ocean Protocol, and Xy Labs. Ocean Protocol, in particular, stands out as a progressive project aiming to make AI, algorithms, and data sets more accessible. At its core, Ocean Protocol operates as a two-sided marketplace, connecting data consumers and data providers through the use of the Ocean token. Acentrick, on the other hand, is a web3-native startup focused on enterprises. They assist enterprises in unlocking value by facilitating data sharing and also offer a white-label solution that can be adopted by other enterprises.
Examples in web2 - Snowflake Data Marketplace & web3 - Ocean Protocol, and Acentrick.
Note: Ocean Protocol is a comprehensive project encompassing data tokenization, access controls, Data NFTs, and Data Tokens, offering a wide range of capabilities in the data marketplace domain.
New business lines with existing Data
Data silos exist, but new business opportunities can be created. Banks can offer "identity-as-a-service" using customer data, charging retailers and fintech for verifying customer details. Collaborative projects like ConnectID and partnerships such as Mastercard with the Australian Post showcase the potential. A similar model can be built with web3 Identity solutions like Polygon ID and Kilt. Additionally, Web3 identity and reputation techniques, like Gitcoin Passports, open up endless possibilities.
Data Tokens
Data tokens serve as a bridge between data assets and DeFi tools, enabling a wide range of use cases with access control. Data has the potential to generate income for individuals, but the lack of an effective price signal has hindered its monetization. Data tokens aim to address this challenge by creating an open data economy, where data producers are incentivized to generate data, and buyers can easily access and purchase it. This concept has the potential to unlock new opportunities and promote the widespread production and exchange of valuable data.
Read: Data Tokens
Data Unions
A Data Union is an organization that crowdsources data. Here individuals contribute valuable data through an application. The data is then offered for sale on a marketplace, and members are rewarded with tokens for their contributions. By building a Data Union, you empower users to earn value from their data and incentivize them to use your app. Data Unions are particularly useful for collecting challenging datasets like real-time health data, web user data, pollution monitoring, smart city data, and more. Examples of Data Union platforms include Swash for browser data, dimo for smart cars, and unbanx for banking data.
Data Wallets
Dataswift and Alga are emerging projects in the field of data wallets, which aim to provide individuals with comprehensive control over their data. Similar to how a cryptocurrency wallet allows users to have full access and ownership of their digital assets, a data wallet empowers individuals to have complete control over their personal data. This concept applies the principles of ownership and control that are fundamental to web3 and extends them to the realm of data.

Marketing & Advertising in a cookieless world
Evolving data regulations and growing customer concerns about privacy are driving the phasing out of traditional digital ad targeting methods relying on third-party cookies. The rise of NFTs introduces a new paradigm for gaining customer insights. Prominent web3 marketing approaches include token or NFT airdrops. Eg- where users can participate by filling out forms to have a chance to win exclusive access to products or services.
However, it's important to note that tracking wallet addresses in web3 marketing campaigns may raise privacy concerns. Early movers in this space, such as Cookie3 and Adshares, offer innovative solutions. Cookie3 utilizes AI and ML tools to perform wallet scoring and on-chain activity analysis, enabling web3 projects to identify and engage ideal community members. Adshares, on the other hand, is a protocol built specifically for web3 advertising.
The integration of NFTs into social media platforms opens up a vast array of untapped marketing opportunities that are yet to be fully explored.
Note: refer to articles on Google phasing out third-party cookies and Pepsico's involvement in web3 marketing.
Privacy Projects
Blockchains are mostly public, exposing wallet details and financial history. Innovations are needed to enhance consumer protection, security, and privacy. Fortunately, solutions are fast arising, empowering individuals to control and selectively reveal their data. ZK and ID solutions add privacy to blockchain networks.
-
Zero Knowledge Airdrops - Projects often face the challenge of airdropping tokens to community members without requiring their public keys(preserving anonymity) and for off-chain activities. To address this, a system has been developed where prospective recipients provide commitments via public channels. A Merkle tree is then constructed using these commitments, and recipients can later claim their share by providing a zero-knowledge Merkle proof without revealing their specific commitment. This process ensures anonymity by mixing public addresses with other entitled users.
-
Programmable Privacy - Meta's partnership with Oasis Labs aims to utilize Oasis Labs' privacy layer and confidential computing capabilities to measure fairness in AI models. This involves computing data with smart contracts in a secure enclave, preventing transaction IDs and account addresses from being traced on analytics platforms and block explorers. Another project, Secret Network, is also working on similar initiatives. However, it is important to note that these projects are still in their early stages and may require several more years before achieving widespread market adoption.

Composable & Reusable Data
Ceramic Network is a project that seeks to expand the capabilities of data composability and reusability beyond web browsers. It aims to enable users to export and import their data across various social media and communication platforms such as Linkedin, Instagram, and Whatsapp. Ceramic simplifies the process of building applications with composable Web3 data by providing a marketplace of data models that can be seamlessly integrated into applications. This allows for storing, updating, and retrieving data from these models. Additionally, when multiple applications use the same data models, their data becomes interoperable. By decentralizing application databases, Ceramic promotes data composability and reusability across all applications.
Blockchain-ready sensor technologies
Integrating sensor technologies with blockchain can indeed enhance the capabilities and applications of existing blockchains. One practical instance for examples sake is the implementation of a decentralized and autonomous water management system in an apartment complex, aiming to improve allocative efficiencies and overcome the tragedy of the commons. (Duh, we’re running out of water and we don’t care :()
A combination of blockchains, protocols, and trusted sensors can be employed. Trusted sensors equipped with crypto chips provide tamper-proof digital identities, making them reliable sources of data. By leveraging this added trust, society can authorize an industrial robot to autonomously manage various tasks, including water consumption regulation.
For further information on this topic, you may explore resources such as RIDDLE&CODE + IOTA and the concept of smart meters. These sources delve deeper into the integration of blockchain and sensor technologies for improved water management and other related applications.
Public-Private data partnerships
Finding a balance between data protection and data-driven innovation is a “catch-22” that needs to be negotiated between governments & corporations. GaiaX is one such project that brings together representatives from various sectors such as policymakers, regulators, Enterprise C suite, and upcoming projects to develop a framework that promotes sovereignty and innovation for Europe’s data infrastructure. GaiaX is further broken down into light house projects that carry forward the GaiaX framework into their respective and specific industries. Center for the fourth industrial revolution is a similar initiative by the world economic forum. It is a global multi-stakeholder platform focused on inclusive technology governance and responsible digital transformation.
The road to perpetually sustainable crypto economic activity
Blockchain's role in the data ecosystem is indeed an evolving process that requires continuous trial and error and iterative improvements. The key objective should be aligning the ecosystem with the market's needs and addressing the challenges and requirements of data management effectively.
To achieve this, a protocol must ensure that most of the on-chain activities related to data, such as computation within smart contracts and transactions between users, occur on the blockchain infrastructure. This approach should be designed in way that it minimizes costs for users while maintaining fair decentralization, minimal trust, and security.
In terms of architecture,
-
one conceptualization involves designing an application on top of a protocol that operates on a sovereign chain, serving as a layer 3. This layer provides control, predictable operational costs, and avoids congestion within the network.
-
This layer can then communicate with layer 2 solutions like Polygon, Arbitrum, or Optimism, which offer scalability.
-
Finally, Ethereum serves as the base layer 1, providing decentralization and security.
By leveraging this multi-layered architecture, the data ecosystem can benefit from the strengths of each layer, ensuring efficient operations, scalability, and security while minimizing costs for users. It allows for flexibility in adapting to changing market needs and evolving technological advancements.
Stack
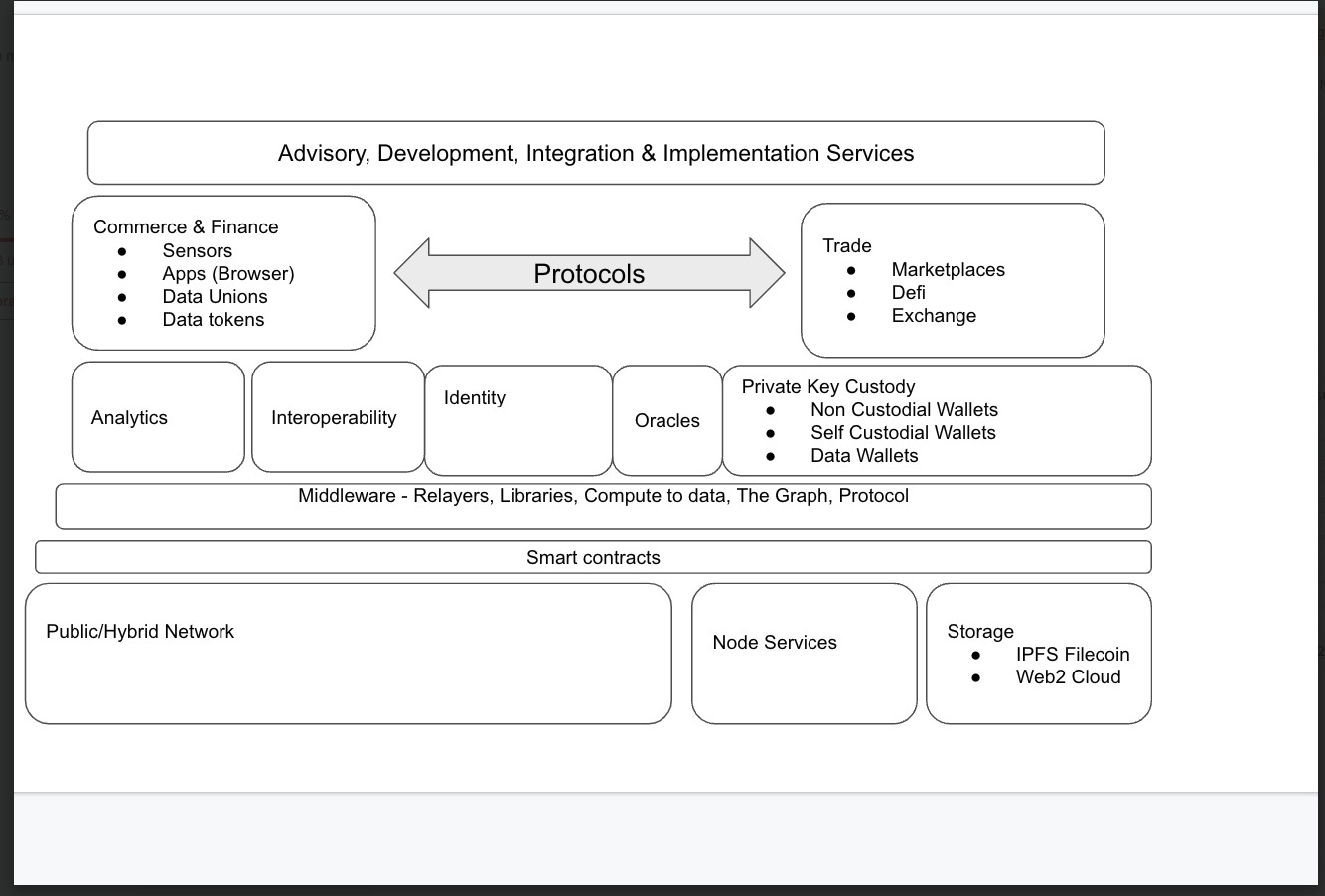
The data economy will be deployed in
-
Side-chains, sovereign chains, and rollups: These chains offer low transaction costs, high throughput, and leverage the security of the Ethereum network. They are well-suited for data applications that require high-volume computation and frequent trading of data sets.
-
Hybrid chains: Hybrid chains provide a flexible framework for use cases that require a faster time-to-market or additional security measures. They can strike a balance between public and permissioned features, while also offering more predictable operational costs in terms of gas fees.
-
Private chains: Privacy chains can address the privacy requirements of data projects. They allow for secure and private computations without revealing the underlying data.
-
NOTE-Identity frameworks: As identity plays a crucial role in data projects, having a robust Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) framework is important to meet compliance requirements. Projects like Acentrik emphasize the need for sound identity solutions to ensure privacy, security, and compliance in data-related activities.
By considering these components and designing a stack tailored to specific use cases, the data economy can benefit from optimized performance, scalability, privacy, and compliance. It's important to brainstorm and evaluate the most suitable combination of chains and technologies based on the specific requirements of each data project.
Conclusion
How should blockchains strategize
-
Enterprise Logo acquisition: The focus is on acquiring new enterprise partners and investors to enhance the blockchain's credibility and attract more participants to the ecosystem. (investors love enterprises)
-
Real Value Use Cases: Identifying and implementing use cases that bring together the solutions provided by the protocol, collaboration with ecosystem partners, addressing market problems, and most importantly aligning all the stakeholders with the values and philosophy of Web3 while maintaining pragmatism.
-
Find your Dapp: Every blockchain needs just one killer Dapp that is ready for mass adoption and can onboard the next billion users.
Metrics to consider
-
Total DApps: The number of decentralized applications built on the blockchain platform, indicating the level of developer activity and ecosystem growth.
-
Total Generators: The number of individuals or organizations generating data, services, or applications within the ecosystem, reflecting user engagement and innovation.
-
Total Wallets: The number of digital wallets holding tokens or assets on the blockchain, representing user adoption and participation.
-
Monthly active wallets: The number of wallets that engage in transactions or interactions within a given month, measuring user activity and retention.
-
Number of transactions: The total volume of transactions occurring on the blockchain, indicating the level of economic activity and usage.
-
Monthly NFT volume: The volume of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFT) transactions taking place on the blockchain, reflecting the popularity and demand for unique digital assets.
-
Speculative bets: Whether we like it on it, the industry is driven by speculation. If a project has less value but is good for public sentiment. It should be prioritized
-
Fundamental use case bets: Evaluating the adoption and success of blockchain applications that provide tangible value and solve real-world problems.
By following this framework and focusing on these priorities, blockchain platforms can tier-1 partnerships, drive real value through meaningful use cases, and achieve sustainable growth in the data-driven economy.

