Introduction
If you ever find yourself intrigued, curious, or perhaps a bit overwhelmed by terms like Ethereum and ENS, you're in the right place. Ethereum Name Service (ENS) is a decentralized and open-source technology built on the Ethereum blockchain. Much like the Domain Name System (DNS) governs the traditional internet, the Ethereum Name Service (ENS) plays a parallel role in simplifying interactions within the Ethereum blockchain. To understand its impact, let’s take a look at how ENS works.
What is ENS
ENS was founded in 2017 by Nick Johnson (nick.eth), an alumni of the Ethereum Foundation and ex-Googler. He has been actively involved in the development of various Ethereum-related projects and has made substantial contributions to the blockchain space.
ENS serves as a decentralized domain name system for the Ethereum blockchain. Its primary purpose is to provide a user-friendly and human-readable naming system for Ethereum addresses and other resources on the blockchain. It allows users to register and manage domain names that end in ".eth." These domain names can be associated with Ethereum addresses, making it easier for users to interact with decentralized applications (dApps) and services.

Registering an ENS Domain
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to buy an ENS domain:
-
Open the ENS App: Visit the ENS app at https://app.ens.domains/
-
Connect Your Wallet: Connect your cryptocurrency wallet to the ENS App to enable transactions and registrations.
-
Search for Your Desired .eth Name: Use the ENS App to search for the desired domain name you want to register, such as "chintu.eth."
-
Select an Available Domain Name: Choose an available domain name that you'd like to register.
-
Register: Initiate the registration process by requesting to register the selected domain name.
-
Complete the ENS Domain Registration: Follow through with the necessary steps to finalize and complete the registration of the ENS domain.
-
Association with Ethereum Address: Associate the newly registered ENS domain (e.g., "chintu.eth") with Chintu’s Ethereum address (e.g.,
0xC0cac01ac0ffEeCafeca34a2973ae03fba3070a1) through the ENS system.
Now, whenever you want to send cryptocurrency to Chintu, you can simply use the ENS domain name "chintu.eth" instead of his long Ethereum address. You enter "chintu.eth" in your wallet's recipient field, and the ENS system resolves it to Chintu's actual Ethereum address.
How does ENS work?
ENS operates on the Ethereum blockchain and is built on two primary smart contracts: the ENS registry and resolvers. The ENS registry is the Smart contract that records all domains registered on ENS. Each domain entry in the registry contains information such as the owner of the domain, the resolver contract associated with it, and the caching time for records under the domain. The ownership details of a registered domain are stored on the Ethereum blockchain and the domain owner has control over the domain and can manage its settings.
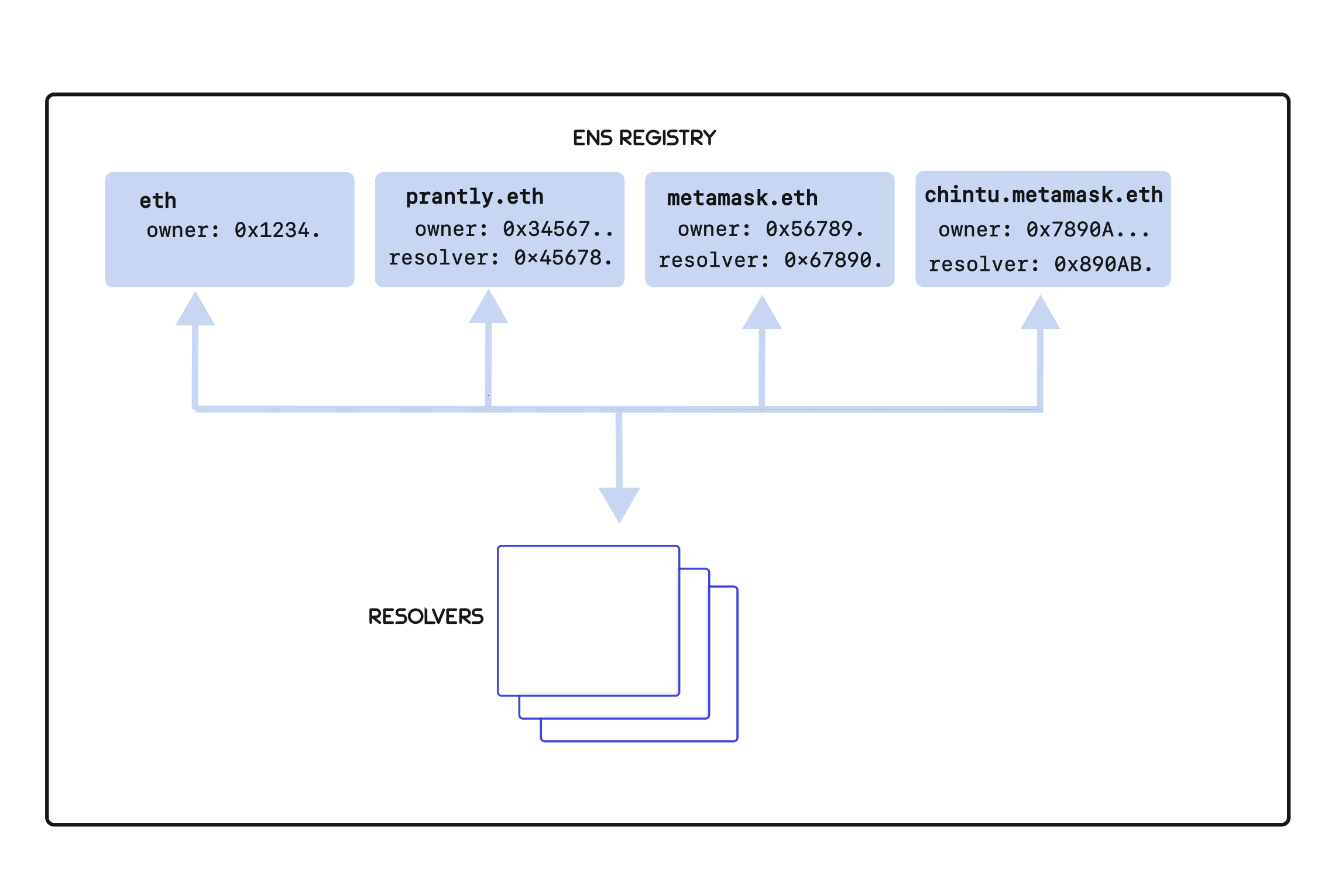
The owner then associates the domain with a resolver, which is another smart contract responsible for translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable Ethereum addresses and vice versa. When someone wants to interact with an ENS domain (e.g., send funds to "chintu.eth"), the resolver translates the human-readable domain name into the corresponding Ethereum address, making it possible for transactions to be directed to the correct recipient.
ENS operates in a decentralized manner on the Ethereum blockchain, meaning there is no central authority controlling the entire system. Ownership details and domain associations are secured through Ethereum's consensus mechanism, ensuring transparency and resistance to censorship.
Benefits of ENS
The Ethereum Name Service (ENS) offers several benefits that contribute to a more user-friendly and efficient experience within the Ethereum ecosystem:
-
Human-Readable Addresses: ENS allows users to associate human-readable names with complex Ethereum addresses, making it easier for individuals to send and receive funds without needing to remember or type lengthy hexadecimal strings.
-
Decentralization: ENS operates on the decentralized Ethereum blockchain, reducing reliance on central authorities. This ensures that domain ownership and management are resistant to censorship and external control.
-
Versatility with Various Domain Extensions: ENS is not limited to ".eth" domains; it supports popular DNS extensions like ".com," ".org," ".io," and more. This flexibility allows users to choose familiar domain names, enhancing accessibility and integration with traditional internet structures.
-
Integration with DApps and Services: ENS is widely integrated into decentralized applications (DApps) and services, enabling users to interact seamlessly across the Ethereum ecosystem. Wallets, exchanges, and other platforms can leverage ENS for a more user-friendly experience.
-
Simplified Payments: Users can associate their ENS domain with cryptocurrency addresses, simplifying the process of receiving payments. This feature is particularly beneficial for merchants and individuals who regularly transact in the crypto space.
-
Renewable Ownership: ENS requires domain owners to periodically renew their registrations, preventing domain squatting and ensuring active use of registered domains. This approach promotes a fair and responsible distribution of domain names.
-
Subdomain Management: Domain owners have the flexibility to create and manage subdomains under their primary domain, allowing for the organization of various services or functions under a single, easily recognizable name.
-
Support for Reverse Resolution: ENS supports reverse resolution, allowing users to associate metadata like canonical names or interface descriptions with Ethereum addresses. This feature enhances the overall functionality and information associated with Ethereum addresses.
What is the $ENS Token?
On November 8th, 2021, the Ethereum Name Service (ENS) launched its native currency, the ENS token. The $ENS token serves as the governance token for the Ethereum Name Service (ENS) protocol. $ENS allows holders to participate in the governance of key aspects of the ENS protocol through proposals and voting. As an ERC-20 token, the ENS token operates with the same characteristics as every other cryptocurrency on Ethereum.
The ENS token has a human-readable contract address: token.ensdao.eth (0xC18360217D8F7Ab5e7c516566761Ea12Ce7F9D72). After its launch, major centralized exchanges like Binance, KuCoin, and OKEx began offering trading services for the ENS token. Furthermore, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) such as Uniswap, SushiSwap, and ByBit also listed the ENS token for trading.
ENS DAO: Decentralized Governance
The ENS DAO is a decentralized autonomous organization responsible for governing the Ethereum Name Service (ENS) protocol. The ENS DAO operates as a decentralized organization, decisions here are made collectively by its members rather than a central authority. The rules governing the organization are encoded on the Ethereum blockchain through smart contracts. Members of the ENS DAO are individuals who hold ENS tokens. These tokens grant them the right to participate in the governance process. ENS token holders have the ability to propose changes, vote on proposals, and engage in the overall governance of the protocol.
The governance process is designed to be democratic and transparent. Members can propose various changes, which may include technical upgrades or alterations to the governance structure itself. Once a proposal is submitted, members have a set amount of time to vote on it. If the proposal receives enough votes, it is automatically executed through the smart contract. Besides technical upgrades, the ENS DAO also determines how funds are allocated for different purposes, such as supporting development, marketing, or community initiatives. The ENS DAO actively encourages participation and engagement from its community members through discussion forums, governance meetings, and other channels.
Conclusion
Beyond its user-friendly interface, ENS plays a pivotal role in decentralization. Operating on the Ethereum blockchain, ENS ensures that there is no single controlling entity, thus establishing resistance against censorship and eliminating the risks associated with central points of failure. This characteristic aligns with the core principles of blockchain technology, fostering a more open and resilient ecosystem.
ENS goes further by enabling interoperability with decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts. This integration allows developers and users to interact with domain names rather than complex cryptographic addresses, streamlining processes and making Ethereum more accessible to a broader audience.
Asset management is another area where ENS showcases its importance. Users can associate domain names with various digital assets, including cryptocurrency wallets and decentralized websites.
Ethereum Name Service is pivotal in simplifying user interactions, advancing decentralization principles, and promoting the seamless integration of blockchain technology into various applications. Its role extends beyond mere convenience, impacting the broader usability, accessibility, and robustness of the Ethereum network.
We hope you enjoyed reading our blog. Don't forget to stay connected with us on Twitter @namesys_eth for the latest updates. Your feedback is important to us, so feel free to drop your suggestions—we would love to hear your thoughts. Thank you for being part of our community!