Welcome to this blog !! Let’s explore blockchain technology in detail ⤵️
What is Blockchain Technology🤔?
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary system for recording information in a way that makes it difficult or impossible to change, hack, or cheat the system.
A blockchain is a digital ledger of transactions that is duplicated and distributed across the entire network of computer systems on the blockchain.
How Blockchain Technology Works❓
At its core, blockchain technology allows data to be stored in blocks that are linked together in chronological order. Each block contains a limited number of information, and once a block is completed, it is added to the chain.
🔰What is block?
A block in a blockchain is a fundamental component that contains a list of transactions. Each block consists of two main parts: the block header and the block body.
Block Header: The block header contains metadata about the block and is crucial for ensuring the integrity and security of the blockchain. It includes the following components:
-
🟪 Version: Indicates the software or protocol version, helping nodes understand how to process the block.
-
🟪 Previous Block Hash: A reference to the hash of the previous block in the chain, ensuring all blocks are linked and providing security by making alterations to any block difficult.
-
🟪 Timestamp: Records the exact time when the block was created, aiding in maintaining the chronological order of the blockchain.
-
🟪 Complexity: Represents the current difficulty level of the proof-of-work puzzle that miners must solve to add the block to the blockchain. This ensures a steady and predictable rate of block creation.
-
🟪 Nonce: A unique number that miners adjust to solve the proof-of-work puzzle. When the correct nonce is found, it validates the block, allowing it to be added to the chain.
-
🟪 Merkle Root: A cryptographic hash of all the transactions in the block, arranged in a tree structure. It ensures data integrity and quick verification of transaction data within the block.
Block Body: The block body contains the actual list of transactions. In a simplified view, the body holds all the transaction data that is being recorded on the blockchain.
Each of these components plays a vital role in maintaining security, integrity, and functionality, ensuring that data remains tamper-proof and the network operates smoothly.
How are blocks chained together❓
The mined blocks of the blockchain network are chained together by using cryptographic hash functions like SHA-256
🔰 Features of Cryptographic Hash Function:
-
👉 Deterministic: The same input will always produce the same hash output.
-
👉 One-way function: It is computationally infeasible to reverse the hash back to the original input.
-
👉 Collision resistant: It is extremely difficult to find two different inputs that produce the same hash output.
-
👉 Avalanche effect: A small change in the input results in a significantly different hash output.
Types of Blockchain ✨
🔶 Public Blockchains: Open to anyone, like Bitcoin and Ethereum. They offer transparency and security but can be slower and resource-intensive.
🔶 Private Blockchains: Restricted to a specific organization, offering more control and efficiency but less transparency.
🔶 Permissioned Blockchains: A hybrid that allows certain controls and permissions, suitable for enterprise applications.
🔶 Consortium Blockchains: Managed by a group of organizations, balancing transparency, efficiency, and control.
Advantages🔥of Blockchain :
-
➡️ Transparency: All transactions are visible to participants, enhancing trust.
-
➡️ Security: Immutable records and decentralized nature make hacking nearly impossible.
-
➡️ Efficiency: Reduces the need for intermediaries, speeding up transactions and reducing costs.
🔴 Disadvantages:
-
➡️ Scalability: Managing large numbers of transactions can be slow and costly.
-
➡️ Energy Consumption: Particularly in public blockchains like Bitcoin, mining requires significant energy.
-
➡️ Regulation: The legal and regulatory environment is still evolving, posing potential risks.
The Blockchain Trilemma🔺:
The blockchain trilemma, proposed by Vitalik Buterin, founder of Ethereum, highlights the challenge of balancing three critical aspects:
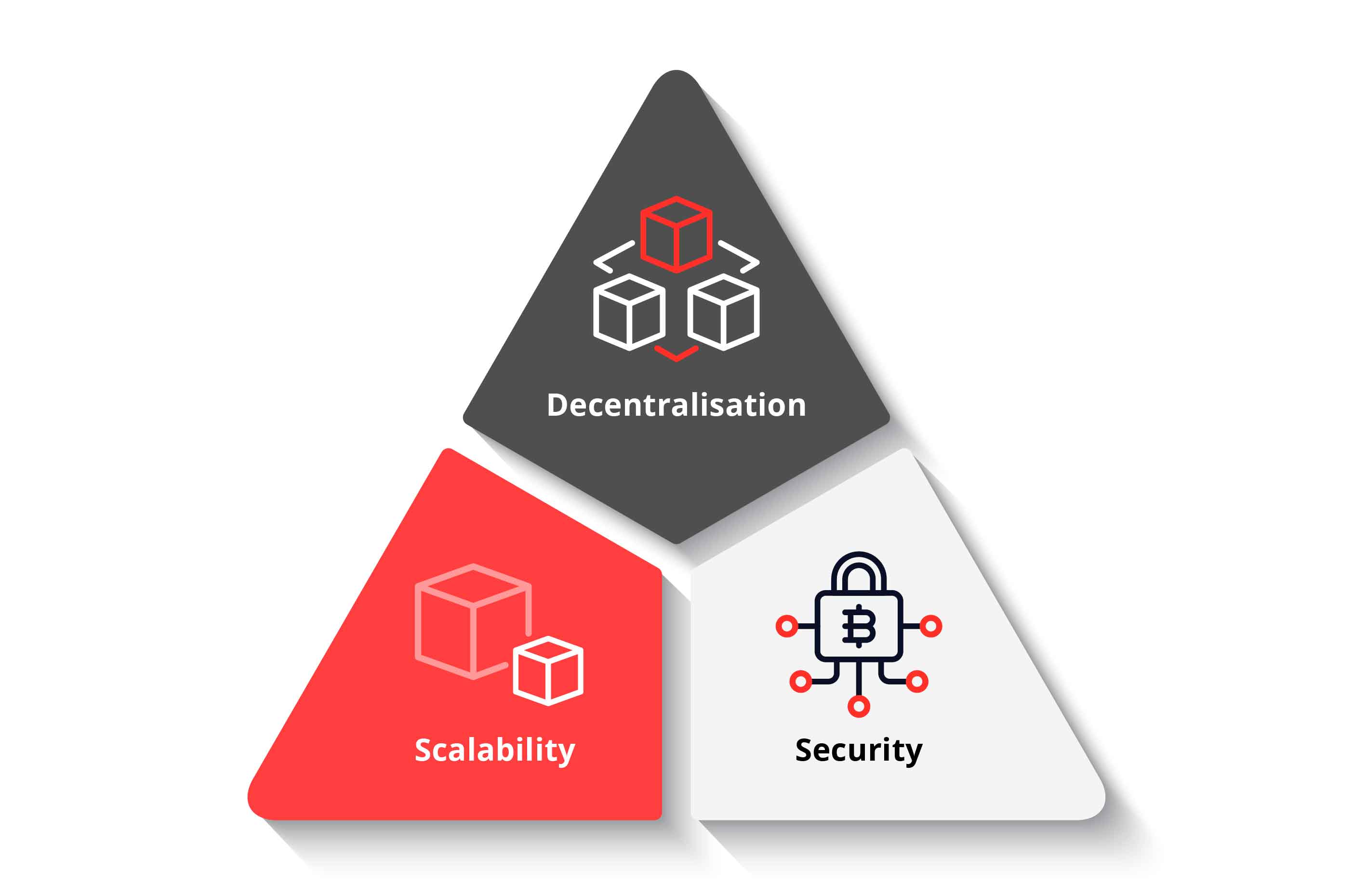
📌 Decentralization: Distribution of control of power across the network.
📌 Scalability: Ability to handle a growing number of transactions.
📌 Security: Protection against attacks and fraud.
Achieving all three simultaneously is challenging, and often, improving one aspect may compromise another. The blockchain trilemma can be solved by following ways:
Trade-off: By trading off between important parameters of the required blockchain network. Even though this approach is not an efficient solution.
You can understand it by following image:

Layer-1 Solutions: It aims to modify the underlying blockchain fundamental architecture and protocol of the network itself.
Layer-2 solutions: These are designed to be implemented atop existing blockchain networks, enhancing scalability, functionality, or transaction efficiency without altering the base layer's core design.
Applications of Blockchain🛠️:
-
↖️ Finance: From cryptocurrencies to decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain is revolutionizing the financial industry.
-
↖️ Supply Chain: Enhances transparency and traceability from production to delivery.
-
↖️ Healthcare: Securely manages patient records and improves data sharing.
-
↖️ Voting Systems: Provides secure, transparent, and tamper-proof voting mechanisms.
-
↖️ Real Estate: Simplifies and secures property transactions.
Blockchain technology is poised to transform numerous industries by providing a secure, transparent, and efficient way of recording transactions. Its potential is vast, but challenges like scalability and regulatory acceptance must be addressed.
As technology evolves, blockchain is impacting the web3 evolution.
⚠️ Note: I have created this blog from my understanding and learning at #BRBBootcamp by Push Builders.
