Author: YaoYao Liu
Editor: Mark Wang
Translation: Team Tourou
The pricing revolution NFT needs may not be a complete reversal of refactoring, but a steady stream of imaginative proposals to improve the efficiency of price discovery. In terms of NFT and DeFi collaboration, fragmentation is still a direction worth exploring.
When it comes to the benefits of fragmentation, we use these words: democratization, liquidity, and price discovery.
Some argue that most NFTS are proprietary to individuals, with exclusive benefits. It runs counter to the idea of decentralization proposed by blockchain. Hence the need for fragmented NFT, designed specifically for decentralized ownership and use.
On the other hand, there is also criticism that NFTs determine the inseparable nature of NFT, which is bound to bring very low liquidity. In the NFT hype, high prices further hindered the market flow of NFT.
In our last article on fragmentation, we explained how fragmentation leads to democratization and mobility.
In terms of price discovery, our point is that today’s price discovery dilemma of NFT represents a limitation to the use of NFT and a hindrance to the development of NFT. NFT needs a pricing revolution.
How to Comprehend “Price”
Let’s re-understand the concept of price in NFT markets from two perspectives. These two concepts answer two of the most frequently asked questions about NFT:
- Why can a JPEG be sold for thousands of dollars or even millions of dollars?
- What does this JPEG sold for thousands of dollars or millions of dollars mean?
- Prices are determined by the value judgments of consumers
Let’s review the seven pricing principles of “The Psychological of Price”:
- Prices should be based on consumers’ perceived value of the product, not what you think it costs.
- Prices should be realistic, so consumers understand what they are getting for their money.
- Prices should be comparable within your control.
- If you want to adjust the price, you have to change the structure of the service or product.
- Price differentials are essential contributors to profitability.
- Pricing communication influences how consumers perceive the value of goods.
- If you want to increase profits, you must be prepared to sacrifice some sales.
In economic literature, goods tend to fall into two main value camps: functional value and emotional value, which is, “What can I do with this thing? ” And “How much I love this stuff.”
Principles 1 and 7 in “ The Psychology of Price” say that the ultimate factor in determining price is the value judgment of consumers. When dealing with the pricing process, it is necessary to go back to the fundamental category of action, namely trade-offs. So, if we want to understand pricing, we need to understand users’ trade-offs.
The concept of value in NFT currently comes more from functional value- that is, what can I get with this thing? Investment benefits, social capital, etc., rather than sentimental value. After all, in a speculative market, there are very few people who really pay for art. There are the trade-offs of most NFT users.
So Why can a JPEG be sold for thousands of dollars or even millions of dollars?
It is a value judgment made by the trade-offs of NFT users.
- Information can only be realized through price
“The Decentralized Alternative to Central Banking” argues that price is how knowledge (economic information) is spread and the information system of economic production. Any attempt to control prices would be disastrous. The latter part of the sentence is easy to understand because the empirical comparison has been made in many cases in history. What about the first part?
In short, the socio-economic problem is one of ensuring that what is known to individuals is put to best use.
Ludwig Von Mises and Friedrich August Hayek, the representatives of the Austrian school of economics, regard price as the medium for achieving Dispersed knowledge in the market. Hayek emphasized price as a signal of free-market coordination. It means that information can only be realized through price. For example, if you find that bread is going up in price, you’ll find more people involved in the production of bread.
So is the NFT market. The price of NFT, in addition to the irrationality of the bubble, represents a kind of rationality, which is the information system by which the NFT market performs economic production.
What does this JPEG sold for thousands of dollars or millions of dollars mean? It conveys the market consensus on the value of NFT dispersive knowledge information, as well as the signal of market coordination.
The NFT Dilemma: Liquidity and Financialization
What is NFTs’ current dilemma? There are many, but ultimately it comes down to low liquidity, and the core reason behind it comes from pricing difficulties.
Firstly, NFT is indivisible and has few transactions. There is not enough historical data to make a fair assessment, resulting in low capital efficiency. Secondly, the current NFT market is highly speculative, so even with comparable NFT, current price lists are not very relevant, e.g., Decentraland’s speculative land resales.
Looking at the development of NFT, the trend is clear: NFT is inevitably becoming a new, large number of financial asset classes with a large market.
In his article “All Digital Content Is Going on-chain”, the founder of CoinFund argues that we should think of NFT as “liquid IP”. As a result, trillions of digital contents will move to the secondary market as intellectual property is inevitably transferred to the blockchain as NFT. This will unlock huge illiquid value and become the most significant asset category in the blockchain area.
However, it should also be noted that NFT is a kind of low-velocity asset, similar to real estate and antiques in the traditional world. In the traditional world, such low-velocity assets can be valued in two ways: trading and valuation. There are two main types of problems: fewer transactions, less data; Pay for potential costs by seeking third-party estimates that are not transparent.
Based on these two points, we rule out the possibility of NFT appearing in those familiar and valuable financial instruments. For example, we can’t use NFT as collateral for a Compound loan. The reason is that the financialization of the NFT asset class is inseparable from price discovery or valuation pricing. In a decentralized world, most loan agreements use a price predicting machine such as Chainlink to aggregate prices from multiple sources of liquidity to determine the price of an asset or currency. NFT price discovery has proved more challenging, as selling prices, asking prices, and valid values can be inconsistent.
If NFT does not have an effective valuation system, its assets are difficult to be included in the process of financialization, which is undoubtedly an obstacle to the development of NFT.
Pricing Attempt
In response to this dilemma, there are also agreements on the market that provide NFT pricing. These liquidity protocols are necessary financial infrastructure to provide NFT value discovery for sophisticated applications above.
At present, there are three solutions:
The first solution is the price set by the buyer, such as TopBidder pricing through auction.
The second solution is seller pricing. For example, NiftEx/NFT20/NFTX provides initial liquidity by pledging NFT and generating ERC-20 to generate pricing.
The third solution is third-party pricing, such as Upshot, which generates pricing through the predictive behavior of random users.
You will find that it is still difficult for us to do pricing because NFT is a Low-velocity asset. Its price discovery is a dynamic process. In the futures market, price discovery is a process in which the price level of the commodity is constantly updated and spread to the whole world through fierce competition. The price of the commodity becomes the world price through open bargaining between the supply and demand.
Simply put, price discovery is the process of discovering competitive prices and world prices. Price discovery is also one of the important economic functions of NFT markets. Understanding these price discovery methods helps someone verb the pricing logic of NFT, and on this basis, to constantly reshape the framework of thinking.
At present, there are NFT price discovery methods:
1. Sale at a fixed price
There is a fundamental issue price when each NFT is issued. For example, the NFT dark horse Bored Ape Yacht Club has created a lower entry cost and incredibly imaginative price with an issue price of 0.08 ETH. It is worth noting that if there are not many initial participants in the market and the community background is weak, with the lack of pricing information (the reference to historical data, KOL endorsement), the liquidity will be poor.
2. Blind box
also a kind of sales mechanism. Buyers snapped them up at fixed prices.
3. Auction
The behavior of “bidding” itself is part of the formation of commodity prices.
For example, PartyBid is a product for collective bidding on NFTs. Anyone can create or join a PartyBid, trustlessly pool funds with friends, place bids on auctions, and have fun. After winning a specific NFT auction, the NFT will be deposited in a vault jointly owned by DAO holders, and DAO holders jointly own the assets.
For example, the cross-chain DeFi platform Alpha Finance Lab launched the NFT floor bid auction platform Alpha Buy Wall, which conducts auctions in the form of call auctions, which can be sold in real-time without slippage, and the platform does not charge any fees other than Gas fees. Buyers in this platform are not bidding for a certain NFT, but the lowest purchase price (floor price) of a certain NFT series. When the seller believes that the current bid has reached their expected price, they can sell at the highest bid. In addition, the platform allows sellers to set the minimum bid accepted, preventing the cancellation of the maximum bid when the transaction is completed.
4. Multi-form auction
Beeple’s work created a new historical record on the well-known British auction platform Christie’s at a price of US$69.34 million, which illustrates the artwork’s preference for auction formats once again. The auction format is indeed suitable for art because art is more subjective. But for most NFT assets, capital efficiency is not high. Specifically, there are the following types of auctions:
• Dutch Auction
Algorand used the gimmick of Dutch Auctions to raise 60 million US dollars in 4 hours, which also made Dutch Auctions widely known. In the NFT market, Dutch Auction is also a standard method. The specific auction mechanism is as follows: In the bidding process, the bidding price of the auction object is increasing according to the bidding ladder from low to high, and the highest bidder becomes the winner of the bidding, and the highest bidder becomes the winner of the bidding. The seller (the creator of this auction) can accept any bid at any time, and there is no time limit.
For example, the decentralized auction tool Bounce. finance will be launched to support the Dutch auction function of NFT auctions.
• Radical auction
This mechanism motivates bidders to make the price of a lot quickly reach the market’s reasonable pricing. The price of the lot increases monotonously according to the joint curve model set by the system, and the bidders who bring the price discovery can get the income compensation corresponding to the risk.
For example, TopBidder, combined with the auction protocol of the radical market theory, realizes a non-permanent-occupied crypto assets production and issuance mechanism. Any bidder can obtain ownership of the asset as long as the bid is not less than 10% of the upper bidder.
• Simultaneous multi-round auction
The simultaneous multi-round auction was proposed by the 2020 Nobel Prize winner Paul Milgrom (Paul Milgrom was hired as an Algorand consultant in September this year) and Robert Wilson. It means to provide all items (radio frequency bands in different geographical areas) at the same time of an auction, start with a low price, and allow repeated bids, thereby reducing uncertainty.
For example, the NFT pricing platform PawnHouse has incorporated its concept into the design product. NFT assets circulating through the platform use three expected pricing mechanisms: mortgage loans and pawn bond circulation, limited-time bidding, and the upcoming simultaneous multi-round auction (SMRA) system, which aims to help NFT market participants better obtain pricing services and incentives the bidder provides price information.
The specific process of realization: SMRA allows users to bid and win multiple assets at the same time. In each auction, multiple assets of the same or related categories will be auctioned simultaneously. The auction is conducted in rounds, and all bidders can bid before the countdown. After reaching the criteria for starting the auction, the system will automatically guide the countdown to the first round of auctions. After the countdown is over, the system only displays the current highest bid for each asset (other bids below this price are not displayed), and the next round of bid countdown starts. When no asset gets a higher bid, the auction ends. The highest bidder for each asset wins.
In traditional Dutch Auctions and English auctions, bidders may try to hide their true intentions to avoid the winner’s curse (the winning bidder overvalues the auction item, and its income is lower than normal or even negative). SMRA forces bidders to be active from the beginning of the auction. The comprehensive information and timely disclosure strategy not only avoid the winner’s curse but also provide sellers with an ideal price to the greatest extent. In the same period, bidders with diversified needs (including bidders from multiple NFTs) bid for multiple NFTs simultaneously. This result is also more meaningful for the price discovery of non-standard assets.
PawnHouse’s NFT mortgage lending platform has a transaction volume of more than 100 million dollars in a month. It uses more open and timely information to encourage and strengthen bidding behavior and build a “price corridor” for NFT assets through a real and dense quotation range.
5. The Oracle mechanism
It is equivalent to ChainLink to DeFi. Without such products, infrastructure such as NFT index products will be difficult to improve.
For example, Upshot One launched by Upshot uses a design mechanism called “Peer Prediction” to motivate people to answer questions honestly. Peer prediction uses a “mutual information” (it is a generalization of relevance) method to evaluate quality, that is, the more honest the answer, the more “mutual information” it receives. In these environments, participants will be compensated for answering questions. The amount of “mutual information” the participants answered determines how high the reward is, which creates a clear motivation to answer questions and answer honestly. Upshot’s Peer Prediction is the first on-chain mechanism widely applicable to NFT price discovery.
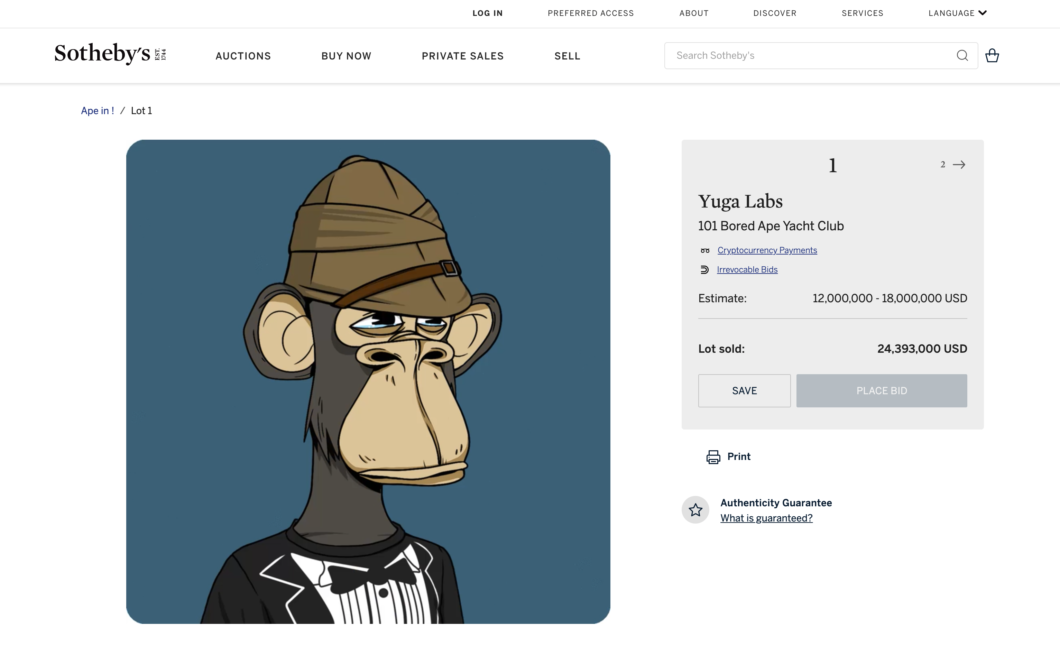
Not long ago, Sotheby’s Auction House held 101 Bored Ape Yacht Club NFT auctions. Before the auction, Sotheby’s estimated the value of the collection to be 12–18 million US dollars. Upshot runs a machine learning model to evaluate the NFT provided and stores the estimate on the blockchain before the auction ends. Its valuation of the bundle is 25.3 million US dollars, and the final bid price is 24.4 million US dollars, which is better than Sotheby’s Estimate. And recently, the fragmented NFT trading platform Unicly and Upshot have reached a partnership to introduce an NFT evaluation system.
6. Derivatives pricing
NFT lending represented by NFTfi and the NFT index represented by NFTX has created another vector for NFT price discovery-the implicit pricing of derivatives with NFT as the underlying asset. The emergence of NFT derivatives has made reasonable pricing a rigid demand because the instability of pricing is affecting it to become a real asset class.
Since the 1980s, banks have provided loans with traditional art as collateral. According to Deloitte estimates, the global value of art mortgages in 2019 is between US$2.1 and 24 billion. Currently, the debt market is the missing component of the NFT ecosystem. A mature NFT ecosystem needs to establish a market where people can use NFTs to obtain loans or lease their NFTs to obtain benefits.
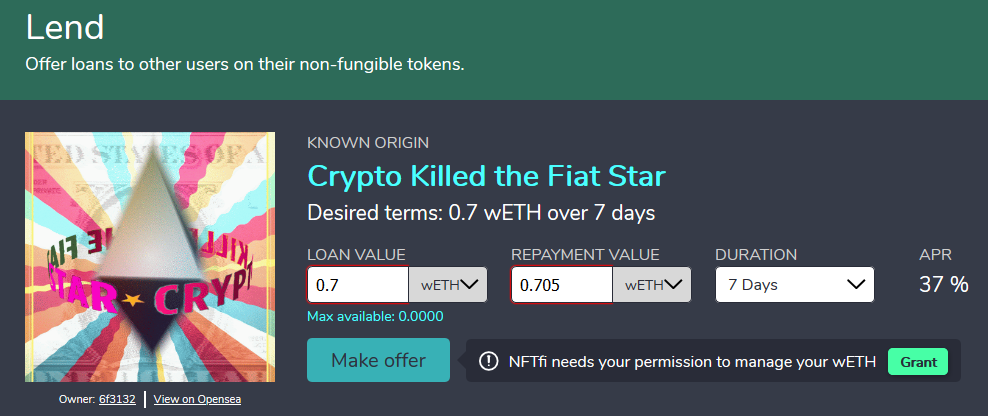
Launched in mid-2020, NFTfi is a Point-to-point NFT mortgage loan market that allows NFT asset holders to use their NFT as collateral to borrow assets (currently supports wETH and DAI) and lend to others. Here, for borrowers who lend for profit, how to price the NFT is the key to balancing the benefits and risks.
After the cancellation of the NFT redemption right, if the value of the NFT loan can be increased to 2 to 4 times the original value, if it is operated properly, this can actually bring huge returns. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that the NFT can be sold at a price higher than the loan amount or even profitable within 24–48 hours. Therefore, valuation is particularly important. If you do not understand how to evaluate, do not make an NFT quotation. Generally, you can find the latest selling price and the lowest price by referring to OpenSea. At the same time, we can use our relevant knowledge to estimate the NFT to balance the risks accurately. In this case, the uncertainty and risk of pricing are incredibly high.
In the past ten years, traditional index-based financial market investment has become popular because it provides a transparent and low-cost way to achieve diversified investment across various markets. Similarly, index funds that focus on NFTs can allow investors to access specific types of NFTs without requiring them to evaluate specific NFTs.
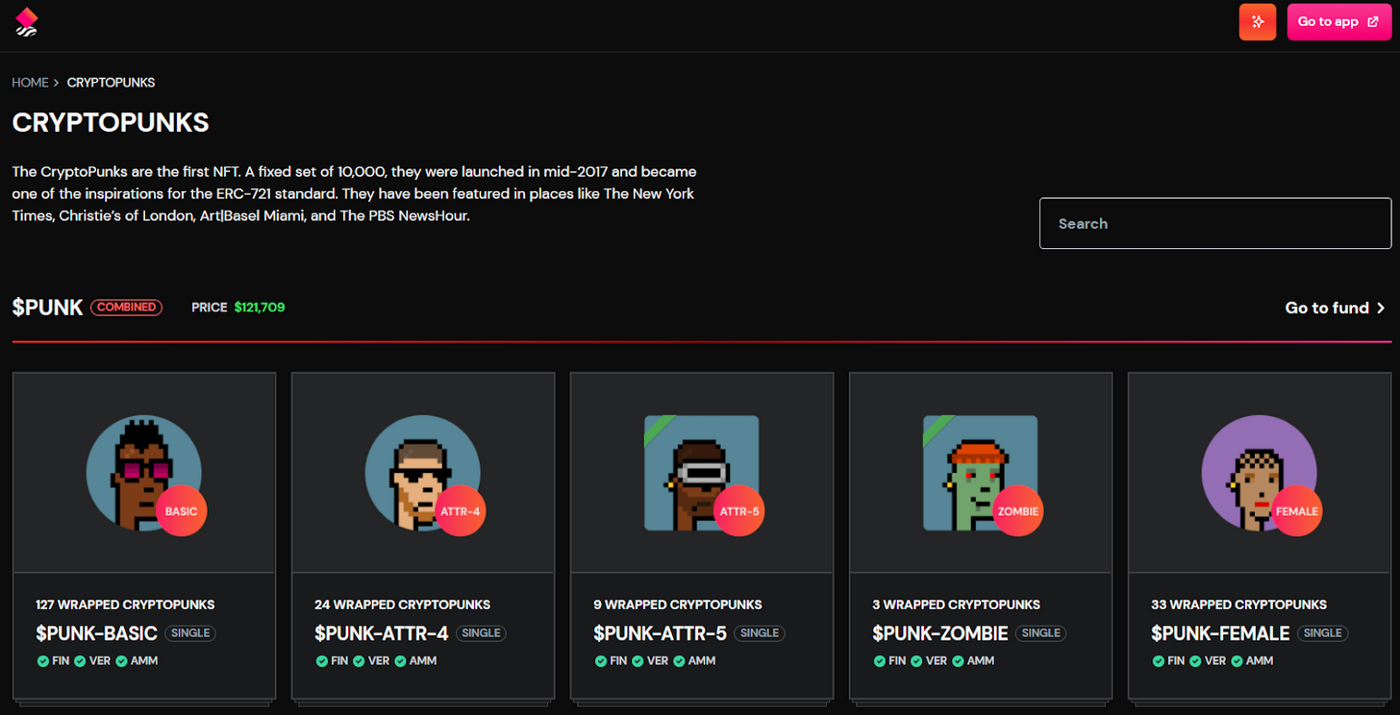
NFTX does this by creating index funds for various collectibles. Users can directly use NFTX to create and trade funds from DEX such as Uniswap based on the collections like CryptoPunk, Axies, CryptoKitties, and Avastars.
There are currently two types of funds:
• D1 Fund: ERC-20 tokens and a single NFT contract are minted 1:1. For example, if a user has five NFTX basic CryptoPunk fund tokens (token code: PUNK-BASIC), they can exchange these five PUNK-BASIC tokens for any five primary CryptoPunk NFTs at any time.
• D2 Fund: The Balancer fund pool is a mixture of multiple D1 funds. For example, D2’s PUNK fund can be composed of five different D1 CryptoPunks (PUNK-BASIC, PUNK-FEMALE, PUNK-ZOMBIE, PUNK-ATTR-4, PUNK-ATTR-5). D2 trading pairs set up a fund pool in Balancer. Each D1 fund component accounts for 20%.
• How the D1 fund works: Investor A owns three Hashmask works and deposits them in the MASK D1 fund to obtain MASK tokens. These tokens can be traded on SushiSwap, which can get better liquidity. Investor A deposits Hashmask into D1 fund, which means giving up his own Hashmask ownership, but it releases the liquidity of these Hashmasks.
It is easier to buy funds in NFTX, for users who do not want to study a single NFT work but want to invest in the field of NFT. Index funds that focus on NFTs can also improve the liquidity and price discovery of underlying NFTs by attracting additional demand and trading activities from a larger user base.
However, there are also views that as individual base assets in the fund pool increase in value, arbitrage will be stimulated, and ultimately only cheap assets will remain in the fund pool. This will cause major profits to be taken away by arbitrageurs, and thus will not be able to maintain long-term value for token holders and fund liquidity providers. To maintain the balance of asset value in the fund pool, it is necessary to constantly adjust fund asset parameters, which will increase the complexity of fund establishment.
7. Other attempts
Dave White, Paradigm’s research partner, once proposed a kind of NFT derivative solution “Floor Perps”, that is, “Floor Perpetual Contract.”
In simple terms, Floor Perps tracks the floor price of a given NFT project and provides market participants with tools to hedge against NFT floor price fluctuations and leverage trading: by locking their own NFT to create a synthetic NFT, this synthetic NFT can be regarded as A perpetual contract. After selling it to market makers, market makers can provide it to longs and shorts in the NFT market. Longs and shorts can increase leverage to participate and benefit from the rise and fall of the floor price of the NFT project. The benefits of this approach are obvious: it allows NFT holders to obtain liquidity and defend against floor price fluctuations without giving up ownership of the NFT.
In July, Stani Kulechov, the founder of the decentralized lending agreement Aave, tweeted that Aave is currently experimenting with NFT as collateral and hopes that the agreement will be suitable for various NFT use cases when it is released.
Although these are just ideas, for the time being, such derivative solutions can expand the application scenarios and the number of participants of the NFT. We have reason to believe that Financial NFTs are a necessary way to improve liquidity and an important driving force for the continuous expansion of the NFT ecosystem.
Talking about Fragmentation
What constitutes the market? The seller, the buyer, and the goods are available for exchange. In the NFT market, commodity price discovery has always been a complex problem, and this is also a key entry point for us to understand the benefits of fragmentation. Every time the fragmented ERC20 token is traded, a new price will be generated, which will update the total value of the NFT (that is, the issuance multiple of the transaction price).
Through fragmentation, we can evaluate the value of commodities relatively accurately. It is the fundamental factor that enables fragmented trading to drive market movements.
We also already know that price is a way of disseminating knowledge (economic information) and an information system for economic production; we also know that NFT is a financial asset, so to obtain its financial value, we need a place for selling, auctioning, and trading NFT assets.
But most places and their price discovery methods are very inefficient.
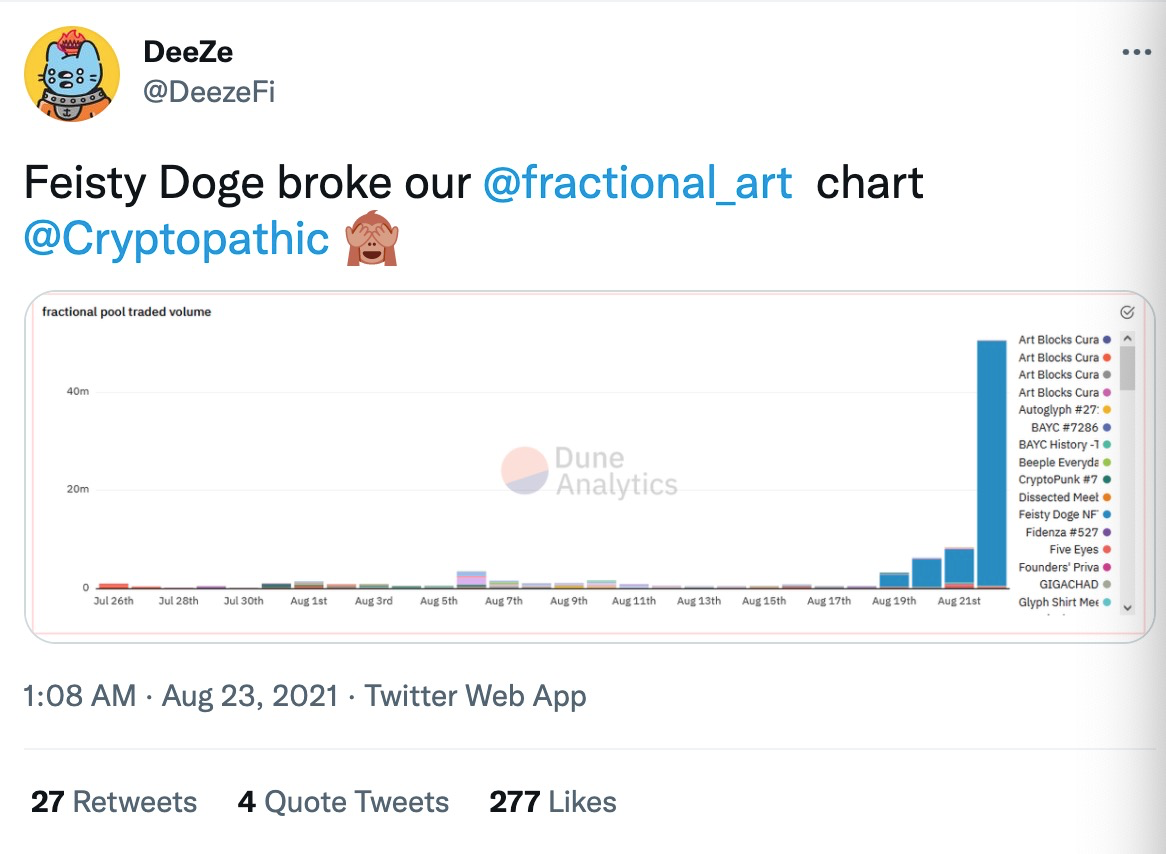
Fragmentation is an exception. In addition to the benefits of lowering participation thresholds, enriching investment portfolios, and increasing returns, the core of fragmentation is still to optimize price discovery, thereby enhancing liquidity. According to data provided by DeeZe@DeezeFi, fractional. art community manager, FeistyDoge’s trading volume on August 23 broke the highest historical record of the platform’s trading volume.
In the last fragmentation article, we compared the fragmented liquidity agreements currently on the market: Although they exhibit considerable Lego brick effects, they cannot meet multiple needs simultaneously.
The pricing revolution that NFT needs may not be a complete overthrow and reconstruction, but an imaginative proposal that is constantly emerging to improve the efficiency of price discovery. In the collaborative thinking of NFT and DeFi, fragmentation is still a direction worth exploring at present.
The reason is that fragmentation improves liquidity through tokenization, allows NFTs to be used as collateral without an order book, and creates a large number of NFT-based derivatives; for investors seeking to invest in the NFT field, it is also The NFT index can be used without the need to assess assets item by item, which greatly improves investment efficiency. The core point is that a capital-efficient price discovery mechanism can facilitate transactions faster.
So, it is obvious that most of the fragmented protocols in the past have been peer to peer, and this is not a more capital-efficient choice, whether it is from the perspective of price discovery or other dimensions.
The following are some practical benefits of peer to pool (the pool transaction model proposed in the DODO fragmentation scheme) in improving the capital efficiency of price discovery:
• Pool trading optimizes the NFT pricing description, which is the core tool of NFT pool trading, which provides the basic framework for NFT market making
• There are more and more frequent pricing participants in pool transactions, The pricing of pool transactions has more participants and higher frequencies, which is equivalent to allowing more people to participate in the pricing, and the price information is more prosperous; it has a certain degree of objectivity and is more accurate than the subjective pricing of the auction method
• Can help investors make purchasing decisions faster and more efficiently at the recommended price
• For a large number of low-priced NFTs in the market, pooling and packaging will help achieve the overall floor price valuation; at the same time, for low-priced NFT holders, it is better to put them in the pool to increase passive income instead of putting them in OpenSea where no one cares
• With the help of its DEX platform, the pool-building capabilities of fragmented NFTs will allow greater liquidity and provide market makers with arbitrage opportunities
Conclusion
NFT needs an effective price discovery mechanism. There will be a series of experiments surrounding this proposition. It is the revolution that NFT must face in the next step. When one day, NFT can appear as collateral in financial instruments that we are familiar with, it means that digital assets have been considered as an asset category, rather than bubble art.
Reference
- https://blog.coinfund.io/all-digital-content-is-going-on-chain-ae26a7071657
- https://www.chainnews.com/news/883324602818.htm
- https://pawnhouse.medium.com/pawnhouse-litepaper-728c081dc049
- https://www.paradigm.xyz/2021/08/floor-perps/
- https://upshot.io/the-sothebys-ape-auction-how-upshots-appraisal-performed/
- https://medium.com/1kxnetwork/fungible-non-fungibles-the-financialization-of-nfts-32565adf454a
- https://dexplain.com/what-is-nftfi-marketplace-for-nft-collateralized-loans/
- https://nftfi.medium.com/nftfi-com-f9ecf4ab1e7d
- https://www.chainnews.com/articles/619797886856.htm