There are a number of DeFi building blocks that are worth understanding in order to recognize patterns that are deployed on different chains or tweaked for the next stage of innovation. I’ll do a separate post with those frameworks at some point, but today’s article is about understanding the Curve Wars and their significance in the overall DeFi ecosystem. We’ll cover the following topics:
- What is Curve?
- What are the Curve Wars?
- DeFi implications
- Pattern matching across other ecosystems
I should caveat and say this is a super high level overview. I’ll link resources that go into way more depth. The whole thing is pretty complicated but this should give you a reasonable new to DeFi POV.
1/ What is Curve?
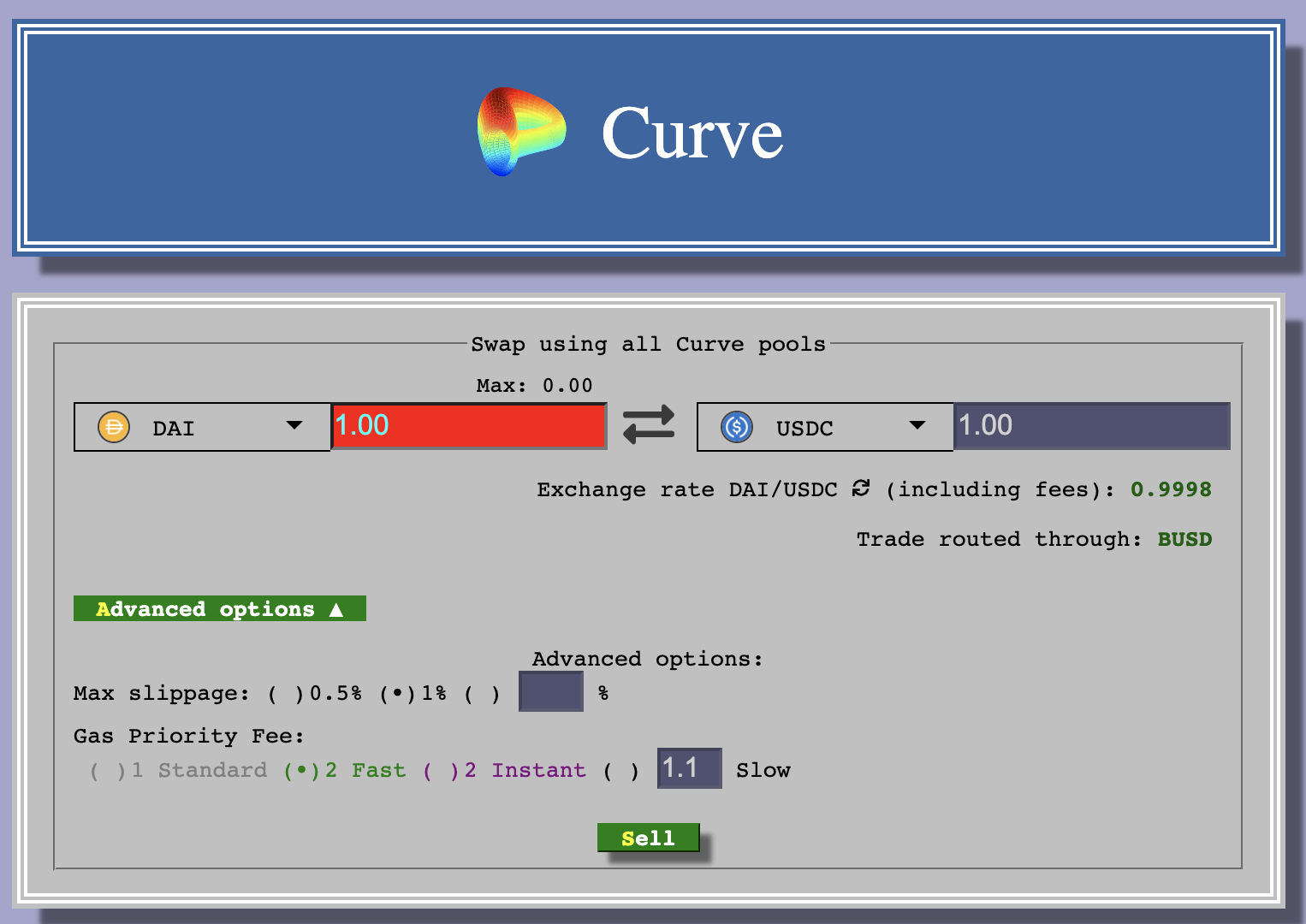
Curve is a decentralized exchange for swapping stablecoins. If we go back to the building blocks of DeFi, you may recall that AMMs and DEXs are key pieces to a functioning DeFi ecosystem.
From their documentation:
The easiest way to understand Curve is to see it as an exchange. Its main goal is to let users and other decentralised protocols exchange stablecoins (DAI to USDC for example) through it with low fees and low slippage. Unlike exchanges out there that match a buyer and a seller, the behaviour of Curve is different, it uses liquidity pools like Uniswap. To achieve this, Curve needs liquidity (tokens) which is rewarded by those who provide it.
The primary value of Curve is that you’ll get the best deals on swapping your stablecoins on Curve relative to other surfaces.
Curve is able to offer these options because users contribute their liquidity for rewards. Liquidity pools are pools of token that sit in a smart contract. Different DEXs use different liquidity pool formulas for balancing their tokens, but the basic premise is, people put in their stablecoins of choice, get a token receipt back that acknowledges their deposit, and then earn rewards off of portion that they’ve put into the pool.
Why do people do this? Usually providing liquidity is a great way to earn extra money on something that you already have. Check out these potential rewards you could get by adding liquidity.
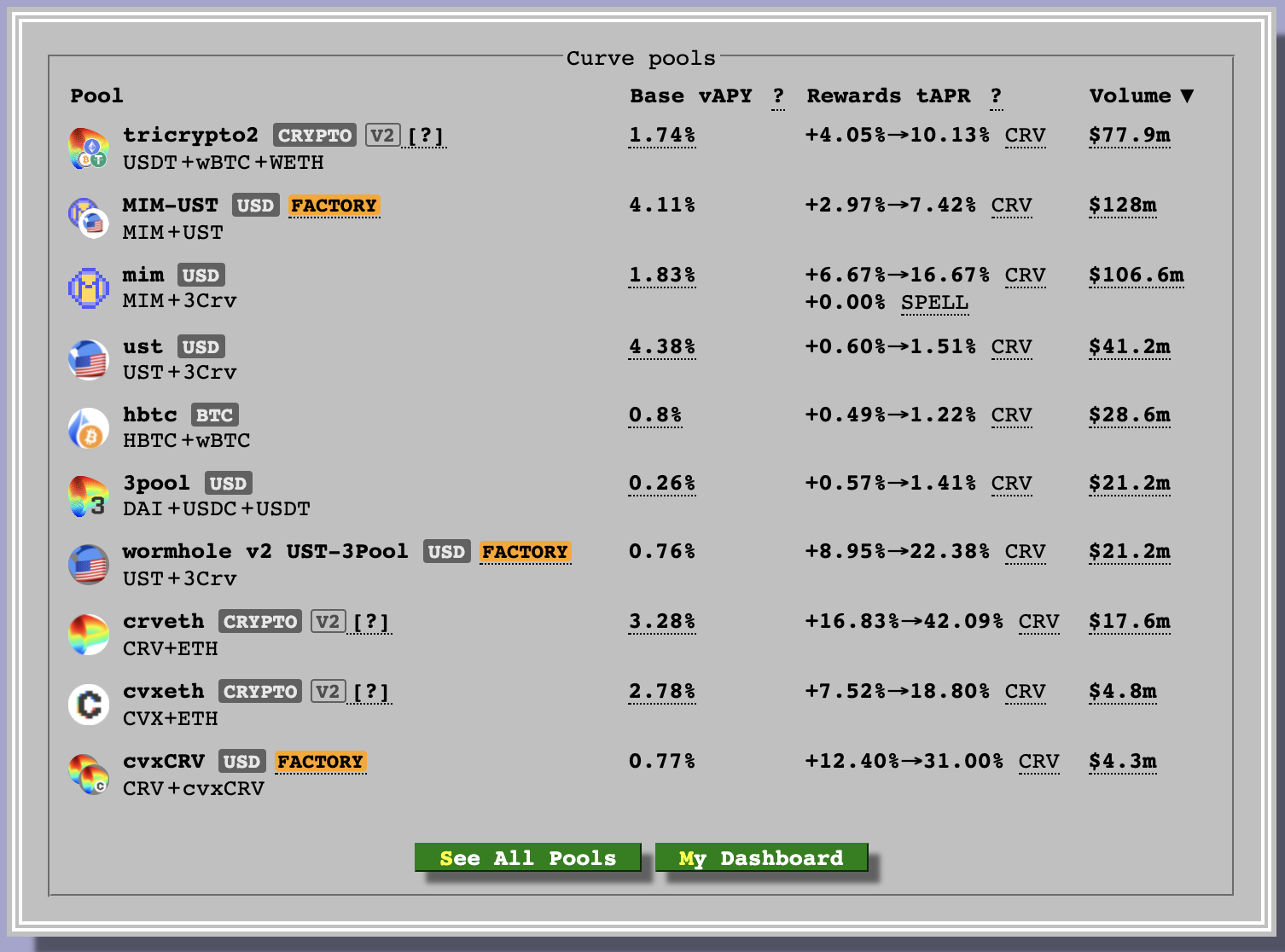
In Curve’s case, when someone contributes to a liquidity pool, they will receive Curve ($crv) in return. $crv is like any other token. You can hold it, sell it on an exchange, etc. You can lock it up for $veCRV (vote escrow CRV) which will give you voting rights to which pools receive $crv rewards for providing liquidity.
It’s this $crv token that is the center of the Curve Wars.
2/ What are the Curve Wars?
The Curve Wars are a war between different protocols and their desire to hold as much veCRV as possible to influence votes on where rewards for $crv should go. Convex Finance has been the most successful here, and nearly half of all veCRV supply is owned by Convex (ref)
Let’s go through the details.
- What do you do with $crv?
- Who else wants your $crv?
What do you do with $crv?
Let’s say you contributed to one of the liquidity pools. You’ll now start earning $crv as a reward for your liquidity. Most people will actually choose to lock up their $crv so it becomes veCRV.
- Why would the platform want to lock up Curve? It takes off pressure from people selling the token immediately after it vests.
- Why would you want to lock up your Curve? You’ll be eligible to get even higher boosts on the rewards you’re already getting from your liquidity pools.
- Unlike most tokens in crypto, veCRV cannot be transferred between users. When you lock up your $crv, you’ll get veCRV back. Locking up veCRV for longer periods of time (max is 4 years) will make you eligible for higher boosts and rewards on the liquidity that you’re providing.
- veCRV is also interesting since it decays linearly over time, meaning that if you want to keep up high yields, you’ll need to continue locking up more $crv.
- You can use your veCRV to vote on different Curve proposals. A number of larger protocols and players are also interested in your veCRV because the bribes they pay to get your votes will be worth the incremental liquidity their pool gets (ref)
Yuga has a great overview diagram here
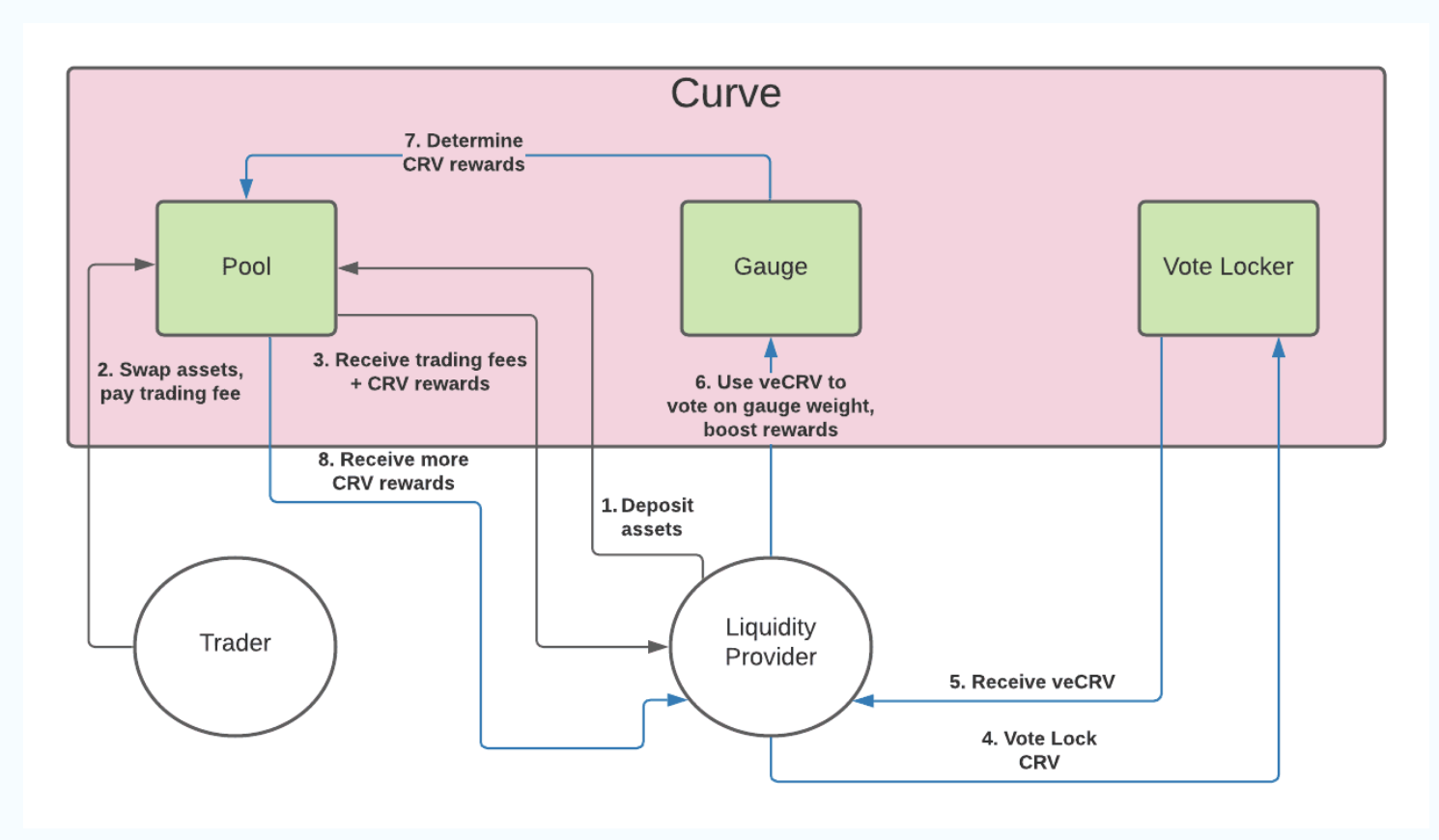
Who else wants your $crv?
Remember when I said above that influencing where the result of votes go is something protocols really want to do? Here enters Convex.
Yuga’s summary is better than anything I’d write, so read this:
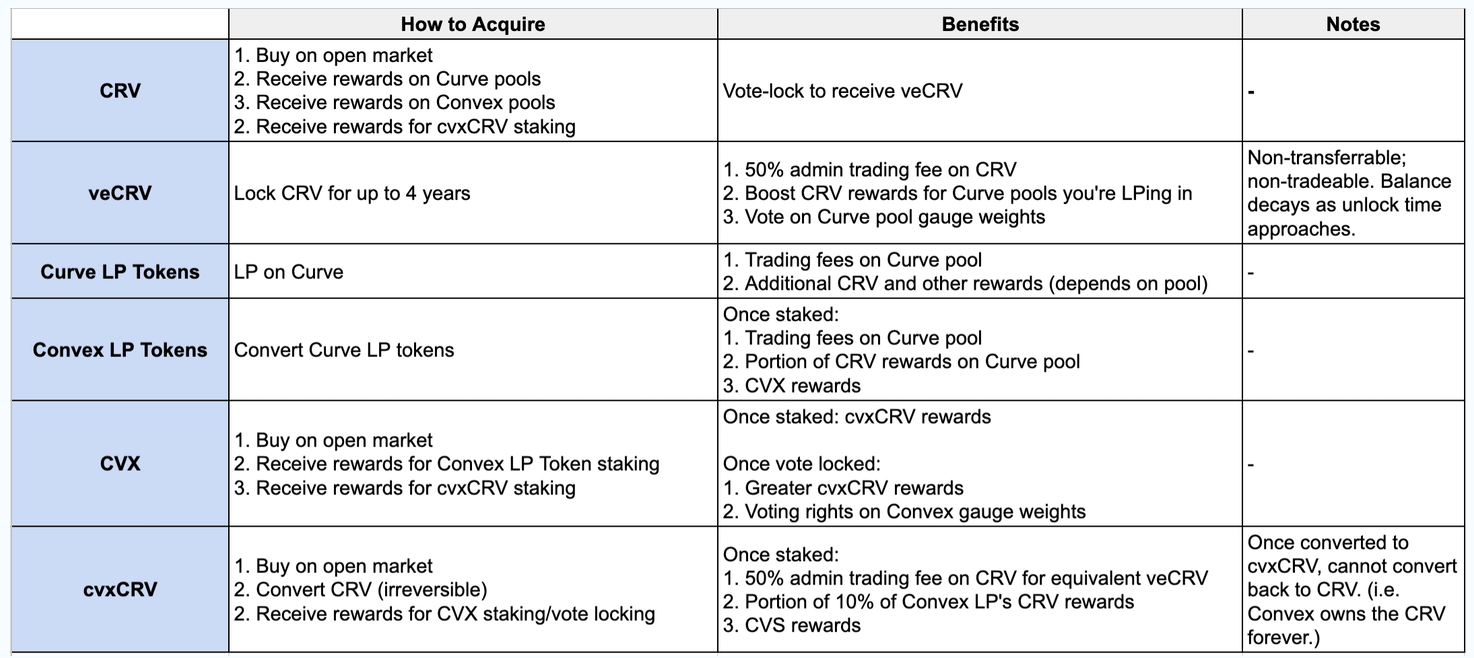
- Convex is a DeFi protocol built to maximize CRV holdings
- It does so by pooling Curve LP tokens and CRV together, and using it to increase future CRV earnings through veCRV boosting and gauge weight voting
- For users without sufficient veCRV to obtain a significant boost, it may be worth it to stake their Curve LP tokens with Convex.
- CVX is a token used for rewards in Convex
- CVX can be vote-locked for 16 weeks to vote on how Convex will vote on Curve gauge weights
- cvxCRV is another token used for rewards in Convex
- CRV can be irreversibly converted to cvxCRV
- cvxCRV can be staked to receive further rewards
- The interdependence of CVX and cvxCRV makes them difficult to reason about
- But Convex has successfully captured ~47% of veCRV using this strategy
Yuga’s cheatsheet of the tokens:
In addition to this, there are tools like Bribe for Curve and Votium for Convex where protocols will add rewards to encourage votes. There’s also REDACTED, #btrfly, which leverage Olympus ($ohm, 3,3) mechanics but for acquiring $crv and $cvx assets (ref)
So to recap:
- Adding liquidity gets you $crv. Locking up $crv gives you $veCRV which allows users to vote on where future $crv rewards for liquidity pool providers go.
- You are incentivized to lock up $veCRV because it’ll add a bonus multiplier on top of rewards you’re already getting
- Protocols are interested in acquiring your $veCRV because it’ll allow them to vote to get proposals they care about passed. They’re willing to bribe you to get your votes since bribes are cheaper than the gains a protocol will get from increased liquidity.
- Convex is a protocol that exists to aggregate your $crv. You can convert it into cvxCRV for ~50% APR and also stake your Curve LP tokens with Convex to receive higher yields than you would otherwise just staking directly in $crv.
- You can also lock up your $cvx to be eligible for bribes on Votium. Currently bribes are yielding another 52% APR (ref). You can also look up the Bribe tool for $crv bribes (ref).
3/ DeFi implications
Part of why I was interested in learning about the Curve Wars was to assess whether or not it made sense to open a position with exposure to them.
High level thesis: The ability for users to reliably swap between different stablecoins will be important as crypto grows as an industry. The player that is able to offer swaps with the lowest slippage and fees will be the one that wins long term.
The Bankless podcast goes into great detail about how although Curve started with stablecoins, they’re now working on some crazy stuff for non stable coins as well.
If you believe in the high level thesis, then it’s a matter of understanding what your options are for investing in it, against what your decision making criteria is. I’m looking into:
- APR: does the APR make sense for the investment?
- Risk level: how risky is this?
- Short-term potential: is this an investment I’d get into to try to exit when the market becomes a bear market? What’s the assessment for a <1 yr time frame?
- Long-term potential: what’s the assessment for a >1 yr time frame?
I don’t have gas as an explicit factor here, but gas is something I’m also considering because this is on mainnet. Meaning, if you’re going to only invest <$500, then gas costs might not be worth it given how many transactions you need to run. Here’s the overall assessment
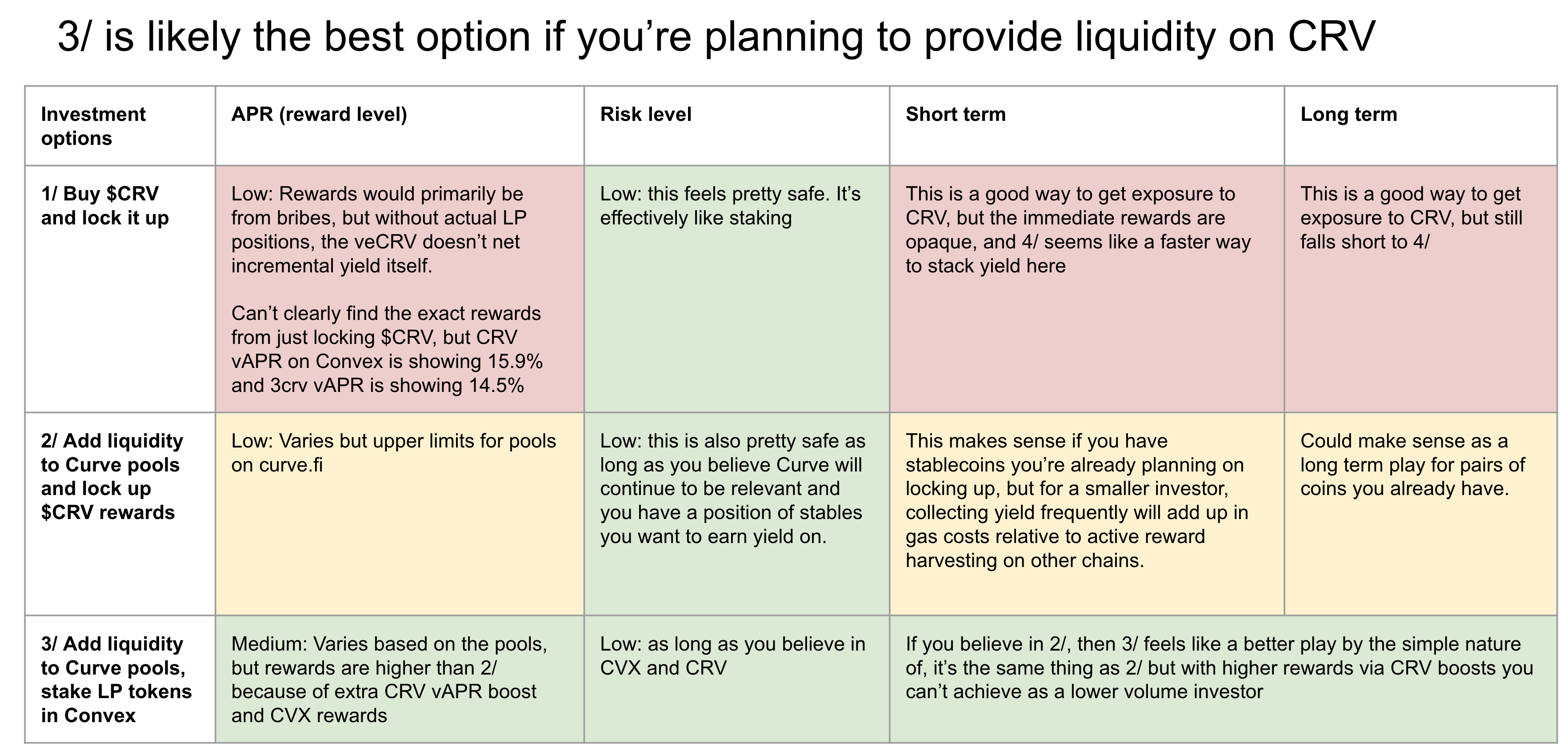
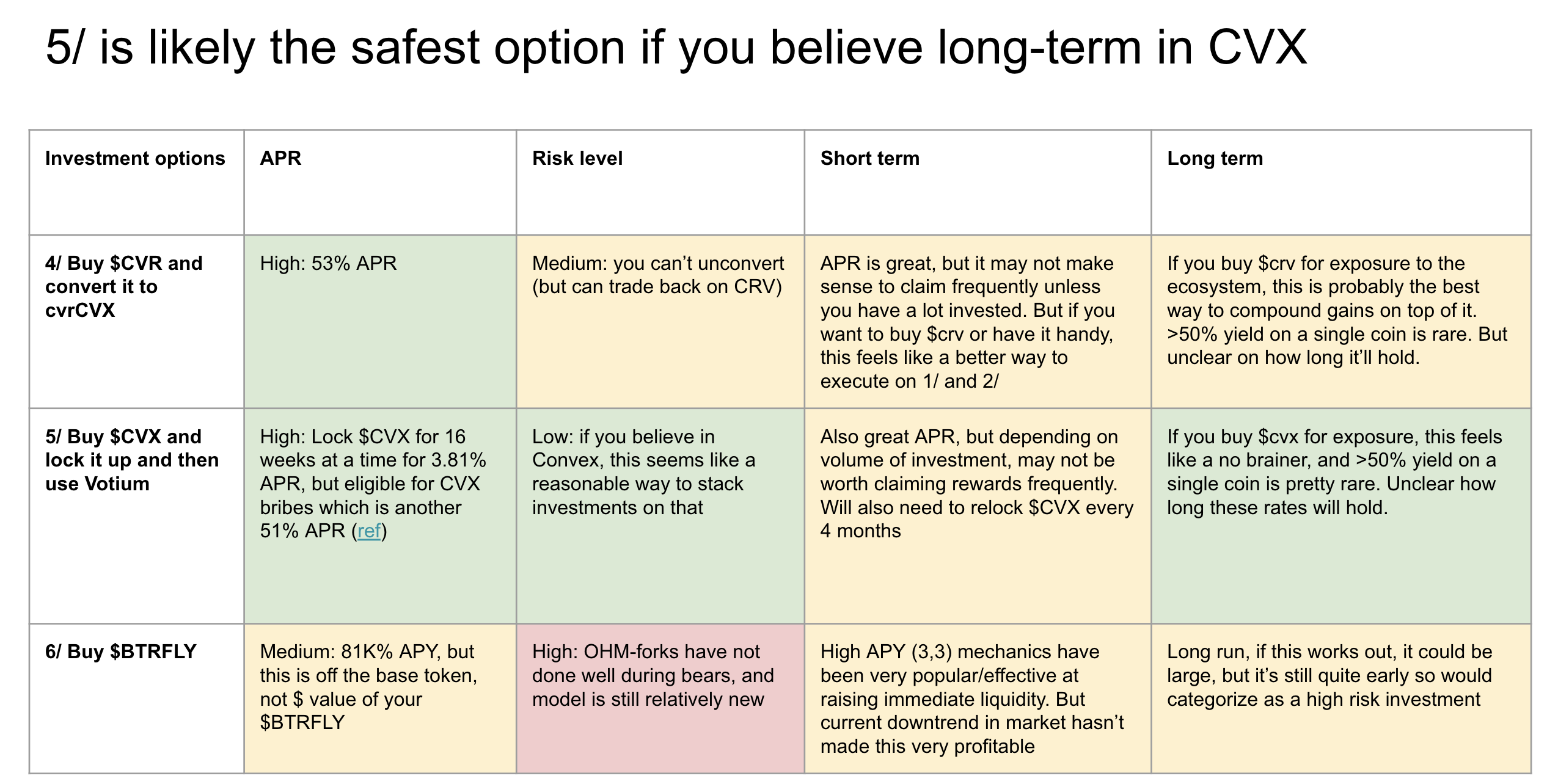
tl;dr
- General caveat: If you are investing <$500, it’s worth doing extra diligence on the gas costs to see if it’d even be worth picking up your rewards given all of this is on mainnet. I actually wonder if one should explore this on a cheaper chain
- If you want to buy $crv, then it probably makes the most sense to lock it up on Convex and get cvrCVX in rewards.
- If you want to buy $cvx, then it probably makes the most sense to lock it up and make sure you’re also using Votium for the extra ~50% APR.
- If you have a large sum of liquidity to provide it’s likely worth pursing option 3/, where you can earn reasonable yields on a large liquidity pool (but note that those rates can vary a lot over time depending on pool size)
4/ Pattern matching on other chains
One thing that’s been interesting to see is how the vote escrow model and protocols trying to capture shares is manifesting across different platforms. We’ll go through a few examples. Since the Curve Wars are effectively being played at the protocol level, there may be an oppt to invest against this thesis on a cheaper chain.
- Fantom and the Spirit Wars
- There’s a similar model to the Curve Wars but playing out on Spirit where:
- Spirit Swap = Curve
- $inSPIRIT is similar to $veCRV
- $linSPIRIT is similar to $cvxCRV
- Liquid Driver = Convex
- $xLQDR is similar to $vCVX
- Spirit Swap = Curve
- However, what’s still yet to be decided is who’s leading the Spirit Wars. There are a number of players making aggressive moves to accumulate more $spirit
- There’s a similar model to the Curve Wars but playing out on Spirit where:
- Fantom and Solid Swap (ref)
- Andre Cronje and Daniele Sestagalli built a new DeFi experiment on FTM called Solid Swap ($rock). The initial airdrop went to the top ~20 protocols on FTM by TVL.
- The new protocol leverages similar ve and (3,3) mechanisms, as well as the the ability to tokenize the ve lock as an NFT that is tradable.
- Avalanche and Echidna Finance
- Platypus Finance recently launched on Avalanche. Platypus lets users stake stablecoins for upgraded yields if they stake their PTP for vePTP. Notably, if one unstakes, they’ll lose all their vePTP, which also means they’ll lose their boosts. So far, Platypus has been holding ~20% yields in the first month.
- Echidna Finance is early but has already stated that they’re trying to build a Convex Finance for PTP (ref)
5/ Appendix
The following resources were a huge part in helping me better understand this:
- yuga.eth’s 5 part series. Part one here
- Bankless podcast on The Curve Wars
- Delphi Digital on The Curve Wars
- The Mythos of Curve Finance
- Cryptoclay’s Spirit Wars coverage 1, 2, 3