前言
在上一章中我们了解了区块是什么以及区块与区块链之间的关系。在这一章中我们将此项目重构,并拓宽区块的头部信息,并讲解区块如何通过共识机制合法的被添加进区块链中。
项目重构
在上一章中,我们所有的代码都写在了main.go中,这显然不利于我们继续构建项目。我们希望main.go只用于最后启动我们的区块链系统,为此我们需要将设计的区块与区块链移植其它文件夹中。重构部分就不做过多讲解了。
我们把之前的int64转byte函数放到utils里
package utils
import (
"encoding/binary"
)
func Int64ToByte(num int64) []byte {
var buf = make([]byte, 8)
binary.BigEndian.PutUint64(buf, uint64(num))
return buf
}
constcoe里面先存上难度系数,这个后面会详细说
package constcoe
const (
Difficulty = 12
)
block.go和blockchain.go把之前写的结构体和函数放入
//block.go
package blockchain
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/sha256"
"lighteningchain/utils"
"time"
)
type Block struct {
Timestamp int64
Hash []byte
PrevHash []byte
Data []byte
}
func (b *Block) SetHash() {
information := bytes.Join([][]byte{utils.Int64ToByte(b.Timestamp), b.PrevHash, b.Data}, []byte{})
hash := sha256.Sum256(information)
b.Hash = hash[:]
}
func CreateBlock(prevhash, data []byte) *Block {
block := Block{time.Now().Unix(), []byte{}, prevhash, data}
block.SetHash()
return &block
}
func GenesisBlock() *Block {
genesisWords := "HelloWorld"
return CreateBlock([]byte{}, []byte(genesisWords))
}
//blockchain.go
package blockchain
type BlockChain struct {
Blocks []*Block
}
func (bc *BlockChain) AddBlock(data string) {
newBlock := CreateBlock(bc.Blocks[len(bc.Blocks)-1].Hash, []byte(data))
bc.Blocks = append(bc.Blocks, newBlock)
}
func CreateBlockChain() *BlockChain {
blockchain := BlockChain{}
blockchain.Blocks = append(blockchain.Blocks, GenesisBlock())
return &blockchain
}
main.go中,就剩下这些了
package main
import (
"fmt"
"lighteningchain/blockchain"
"time"
)
func main() {
blockchain := blockchain.CreateBlockChain()
time.Sleep(time.Second)
blockchain.AddBlock("This is first Block after Genesis")
time.Sleep(time.Second)
blockchain.AddBlock("This is second!")
time.Sleep(time.Second)
blockchain.AddBlock("Awesome!")
time.Sleep(time.Second)
for num, block := range blockchain.Blocks {
fmt.Printf("number:%d Timestamp: %d\n", num, block.Timestamp)
fmt.Printf("number:%d hash: %x\n", num, block.Hash)
fmt.Printf("number:%d Previous hash: %x\n", num, block.PrevHash)
fmt.Printf("number:%d data: %s\n", num, block.Data)
}
}
试着运行一下,运行成功!项目重构完成,这样对以后开发方便多了
区块链共识机制
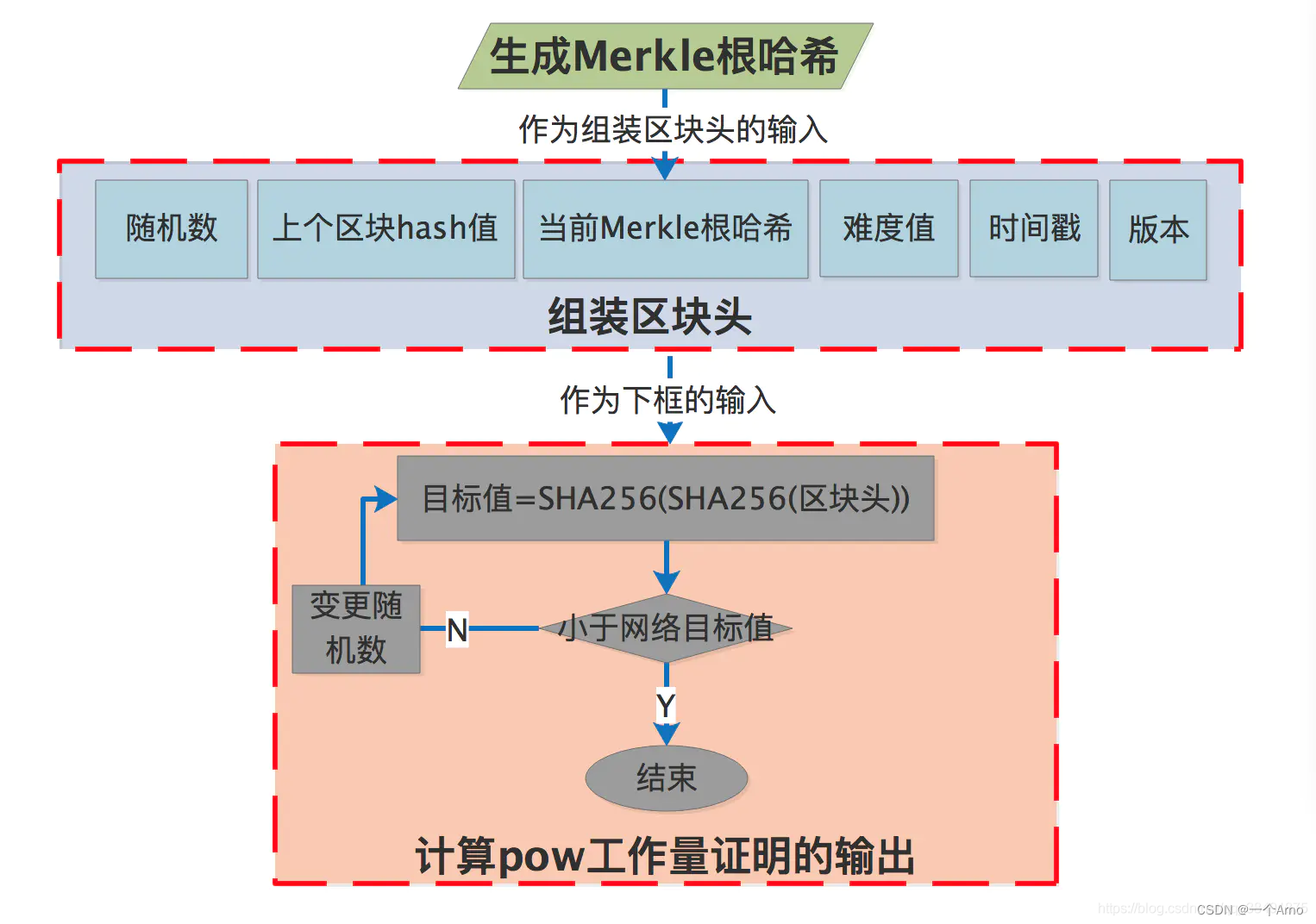
添加Nonce
nonce就是上图中我们要找的那个随机数,这是能证明你工作量的最关键的部分。首先在区块上添加头部信息
type Block struct {
Timestamp int64
Hash []byte //区块hash值就是其ID
PrevHash []byte
Data []byte
Nonce int64
Target []byte
}
接下来会有一些函数报错,我们后面再改
POW实现
在proofofwork.go中,首先实现一个获取target函数,这个函数可以方便我们以后在分布式系统中反复获取target
func (b *Block) GetTarget() []byte {
target := big.NewInt(1)
target.Lsh(target, uint(256-constcoe.Difficulty))
return target.Bytes()
}
Lsh函数就是向左移位,difficulty越小,移的越多,目标难度值越大,哈希取值落在的空间就更多就越容易找到符合条件的nonce。
下面我们进行寻找nonce的计算
func (b *Block) GetDataBaseNonce(nonce int64) []byte {
data := bytes.Join([][]byte{
utils.Int64ToByte(b.Timestamp),
b.PrevHash,
utils.Int64ToByte(nonce),
b.Target,
b.Data,
},
[]byte{},
)
return data
}
func (b *Block) FindNonce() int64 {
var intHash big.Int
var intTarget big.Int
intTarget.SetBytes(b.Target)
var hash [32]byte
var nonce int64
nonce = 0
for nonce < math.MaxInt64 {
data := b.GetDataBaseNonce(nonce)
hash = sha256.Sum256(data)
intHash.SetBytes(hash[:])
if intHash.Cmp(&intTarget) == -1 {
break
} else {
nonce++
}
}
return nonce
}
可以看到,神秘的nonce不过是从0开始取的整数而已,随着不断尝试,每次失败nonce就加1直到由当前nonce得到的区块哈希转化为数值小于目标难度值为止。
那么区块链如何知道这个分布式系统中你这个系统算出来的就是对的呢?下面我们需要写一个验证函数
func (b *Block) ValidatePoW() bool {
var intHash big.Int
var intTarget big.Int
var hash [32]byte
intTarget.SetBytes(b.Target)
data := b.GetDataBaseNonce(b.Nonce)
hash = sha256.Sum256(data)
intHash.SetBytes(hash[:])
if intHash.Cmp(&intTarget) == -1 {
return true
}
return false
}
pow我们实现完了,接下来回到block.go中做点小修改
func (b *Block) SetHash() {
information := bytes.Join([][]byte{utils.Int64ToByte(b.Timestamp),
b.PrevHash, b.Target, utils.Int64ToByte(b.Nonce), b.Data}, []byte{})
hash := sha256.Sum256(information) //软件包sha256 实现 FIPS 180-4 中定义的 SHA224 和 SHA256 哈希算法。
b.Hash = hash[:]
}
func CreateBlock(prevhash []byte, data []byte) *Block {
block := Block{time.Now().Unix(), []byte{},
prevhash, data, 0, []byte{}}
block.Target = block.GetTarget()
block.Nonce = block.FindNonce()
block.SetHash() //所有数据添加好后再计算hash
return &block
}
一切完成!
调试
打开main.go,我们加一行输出来验证pow是否成功
package main
import (
"fmt"
"lighteningchain/blockchain"
"time"
)
func main() {
blockchain := blockchain.CreateBlockChain()
time.Sleep(time.Second)
blockchain.AddBlock("This is first Block after Genesis")
time.Sleep(time.Second)
blockchain.AddBlock("This is second!")
time.Sleep(time.Second)
blockchain.AddBlock("Awesome!")
time.Sleep(time.Second)
for num, block := range blockchain.Blocks {
fmt.Printf("number:%d Timestamp: %d\n", num, block.Timestamp)
fmt.Printf("number:%d hash: %x\n", num, block.Hash)
fmt.Printf("number:%d Previous hash: %x\n", num, block.PrevHash)
fmt.Printf("number:%d data: %s\n", num, block.Data)
fmt.Printf("number:%d nonce:%d\n", num, block.Nonce)
fmt.Println("POW validation:", block.ValidatePoW())
}
}
点击运行,输出
number:0 Timestamp: 1677654426
number:0 hash: 51c810ee37b56f26baaf27ad8c8c271c1e383dcf75c6b8baaca059a9e621ac67
number:0 Previous hash:
number:0 data: HelloWorld!
number:0 nonce:14014
POW validation: true
number:1 Timestamp: 1677654427
number:1 hash: 059131a889810a8484bc072d0bcd7ecba3011a509ab6bc460c7a892357621f82
number:1 Previous hash: 51c810ee37b56f26baaf27ad8c8c271c1e383dcf75c6b8baaca059a9e621ac67
number:1 data: This is first Block after Genesis
number:1 nonce:1143
POW validation: true
number:2 Timestamp: 1677654428
number:2 hash: 055263bd8eea37b526e45b097b1f837c108ab2fc88f26bbf567a4fa9598cadb9
number:2 Previous hash: 059131a889810a8484bc072d0bcd7ecba3011a509ab6bc460c7a892357621f82
number:2 data: This is second!
number:2 nonce:10091
POW validation: true
number:3 Timestamp: 1677654429
number:3 hash: d0b5a049c2780c01e2e66cc23934267c528df80a3bcc69180a3f2231cf08d87f
number:3 Previous hash: 055263bd8eea37b526e45b097b1f837c108ab2fc88f26bbf567a4fa9598cadb9
number:3 data: Awesome!
number:3 nonce:592
POW validation: true
成功!
总结
本章讲解了PoW共识机制,需要重点理解nonce与目标难度值,以及pow的实现。下一章中我们将会实现区块中的数据信息存储方式,以及UTXO模型。
另外,现在区块链主流的共识已经从PoW改为PoS了,以后有时间我再改进一下