The Restaking protocol has made Eigenlayer one of the most popular infrastructure projects in the Ethereum ecosystem. The core team EigenLabs has raised $50 million in funding, with Blockchain Capital leading the investment and participation from well-known VCs in the industry such as Coinbase Ventures, Polychain Capital, Bixin Ventures, and Hack VC.According to an official tweet on May 2, the first phase of EigenLayer's mainnet is about to launch and will support both Liquid Restaking and Native Restaking. By introducing Restaking services, EigenLayer hopes to provide additional staking opportunities for ETH holders who choose to participate, and to promote project innovation in the Ethereum ecosystem by reducing AVS's security costs. Restaking once again demonstrates the power of Web3 composability.
What is Restaking?
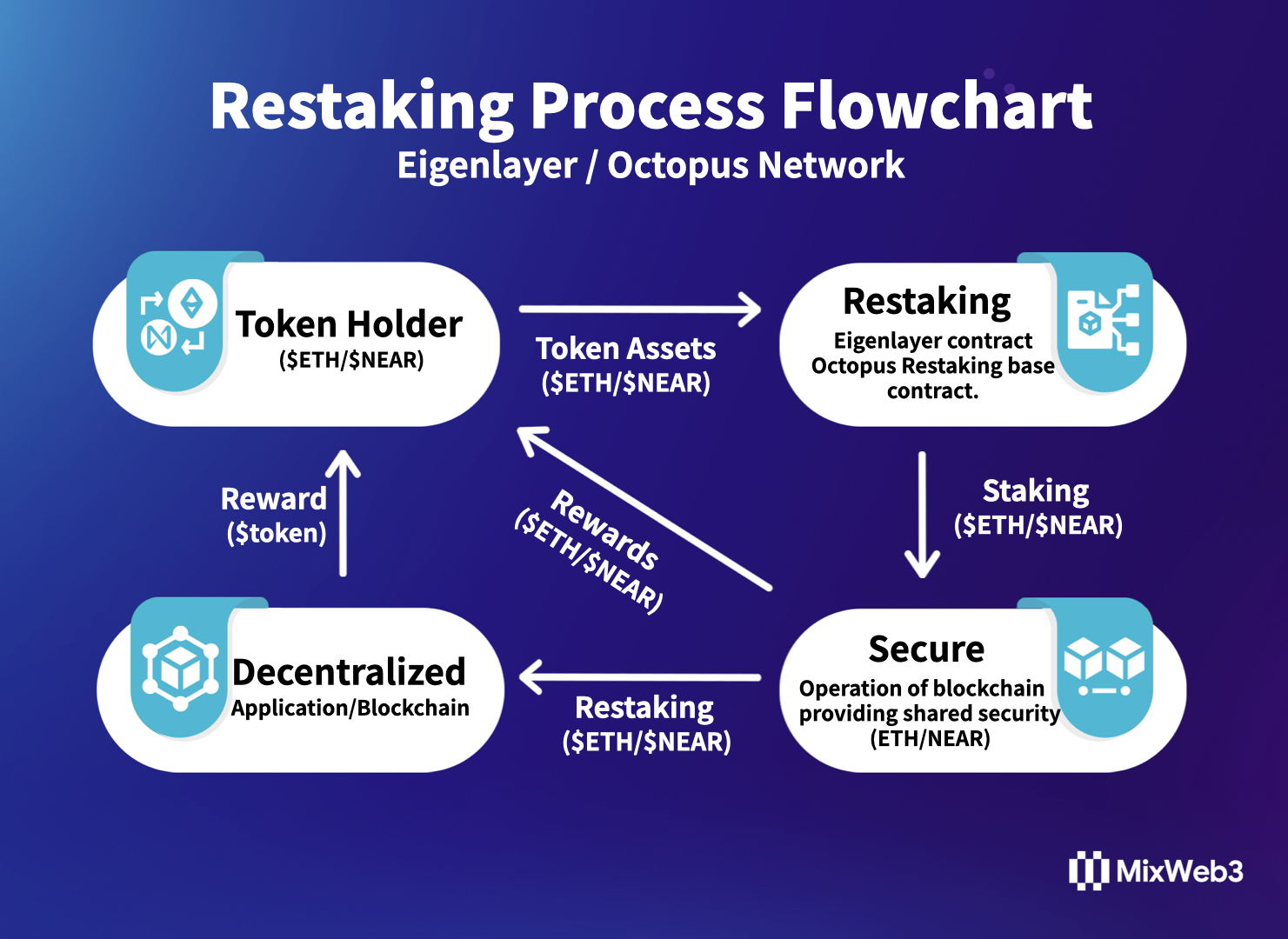
Restaking is a mechanism proposed by Sreeram Kannan, the founder of Eigenlayer, a decentralized trust market in the Ethereum ecosystem that aims to expand the trust network of Ethereum. The core mechanism of Restaking allows ETH that has already been staked on the Ethereum blockchain to be staked again on other consensus protocols, allowing it to share Ethereum's almost unshakable economic security and ensure its own secure launch and operation. In addition to receiving staking rewards from Ethereum, ETH stakers can also receive Restaking rewards provided by AVS.
Essentially, Restaking is a shared security mechanism that allows the same asset to be staked on multiple "decentralized applications/blockchains" simultaneously to provide security. Typically, new "decentralized applications/blockchains" will choose to join a blockchain ecosystem that offers sufficient security and is compatible with their own project to attract stakers through reward distribution. Stakers can stake their assets again on this new "decentralized application/blockchain" and receive additional reward income.
The concept of shared security allows a blockchain to enhance its own security by sharing the value of another blockchain's validation nodes. Players in the shared security field include Polkadot's slot scheme, Octopus Network's LPoS leasing proof of stake, Cosmos' Replicated Security, Avalanche's "subnets," and Polygon's "supernodes."
Just a few months after Eigenlayer proposed the concept of Restaking, the head infrastructure project of the NEAR ecosystem, Octopus Network, announced that it will follow suit and offer Restaking services. Octopus Network allows holders of $NEAR to stake their tokens on the NEAR Protocol while also providing security through Restaking for application chains and receiving staking rewards.
It is believed that other Layer1 blockchain Restaking projects are also in the works, and if any projects are announced, the author will conduct research and share it as soon as possible.
Why is Restaking highly anticipated?
As the narratives of multi-chain networks and application chains gradually gain popularity, providing lower-cost and more decentralized shared security services for blockchain security launch and operation has become increasingly important. In various shared security solutions, there are three key stakeholders: "decentralized applications/blockchains," "blockchains providing shared security," and "stakers." The Restaking mechanism not only maximizes the interests of all three parties but also completely unifies their interests.
1、Decentralized applications/blockchains
Decentralized applications/blockchains, represented by middleware chains and application chains, require high economic and time costs to achieve secure launch and operation through the construction of their own validation node network. By choosing Restaking, they can join a blockchain ecosystem that offers sufficient security and is compatible with their own project, where the community has a large number of stakers who can provide security services. Decentralized applications/blockchains can leverage the existing security of this ecosystem, which is worth billions of dollars, and flexibly obtain and adjust staking amounts and security levels according to their own security needs at different stages of development through rewards. For example, the security level in the early stages of a project can be relatively low, and the security level can be adjusted to a higher level through governance when assets increase in the later stages. At the same time, Restaking allows new projects to be more closely tied to the selected ecosystem, which helps to gain ecosystem support.
2、Stakers
From the perspective of stakers, Restaking is the best choice. In addition to staking tokens on the original blockchain and earning rewards, the Restaking mechanism allows the same staked tokens to be Restaked on other blockchains to provide security and receive security rewards again. This compound income is the most capital-efficient way of staking at present. Gabriel Haines succinctly described the enormous appeal of Restaking to stakers in a seven-second viral video:"You take your staked ETH… and you stake it again"。
3、Blockchains Providing Shared Security
Blockchains providing shared security typically refer to PoS-based Layer1 blockchains.
Firstly, Restaking solves the problem of the difficulty in transmitting and extending the cryptographic economic security of the original blockchain to other protocols in the ecosystem. For example, Ethereum is the most secure blockchain, but the security levels of various middleware protocols in its ecosystem are significantly lower than that of Ethereum.
Secondly, Restaking creates more economic value for staked tokens, and the size of the staked token market will be greatly expanded, while the value ceiling of staked tokens has been unprecedentedly raised.
With the increasing number of Restaking projects, the blockchain providing shared security will become a hub-type blockchain with the highest security, the most stakers, the most application layer protocols, the most Web3 users, and the most crypto assets in the entire ecosystem. The feedback effect of Restaking projects further enhances the economic security and value-capture capability of blockchains.
The most wonderful thing is that blockchains providing shared security do not need to incur additional costs.
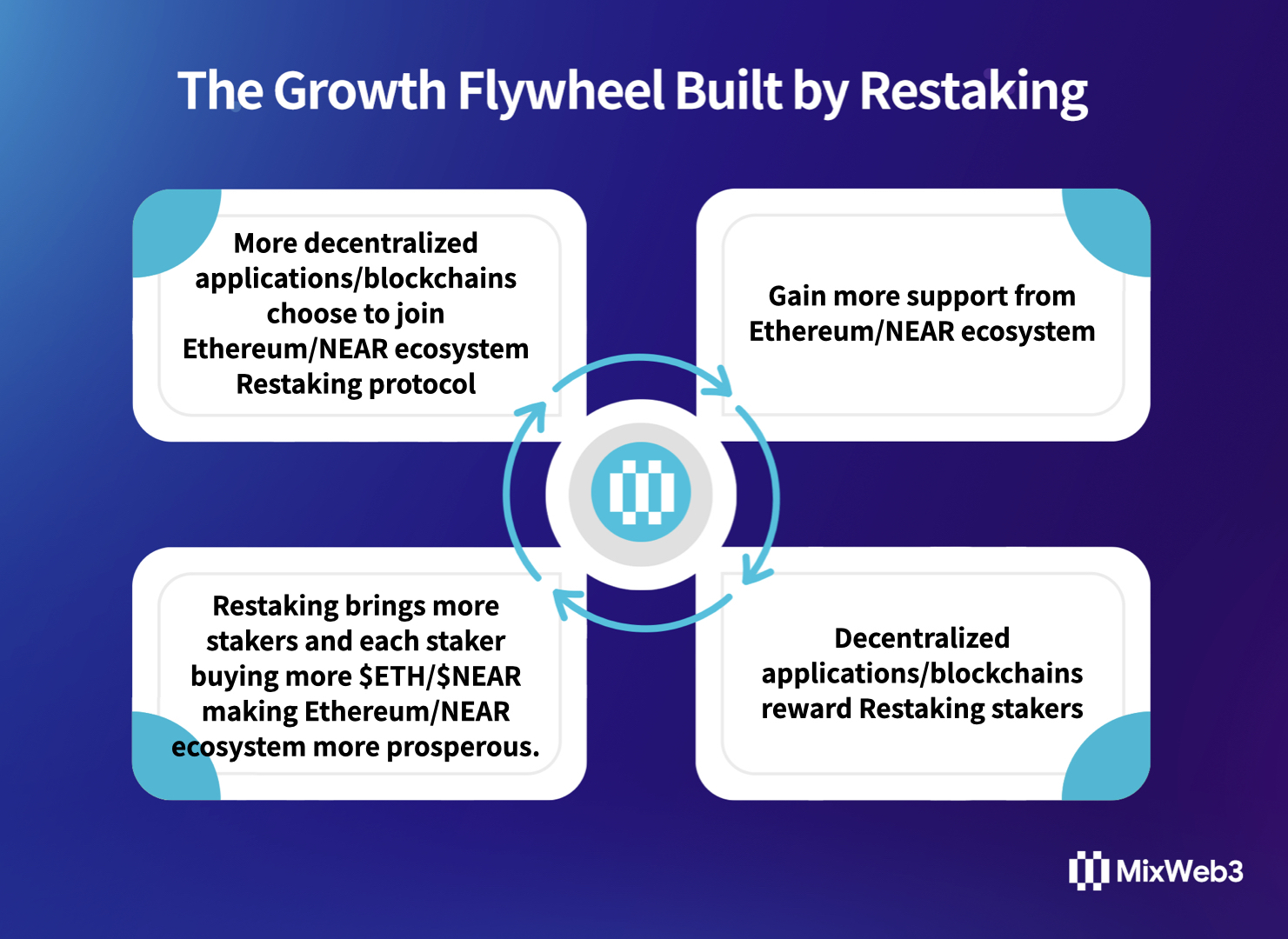
The Growth Flywheel Built by Restaking
Each decentralized application/blockchain using Restaking is like a bond market with different levels of productivity and yields. Part of its value will flow into the blockchain ecosystem and be converted into the appreciation of staked tokens.
Stakers using Restaking bring higher returns, which not only increases the value of staked tokens, but also stimulates the motivation to continue staking. When stakers reinvest these returns back into the staking pool, the entire Restaking shared security model forms a closed loop of logical growth flywheel.
Of course, as a new thing, Restaking also faces various potential risks, such as possible centralization risks, risks brought by high leverage ratios, cross-domain MEV, and how to establish a review market, which needs to be continuously improved in innovation.
