Introduction
The Ethereum Pectra upgrade, launched in May 2025, introduced transformative changes to the network’s gas fee structure, most notably through blob transactions. While this upgrade enhanced Ethereum’s scalability for data-heavy applications, it also triggered significant volatility in gas fees and transaction costs. In this analysis, we combine onchain data from Dune Analytics with gas derivatives strategies to explore how stakeholders can navigate this new landscape and turn challenges into opportunities.
Key Onchain Insights Post-Pectra
1. Surging Transaction Costs
-
Average USD fee per transaction:
-
Pre-Pectra: $0.47 (30-day avg)
-
Post-Pectra: $1.06 (30-day avg)
-
Change: +125.5% increase in average fees.
-
-
Total fees paid:
-
Pre-Pectra: $20.27M over 37.3M transactions.
-
Post-Pectra: $48.89M over 42.5M transactions.
-
Change: +141% increase in total fees, despite only a +14% rise in transaction volume.
-
2. Gas Price Volatility Amplified
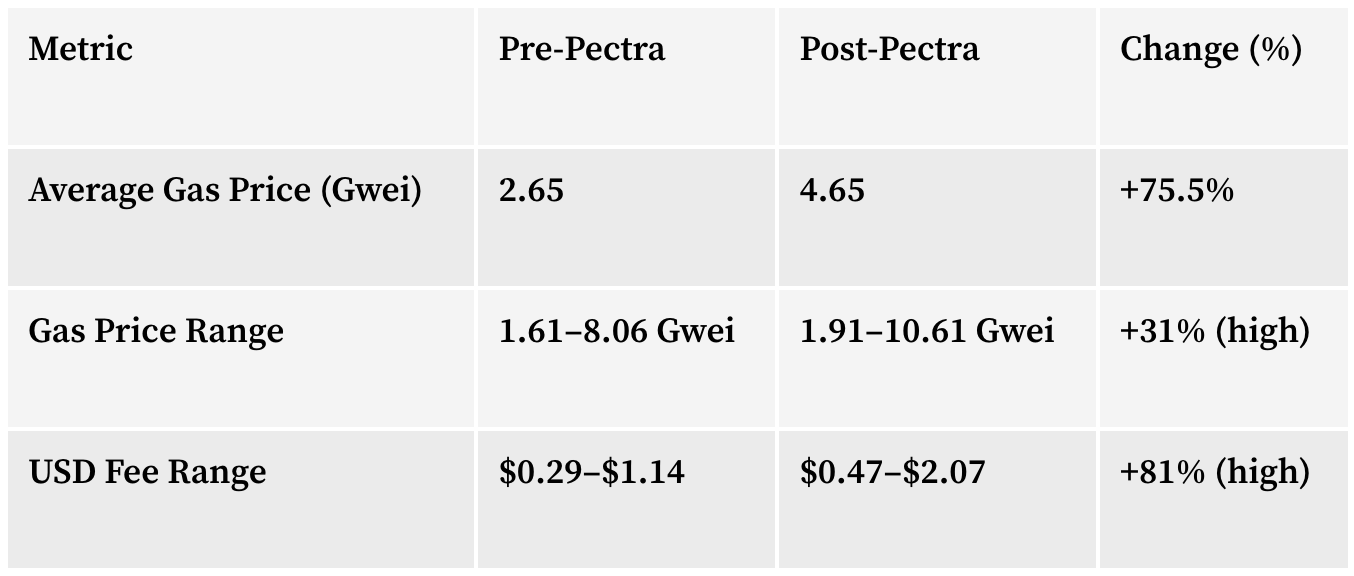
3. Blob Fees: A New Cost Driver
Post-Pectra introduced blob transactions, which added a third fee component (blob fee) to Ethereum’s gas structure. Blob fees now account for ~25% of total transaction costs in USD terms, creating a new layer of complexity for users and developers[1]
The Challenge: Rising Costs and Unpredictability
The Pectra upgrade achieved its goal of scaling Ethereum for data-intensive use cases (e.g., rollups, decentralized storage). However, the trade-off is clear:
-
Higher fees: Users now pay 2–3x more per transaction.
-
Volatility risks: Gas price swings widened by 31% post-upgrade.
-
ETH price correlation: A 40.9% rise in ETH’s USD price amplified fee costs, compounding volatility.
For dApps, traders, and L2 rollups, this unpredictability threatens operational stability and profitability.
The Solution: Gas Derivatives
Gas derivatives are financial instruments that allow users to hedge or speculate on future gas prices. Here’s how they can address post-Pectra challenges:
1. Gas Futures
-
Mechanism: Lock in gas prices today for future transactions.
-
Use Case: A dApp expecting high traffic during an NFT drop could buy futures to cap costs at $1.10 per transaction, avoiding spikes to $2.07.
2. Blob Fee Options
-
Mechanism: Pay a premium for the right (not obligation) to execute blob transactions at a predetermined fee.
-
Use Case: An L2 rollup could use blob fee call options to budget for data availability costs during network congestion.
3. Gas Volatility Index (GVI)
-
Mechanism: Track the 30-day standard deviation of gas prices (similar to the VIX for stocks).
-
Use Case: Traders could short GVI futures if they expect fee stability post-network optimizations.
4. ETH-Gas Correlation Swaps
-
Mechanism: Hedge against ETH price movements affecting USD fees.
-
Use Case: A DeFi protocol could swap variable ETH-denominated fees for a stablecoin payout, neutralizing ETH volatility.
How EQLZR’s GasFi Markets Empower Stakeholders
For Users and Developers
-
Risk Management: By using gas futures and blob fee options, users and developers can hedge against sudden fee spikes that would otherwise increase transaction costs unpredictably.
-
Budget Certainty: This predictability enables better financial planning and user experience, especially for gas-intensive dApps and Layer 2 rollups that rely heavily on blob transactions[1]
For Validators and Miners
-
Revenue Stabilization: Validators can use EQLZR’s derivatives to lock in expected fee income, protecting against volatile fee markets and ensuring steadier revenue streams amid fluctuating network demand and fee structures.
-
New Revenue Streams: By providing liquidity and market-making for GasFi products, validators and miners can earn fees and premiums, diversifying their income beyond block rewards and basic transaction fees[1][2].
For DeFi Investors
-
Uncorrelated Yield Opportunities: GasFi derivatives represent a novel asset class with returns uncorrelated to ETH price movements or traditional DeFi yields.
-
Volatility Trading: Investors can speculate on gas price volatility or hedge their existing crypto exposure, adding diversification and new strategies to their portfolios[1].
Synergy Opportunities
For dApps and L2 Rollups
-
Stable Operational Costs: Use gas futures to budget fees during high-demand periods.
-
Blob Fee Optimization: Batch blob transactions and hedge excess costs via options.
For Miners/Validators
- Monetize Volatility: Sell gas price options to earn premiums during low-activity periods.
For Traders
-
Arbitrage Strategies: Exploit discrepancies between ETH price movements and gas fee trends.
-
Speculative Products: Trade GVI futures to bet on upcoming network upgrades or congestion events.
Case Study: Post-Pectra Fee Hedging in Action
Scenario: A decentralized exchange (DEX) processes 500,000 transactions monthly.
-
Pre-Pectra Cost: 500,000 txns × $0.47 = $235,000/month.
-
Post-Pectra Cost: 500,000 txns × $1.06 = $530,000/month.
Solution: The DEX buys gas futures at $0.90 per transaction, capping costs at $450,000/month and saving $80,000 if fees spike to $1.06[1].
The Road Ahead
The Pectra upgrade marks a paradigm shift in Ethereum’s gas economy. While fee volatility poses risks, it also creates opportunities for innovation in decentralized finance (DeFi). Key developments to watch:
-
Blob Fee Standardization: Protocols like EIP-7516 could formalize blob fee markets.
-
Layer 2 Adoption: Rollups may drive demand for blob fee derivatives as they scale.
-
Regulatory Clarity: Frameworks for gas derivatives could emerge as institutional interest grows.
Conclusion
Ethereum’s Pectra upgrade has transformed the network’s fee structure, introducing both challenges and opportunities. By leveraging gas derivatives through platforms like EQLZR, stakeholders can mitigate volatility, stabilize costs, and unlock new revenue streams. This synergy positions GasFi markets as a foundational infrastructure layer for the evolving Ethereum ecosystem, empowering users, developers, validators, and investors alike[1][2].
Call to Action:
Interested in exploring gas derivatives for your project? Contact us to design a tailored hedging strategy or learn how to integrate fee volatility management into your operations.