1. background overview of ICP
1.1 Project Introduction
1.1.1 Introduction
When mentioning ICP (Internet Computer), one might immediately recall the price manipulation events surrounding its initial launch. These events were later interpreted as a fear-driven response from certain crypto powers who perceived its technology as a significant threat. ICP's core technology, widely recognized for its disruptive potential even before its launch, posed a challenge to the status quo of existing blockchain projects. This led some vested interests to suppress it through price manipulation. However, more than three years have passed, and contrary to the expectations of many, ICP has not faltered. Instead, it has cultivated a thriving ecosystem. Notably, ICP's TPS (transactions per second) remains unparalleled among chains. As shown in the chart below, its real-time TPS outpaces Solana by a staggering sixfold margin, maintaining a commanding lead.
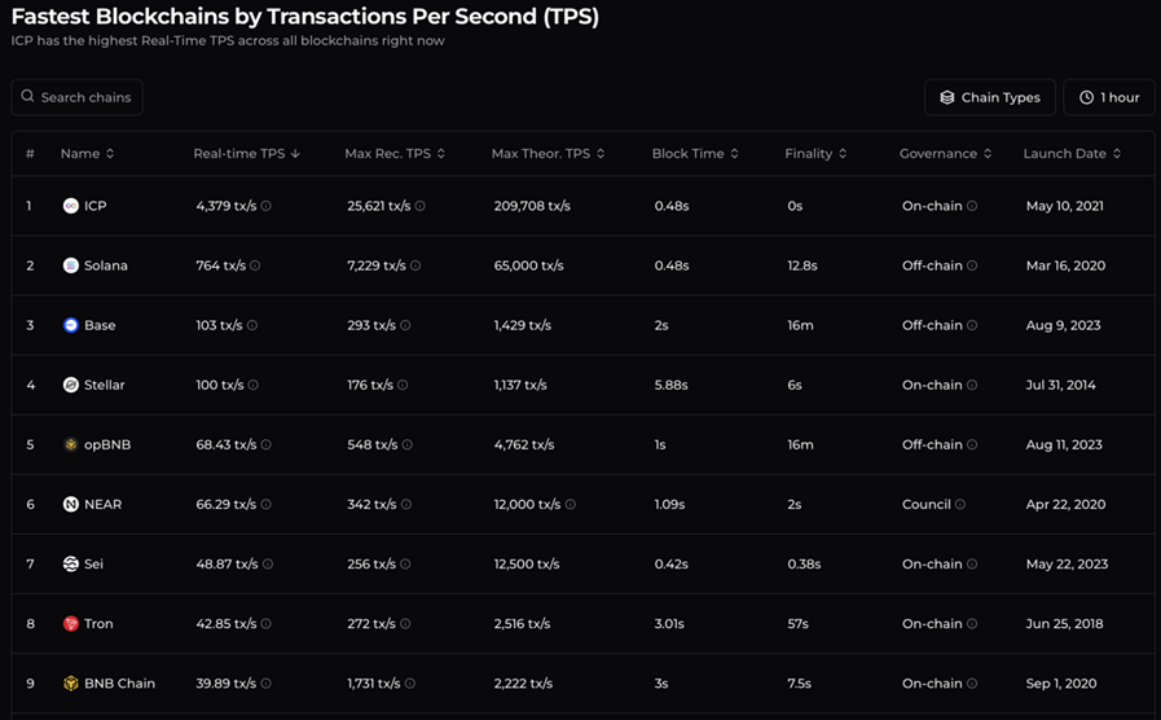
As the world's fastest blockchain, what revolutionary technologies does it possess to garner such a loyal following? In today's article, we will delve into a comprehensive exploration of ICP.
1.1.2 Background and Team Members Creation
The Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) is a blockchain that has been completely re-engineered from the ground up, without sharing technology with any other blockchain. The cryptography that supports this blockchain has been specifically developed by a large team of some of the world's finest cryptographers. When attempting to understand ICP, one must shift their mindset: it is a decentralized infrastructure akin to AWS, designed to support all types of applications globally, not just financial ones.
ICP was developed by the DFINITY Foundation, a non-profit organization based in Zurich, Switzerland. The name DFINITY is a combination of "Decentralized" and "Infinity," reflecting the project's vision of infinite decentralization. DFINITY was a hot topic in the cryptocurrency community in 2021 and raised $200 million in 2018 alone. It was also the first crypto project backed by Andreessen Horowitz (a16z). Other notable investors include Polychain Capital, IOSG Ventures, and Multicoin Capital. DFINITY aims for ICP's underlying technology is designed to serve as a "global computer," enabling the complete hosting and operation of social media, large-scale games, and enterprise systems on the blockchain, thereby eliminating reliance on traditional centralized technologies like those provided by major tech companies such as Google, Amazon, and Meta.
To achieve this vision, the DFINITY Foundation has assembled a large and highly skilled team of experts (comprising cryptographers, academics, and leaders), reportedly the largest R&D team in the blockchain sector with over 1,600 publications among its members. Some key figures include:
● Dominic Williams: Founder, President, and Chief Scientist of the DFINITY Foundation and the ICP project. He established DFINITY in 2015 and has a background as a tech entrepreneur, distributed systems engineer, and theorist. He has made significant contributions to distributed computing and cryptographic theory. His vision is for ICP to represent the third major revolution in blockchain technology after Bitcoin and Ethereum.
● Josh Drake: A principal contributor to ICP and Chief Operating Officer at the DFINITY Foundation. Prior to joining DFINITY, he worked at Coinbase.
● Jan Camenisch: Chief Technology Officer at the DFINITY Foundation. He has published over 120 widely cited papers in privacy and cryptography and served as a chief researcher at IBM for 19 years.
● Samuel Burri: Vice President of Engineering at DFINITY. Over the past eight years, he led a global team responsible for building and maintaining Schindler elevator control software.
● Pierre Samaties: Chief Commercial Officer at DFINITY, an expert in energy and innovation. Formerly a partner at Roland Berger and head of its global crypto and digital assets practice. He also served as CEO of RWE Middle East with over 20 years of experience in strategic consulting and venture building across energy, AI, and crypto industries. He leads global digital assets, Web3, and Metaverse practices and is primarily responsible for promoting the commercialization of ICP's technology and ecosystem development.
1.1.3 Key Milestones

1.2 Tokenomics
Unlike many token economic models, the entire ICP network is governed by a unique economic model. The ICP (native token) does not have a total supply cap; instead, it operates on the concept of supply, which primarily consists of circulating supply and staked portions. The factors that influence the real-time supply of ICP mainly include its consumption and issuance. As of November 22, 2024, the ICP supply stands at 525 million, with 38.4% remaining unlocked.

Before understanding the composition of its tokens, we must first understand its neuron-based governance mechanism.
1.2.1 Network Nervous System
In the Network Nervous System (NNS), the on-chain governance DAO of ICP, anyone can create a neuron by staking ICP. This allows them to propose or participate in governance decisions. If ICP is likened to a massive distributed computer network, with various data centers and nodes providing the necessary hardware infrastructure, then the NNS serves as the administrator of this computer. It determines the operational mechanisms of the ICP network and related matters such as the distribution of benefits within its ecosystem through proposals.
Neuron holders receive rewards proportional to the amount of ICP tokens staked and the duration for which they are locked (up to a maximum of 8 years). When a proposal passes, neurons accumulate "maturity." Once a certain threshold is reached, they can "produce" new neurons (where the ICP amount locked in new neurons equals the old neuron's ICP amount multiplied by its maturity). The rewards for these neurons primarily come from ICP inflation. In the first year, inflation is set at 10% of the total supply, decreasing quadratically over time until it stabilizes at 5% after eight years. Currently, the inflation rate is 6.59%. Users have the option to merge new neurons, akin to reinvesting interest, or to disburse them, converting new neurons into ICP for withdrawal.

Moreover, users may lack the time or expertise to participate in all voting decisions. Therefore, neuron holders have the option to delegate their voting rights to other trusted neurons, instead of voting directly on proposals. This concept of delegating voting power to other voters is known as liquid democracy.
A particularly important aspect is setting the "Dissolve Delay" when staking ICP to generate neurons, which is similar to the term of a fixed deposit. The duration of this dissolve delay is irreversible and can only be reduced through dissolution; it cannot be withdrawn prematurely before maturity. When stakeholders choose to initiate unlocking, the neuron enters a dissolving state and completes dissolution within the pre-set "Dissolve Delay" period. The "Dissolve Delay" can increase the voting weight of neurons, with a minimum requirement of six months to participate in voting. Setting it to eight years can double the voting power. This "eight-year" setting has given rise to the unique community culture known as the "8 Years Gang" within the ICP community, reflecting the commitment of long-term holders in the ICP ecosystem.
1.2.2 Consumption of ICP
The diagram below illustrates the total consumption of ICP. Since the launch of the mainnet, a total of 432,471 ICP have been destroyed through the following three methods:
● ICP Transfer Fees: Each transfer or transaction approval incurs a fee of 0.0001 ICP. To date, transactions have consumed 1,477 ICP.
● Rejected Proposal Fees: Initiating a proposal requires a fee of 1 ICP, which is refunded if the proposal is accepted. However, if a proposal is rejected, 10 ICP are deducted. According to data from the ICP Dashboard, there have been 678 rejected proposals, resulting in the destruction of 6,780 ICP since the mainnet launch (some of which may not yet be destroyed but will inevitably be in the future).
● Network Consumption: Developers of dApps and smart contracts on ICP need to consume Cycles (similar to gas fees on ICP) to cover computational and storage costs. Cycles can only be obtained by destroying ICP (an irreversible process). Based on previous data, as of November 15th, ICP destruction through Cycles amounted to 420,000 ICP, accounting for 97% of total consumption. This indicates that conversion to Cycles is the primary source of ICP consumption.
The diagram also shows a notable increase in destruction from September 9th onward. This surge is largely attributed to the DeFi project Sonic (the first DEX on ICP with a gas-free AMM). Sonic enables a swap mechanism where ICP is destroyed and converted into Cycles to mint XTC (Cycles Token). Driven by demand, all ICP used for swapping XTC on Sonic has been destroyed.

1.2.3 Inflation of ICP
Inflation has two primary sources:
● Rewards for Node Providers: As of November 15, rewards paid to node providers totaled 13 million ICP. Unlike the reward models of many other blockchain nodes, prior to March 2022, ICP node rewards were calculated based on fiat currency value. Consequently, the monthly issuance rewards paid to node operators were determined by the average monthly price of ICP. This meant that the lower the ICP price, the more issuance occurred, and conversely, the higher the price, the less issuance. Subsequently, the monthly rewards for node operators have been pegged to XDR (a basket of five major international currencies, including the US dollar, euro, yen, and pound) as a unit of calculation. If there is a significant change in the ICP/XDR exchange rate, an automatic stabilization mechanism is considered.
● Rewards Allocated for NNS Neuron Governance Voting: All neurons participating in network governance receive voting rewards denominated in ICP, which are sourced from ICP issuance.
Additionally, there are two other avenues for ICP increase:
Neuron Dissolution Release: According to data from the ICP Dashboard, the total staked ICP amounts to 238 million (approximately $2.65 billion). Of this, 85% of ICP is in a non-dissolving state, while 15% is in a dissolving state. In terms of "dissolve delay" years, 59% are set for an 8-year term, with a locked value of up to $1 billion. This positions the ICP network among the top ten blockchain ecosystems by Total Value Locked (TVL), although this is not currently reflected in DeFiLlama's calculations. The next largest segment is for terms between six months and one year, accounting for 9%.


The second method involves minting ICP through maturity. When neuron holders choose to utilize their accumulated maturity, it is converted into ICP. As of November 5th, a total of 42.8 million ICP have been minted through maturity, accounting for 8% of the current supply. In October, 1.09 million ICP were minted, and nearly 160,000 have been minted so far in November.

1.3 Overview of ICP Data
1.3.1 Project-Related Data
The current in-dApp Total Value Locked (TVL) on ICP stands at $53 million. Notably, since the beginning of 2024, the TVL has experienced rapid growth, doubling its initial value at the start of the year.

Based on the composition of Total Value Locked (TVL), there are currently 10 decentralized applications (dApps) on the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) as recorded by DefiLlama. Among these, six dApps have a relatively strong TVL. Of these six, one is ICP's own SNS DAO, while the remaining five are WaterNeuron, ICPSwap, Sonic, ICDex, and Helix Markets.

In terms of revenue levels, ICP ranked among the top 8 major chains in October.

From the perspective of TPS, ICP has consistently maintained a significant lead over other blockchains. Since September, it has experienced a substantial increase, rising from around 5,000 to nearly 7,000.

From the perspective of daily transaction volume, there has been a significant increase in transactions on the ICP platform since September. The volume doubled from approximately 15,000 to around 30,000. Furthermore, on October 1st, it reached a record high of 52,300 transactions.

Based on data from GitHub submissions, ICP exhibits the most active development activity, ranking first with over 7,000 commits (modifications to the project's source code). This demonstrates ICP's continuous efforts to update and refine its project.

1.3.2 Social Media-Related Data
As of November 5, 2024, ICP has amassed nearly 700,000 followers on X and maintains a dedicated Reddit column with frequent updates and discussions.
ICP's hubs around the world each have their own ecosystem accounts and communities, along with accelerator partners, continually contributing to the growth of ICP's ecosystem globally.

Furthermore, the fully decentralized community OpenChat, which is entirely based on ICP, boasts 25.71K monthly active users (MAU). These users will benefit from a completely decentralized community product.
1.4 Technical Architecture
The development of ICP began in 2019 with the release of Copper, which introduced a Software Development Kit (SDK) and Motoko, a programming language specifically designed for writing smart contracts. The primary advantage of smart contracts on ICP lies in their ability to combine the expressiveness and scalability of traditional applications with the benefits of decentralized and trustless execution offered by blockchain technology. As illustrated in the following conceptual diagram, there is a gradual increase in decentralization from centralized servers to Ethereum; however, this comes at the cost of scalability. Positioned in the middle of this spectrum, ICP aims to strike a balance between scalability and decentralization.

The Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) employs a layered architecture, which primarily consisting of canisters, subnets, nodes, and data centers (including resources such as CPU, network, and memory).

We can view the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) as a system composed of multiple subnets, where each subnet essentially functions as an independent blockchain. Smart contracts on one subnet can communicate with smart contracts on another by sending messages. Within each subnet, there are multiple containers that serve as the fundamental interoperable units within ICP. Each container contains user-uploaded code and state.
At the foundational level, independent data centers host dedicated hardware. Nodes operate on top of these data centers, handling data and state execution within the subnet containers. These nodes are independently owned and controlled by node providers distributed across data centers worldwide, thereby increasing the capacity of the Internet Computer blockchain. Currently, ICP consists of 37 subnets, 132 node providers, and 784,000 containers.
This layered architecture provides ICP with enhanced scalability and flexibility, enabling it to support applications of varying scales and requirements. Additionally, its design provides a user experience that closely resembles cloud services.

Below, we introduce the concept of "Canisters", the smart contract system of the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP). Canisters serve as the framework for decentralized applications (dApps) and support programs written in multiple languages. Each Canister has its dedicated memory. If we consider ICP a supercomputer, then "Canisters" function as processes within this computer, with each Canister process containing its own runtime memory. You can encapsulate smart contract-related data within a specific Canister. This represents ICP's unique method of data storage: Canisters allow you to store the program's state, databases, and even frontend data (such as game assets) within this container, aiming to further expand dApps. Essentially, ICP is a platform that hosts Canisters, utilizing containerization technology to deploy numerous Canister containers across ICP nodes.
1.4.1 Powerful "ChainFusion" Technology Let's first see what Samuel Burri, Vice President of Engineering at DFINITY, has to say:
"Chain Fusion refers to the ability of smart contracts on ICP to sign transactions and seamlessly interact with other blockchain networks without relying on any single point of trust." ICP uses Chain Fusion technology to write transactions directly to other chains (cross-chain integration and interoperability controlled by smart contracts at the protocol level) without centralized intermediaries like central bridges, thus achieving a secure multi-chain future.
-
Chain-Key Cryptography The core technology of Chain Fusion is ICP's unique chain-key cryptography. This cryptographic method allows ICP's smart contracts to interact directly with other blockchains (such as Bitcoin and Ethereum). In this way, ICP can verify and generate signed transactions on other chains, creating a set of "virtual nodes" for each blockchain on ICP, enabling secure peer-to-peer communication. For example, smart contracts on ICP can directly control Bitcoin addresses (such as sending or receiving BTC), all achieved through chain-key technology.
-
Chain-Key Tokens ICP offers a special form of token called chain-key tokens (e.g., ckBTC and ckETH). Unlike traditional "pegged tokens," these tokens are entirely managed by decentralized smart contracts, with each chain-key token backed by an equivalent amount of native assets. For instance, ckBTC is a Bitcoin token on ICP that users can exchange for actual BTC at any time. Its creation and circulation are autonomously handled by ICP smart contracts without relying on centralized custodians. This mechanism not only enhances transaction efficiency and security but also significantly reduces the cost of cross-chain operations.
Under the architecture of Chain Fusion, cross-chain communication does not require relay networks or traditional "bridges," thereby reducing complexity and security risks. For example, many cross-chain bridges on Ethereum are prone to attacks, whereas Chain Fusion's approach eliminates these vulnerabilities through fully decentralized verification. This allows for the development of dApps across multiple blockchains in a unified environment, offering features such as:
-
Bidirectional communication
-
Signing and submitting transactions using ICP "container" smart contracts
-
Cost-effective, fast finality, and reverse gas models
ICP's computational capabilities and architectural design also make cross-chain interactions more efficient: handling numerous cross-chain requests per second with low latency and fast transactions. It supports complex on-chain logic, such as multi-chain payments and smart contract calls.
Overall, this powerful technology unleashes "ICP superpowers" for other blockchains, providing them scalability and low-cost transactions. For example, smart contracts on ICP can offer up to 400 GiB of storage space for non-ICP decentralized applications, allowing them to store data on-chain. Additionally, it can support a range of network services, from social networks to sophisticated AI models (which we will discuss later). Of course, the benefits are twofold: they also attract more developers and assets to the ICP ecosystem. Furthermore, this technology has become an essential tool for developers seeking to create more complex applications utilizing multiple blockchain networks.
Chain Fusion has proven to be not just a technological innovation, but also a powerful solution to the long-standing interoperability challenges among isolated blockchains. As this technology matures and gains widespread adoption, it has the potential to revolutionize decentralized finance (DeFi), data management, and many other applications, bringing us closer to the truly interconnected blockchain future we aim to achieve.
1.4.2 Chain Fusion + Artificial Intelligence = Decentralized Artificial Intelligence When it comes to AI, ordinary users often have little knowledge of how its models operate. How is data used? How do models generate responses? Everything remains shrouded in opacity. Decentralization of AI on the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) means introducing the trustworthiness, security, verifiability, and resilience of smart contracts into AI applications to ensure a level of transparency and security that traditional platforms cannot match. However, as is well known, AI is labor-intensive. Running inference on AI models with millions of parameters involves billions of arithmetic operations, such as multiplication and addition. Therefore, to support on-chain inference, a blockchain needs the capability to process billions of operations per second.
To make on-chain AI inference and large model training a reality, ICP's "container" smart contracts need to handle more computation and memory-intensive tasks. In July of this year, Cyclotron made a dazzling debut, marking a historic breakthrough for ICP by directly increasing computational power by about ten times. This milestone not only expanded the computational and memory capabilities of "containers" but also paved the way for future GPU hardware acceleration.
So, how does ICP achieve this? First, let's talk about virtual machines. Virtual machines are crucial for AI computation in blockchains because they execute the code of smart contracts. The functionality and performance of virtual machines directly affect how much AI computation smart contracts can perform. For example, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is tailored for DeFi smart contracts but lacks features like floating-point arithmetic needed for AI computation. In contrast, ICP uses WebAssembly as its virtual machine, which supports floating-point numbers and is designed from the ground up for near-native performance. Cyclotron's goal consensus is to maximize the floating-point performance within ICP's virtual machine. Simply put, ICP has made three major optimizations:
-
Deterministic Floating-Point Arithmetic Most AI libraries and frameworks rely on floating-point arithmetic. ICP requires that floating-point operations be deterministic, meaning that the same input always produces the same result. This is because ICP executes the same code on multiple nodes and runs a consensus algorithm to determine the correct result. If floating-point operations are not deterministic, nodes may diverge, preventing blockchain progress.
DFINITY engineers found a way to accelerate deterministic floating-point arithmetic within a WebAssembly virtual machine called Wasmtime. This is a low-level compiler optimization that generates faster code. This enhancement not only improves ICP's performance but also benefits other platforms using Wasmtime.
-
Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD) SIMD is a common technology in modern CPUs, allowing one instruction to execute multiple arithmetic operations simultaneously. For instance, WebAssembly can perform four parallel floating-point addition operations with one instruction, significantly improving computational efficiency.
-
SIMD Support in AI Inference Engines The final piece of Cyclotron's puzzle is adding WebAssembly SIMD support to AI libraries. The DFINITY team provided a WebAssembly SIMD implementation for the open-source Sonos Tract inference engine. The new code uses SIMD instructions to implement matrix multiplication and other numerical algorithms. This contribution benefits not only ICP but also the wider developer community.
Together, these optimizations significantly increase speed. In end-to-end AI inference workloads, observed improvements range from 5x to 19x, depending on the model used, as shown in the chart below:

It can be observed that the launch of Cyclotron not only distinguishes ICP in the blockchain sector but also paves a bright path for the deep integration of AI and blockchain in the future. This development makes ICP the only blockchain capable of fully executing facial recognition on-chain, while also handling advanced AI use cases such as image classification and GPT-2 inference (provided by DecideAI). This is not merely a technological leap but a redefinition of blockchain application scenarios, opening the door to future on-chain AI exploration.
1.4.3 DePIN Infrastructure
The network nodes of ICP are composed of hardware machines that meet specific requirements, enabling data storage and computation to be fully realized on the blockchain network. This decentralized "on-chain storage and on-chain computation" completely replace centralized "cloud storage and cloud computing," making ICP an ideal DePIN infrastructure network.
1.5 Competitive Landscape
If we look at what ICP is doing, it is almost impossible to find a direct competitor. This is because it is not merely a blockchain; it is an "Internet Computer" capable of hosting a complete infrastructure from storage to computation. This architecture breaks the limitations of traditional blockchain projects, aiming to become a seamlessly integrated open internet service platform that provides developers and users with an experience beyond Web3.
However, if we reflect on the period from 2022 to 2024, we will find that this was a crucial time for the significant acceleration in human technology, especially with revolutionary breakthroughs in AI development. We live in a world dominated by centralized giants like OpenAI, Google, and Amazon, which have abundant talent, hardware, and capital. However, centralized AI always aims for profit maximization, and the closed nature of large tech companies towards large language models hinders the realization of "AI democracy." Against this backdrop, calls for "open-source AI" and "Crypto AI" have become increasingly prominent. This is why the early convergence of two major tech trends (AI + Crypto) is so compelling—this is where miracles happen.
ICP is not specifically a Crypto AI, but it can provide a tamper-proof environment for AI models and other applications, promoting security and trust through open and honest business practices. Containers are high-performance smart contracts capable of managing vast computational resources, allowing for the rapid and efficient deployment of complex AI models. DFINITY's vision also includes creating a decentralized future for AI. In this context, we primarily compare it with other platforms that closely integrate with AI.
1.5.1 NEAR Protocol
Over the past decade, blockchain has undergone three evolutionary stages: Bitcoin, Ethereum and smart contract platforms, and the third-generation blockchains aimed at solving Ethereum's scalability issues. NEAR (NEAR Protocol) is an example of a third-generation blockchain.
NEAR was founded in 2018 and launched its mainnet in October 2020. In 2022, it secured $500 million in funding from renowned institutions such as A16Z Crypto and Tiger Global. As a PoS-based Layer 1 blockchain, NEAR decided to build an entirely new architecture to address scalability issues: it moved away from the idea that every node participating in the network must run all the code by employing sharding technology (Nightshade, one of the methods for horizontal scaling in blockchains). If a blockchain is likened to a highway, sharding technology can widen this highway and divide it into multiple lanes for traffic distribution. Nightshade distributes the task of processing transactions across numerous validator nodes, with each node only needing to handle a small portion of network transactions. This allows nodes to process and validate transactions in parallel across multiple shards, thereby increasing transactions per second and enhancing overall network scalability. NEAR currently ranks sixth among all public chains with a TPS of 68.48 (ICP ranks first with nearly 5k TPS).
According to DeFiLlama, NEAR's current In-dApp TVL is $300 million, with Burrow accounting for 73% at $220 million. Burrow is a decentralized, non-custodial lending platform based on asset pools, similar in nature to Aave, Compound, and other pool-based protocols. The near-vertical TVL surge observed in early April 2022 in the chart below was due to Burrow's launch on the NEAR mainnet.

One of NEAR's major features is its excellent implementation of chain abstraction, which enhances user experience and understanding. For instance, it uses readable account names, allowing users on NEAR to send funds to alICPe.near instead of a complex address like 0x123abc... Additionally, new users can interact with smart contracts without needing a wallet. These characteristics are highly attractive to both developers and users.
NEAR's two flagship projects are undoubtedly the Rainbow Bridge (launched in May 2021 and upgraded in June 2023) and Aurora. The Rainbow Bridge enables users to seamlessly transfer any Ethereum token between Ethereum and NEAR/Aurora. Aurora serves as NEAR's Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) because it is built using Ethereum's coding technology, allowing developers to easily transition to the NEAR chain without rewriting their dApps or learning new development tools. Supported by the NEAR network, Aurora offers extremely low fees (approximately $0.02 according to the official website) and can confirm transactions within 2 seconds. Aurora currently has a Total Value Locked (TVL) of over $15 million and an ecosystem comprising more than 211 projects. According to its latest post on X, Aurora remains the fastest and most cost-effective blockchain solution in 80,000 simulations.
1.5.2 Sentient
Similar to the vision of ICP, Sentient aims to create foundational infrastructure for AI and blockchain. Its approach is worth exploring. Sentient's goal is to develop an open-source AI platform that empowers AI developers with ownership to:
-
Monetize their models, data, and other innovations.
-
Collaborate with others to build powerful AI.
-
Become significant stakeholders in the new open AI economy.
Sentient has announced its development on Polygon.
When discussing Sentient, it is essential to mention its distinguished core contributor team. One of its founders is Sandeep Nailwal, the founder of Polygon, and its advisor is Sreeram Kannan, founder and CEO of EigenLayer. With the support of this top-tier team, Sentient completed an $85 million seed funding round in July, led by Peter Thiel's Founders Fund, which might be the largest disclosed funding for a crypto AI project this year. Sentient is currently in the very early post-funding initial development stage, with its official website yet to launch and actively recruiting a large number of engineers.
OpenAI shifted from open to closed due to funding and capital needs to achieve greater success and revenue. However, Sandeep pondered whether it is possible to remain open while securing funding and developing technology. To address this issue, Sentient proposed a new framework: the OML model, which stands for Open (open-source: anyone can create and use models), Monetizable (models can be licensed by owners for use), and Loyal (controlled by a collective/DAO). This model allows models to be used in a distributed environment while tracking usage and rewarding contributors through decentralized protocols, ensuring both openness and profitability. The OML white paper has already been released.
The official roadmap indicates that Sentient will undertake early platform development and Open AGI hackathons in the short term, followed by the release of the Sentient protocol, early foundational model experiments, and community-contributed early models. The long-term goal is to achieve incentives and monetization for building an AI economy, establish community-based final models, and Open AGI.

1.5.3 AO
AO is an official project by Arweave, launched in June with the release of its white paper by Sam Williams, the founder of Arweave, a decentralized data storage platform that allows for permanent data storage on the network. The model has received high praise from top venture capital leaders, including those from A16Z and SevenX Ventures. The native token, $AO, is used to incentivize participants, ensuring network stability and efficiency. The maximum supply of AO tokens is 21 million, with 100% allocated to the community: 36% to AR holders and 64% to cross-chain users (currently $stETH and $DAI). The AO token follows a Bitcoin-like halving cycle, with the distribution rate gradually decreasing every five minutes.
AO is a scalable blockchain network built on the Arweave data storage platform. In traditional finance, funds are stored in banks and managed centrally, which is inefficient and cumbersome. In DeFi, assets can be automatically staked and moved, improving capital efficiency. On AO, all funds are self-custodied by users and managed through their own bots or AI. Each fund can have its own strategy, significantly enhancing the intelligence level of financial assets. Due to AO's superior performance and architecture, users can inject contract code into their wallets and have strategies automatically executed by proxies. AO's ultimate vision is to achieve seamless integration of AI and blockchain, allowing AI models to be hosted on-chain and run directly on-chain, enabling autonomous decision-making.
Within three and a half weeks of its launch, AO attracted over 3,000 developers to join the Arweave ecosystem for development participation, leading to a surge in AO applications and maintaining growth momentum.
Previously, Arweave as a storage protocol could only be seen as a hard drive; relying solely on a hard drive could not support larger narratives and use cases. Thus, Arweave created AO as a CPU perfectly compatible with its hard drive and integrated it into the narrative of on-chain AI. It can be said that AO saved Arweave, with the market showing great interest and anticipation for AO. A network capable of both storage and computation is what ICP has already achieved. Before February 2024, AR's price lingered below $10, significantly underperforming BTC without rising despite mainnet upgrades and the start of a bull market. After AO's launch, AR's price quickly quadrupled within a month; although it has recently fallen back somewhat, it remains around the $15 level.

1.6 Preliminary Value Assessment
Valuing ICP is a challenging task because it is not merely a blockchain; it aims to reconstruct the entire Web2 world within the Web3 framework. When assessing this platform based on its future plans and visions, its value appears limitless. However, we must also consider the discrepancies and achievements of ICP in relation to its 20-year roadmap at critical time points.
Below is a comparison between ICP and NEAR. Since the price manipulation event by a third party in 2021, ICP's token price has remained low, making its market capitalization less impressive. Nevertheless, it consistently ranks within the top 30 on CoinMarketCap. Furthermore, ICP's ecosystem is continuously being developed and improved, which we will analyze separately later. Notably, its founder has expressed a strong interest in and inclination towards the blockchainization of AI, a sector that holds immense potential for unlocking future value.

2. The Ecosystem of ICP
In the ICP ecosystem, over 300 dApps have been integrated, including 57 in the Social category, 52 in DeFi, 49 in Chain Fusion, 47 in NFT, 29 in Gaming, and more than 60 in AI.

Below, we will analyze the representative leading projects within its ecosystem based on these main categories. As the ICP ecosystem has gradually grown into a vast network, space constraints prevent us from listing each one individually.
2.1 DeFi
2.1.1 ICPSwap (ICPS)
Project Overview: From its name, it is evident that ICPSwap is the native DEX of ICP, and it is also the earliest DEX in the ICP ecosystem. Its products are highly comprehensive, including an all-in-one integration of various DeFi products such as DEX, Staking, Farming, NFT marketplace, Wallet, and DAO governance. In terms of DEX, besides the traditional Swap feature, there is a professional version product with candlestick charts and analysis modules. The Total Value Locked (TVL) ranks second in ICP at $9.95 million.
Social Media Platform:
Discord: https://discord.com/invite/hHzFvUw3SV
X: @ICPSwap
2.1.2 Sonic
Project Overview: Sonic is currently the largest DEX on the ICP chain, with a TVL of nearly 10 million USD. Its features include fast transaction speeds (confirmation within 2 seconds) and low transaction fees (fees within 0.02 USD). The product modules include a Swap, an asset issuance platform similar to LBP (Liquidity Bootstrapping Pool), data analysis tools, and more. The product is relatively highly integrated, providing a seamless user experience. Additionally, in Sonic's V3 version, it has been integrated into Bitfinity, a Bitcoin Layer 2 network that is EVM-compatible based on ICP.
X: @sonic_ooo
2.1.3 Helix Markets
Project Overview: An order book-style DEX on the ICP chain. In addition to supporting assets on the ICP chain, it also supports assets from the Runes protocol, such as Rich. This highlights the powerful chain integration feature of ICP, which enables direct trading of assets like Bitcoin mainnet BTC, Ordinals, BRC20, and Runes protocol on the ICP chain. Compared to the previous two projects, Helix Markets was developed somewhat later and has approximately $2 million in TVL.
X: @HelixMarkets
2.1.4 KongSwap
Project Overview: KongSwap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) based on Automated Market Maker (AMM) technology, offering seamless, bridge-free cross-chain trading across multiple blockchains such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana. It leverages ICP's Chain Fusion technology and stable memory within the ICP protocol to address common decentralized issues such as high fees, liquidity fragmentation, and complex user experiences. KongSwap has also established an active community on GitHub and developer forums to ensure transparency and accessibility for developers. KongSwap officially joined SNS in September.
X: @kongswap
In addition, there are other early-stage DEXs like ICPEx (X: @ICPExchange), which focus on being memecoin-friendly and have become the first ICP chain application integrated into the mainstream web3 world through Dex Screener. Whether it is a traditional project or a memecoin, as long as it brings real on-chain trading volume and liquidity to ICP, it holds certain value.
2.1.5 Water Neuron
Project Overview: Established in 2021, this liquidity staking protocol is specifically designed for ICP, similar to Ethereum's Lido. It aims to provide liquidity for ICP users, allowing them to maintain asset liquidity while staking ICP tokens. As of now, WaterNeuron's Total Value Locked (TVL) has exceeded $15 million, demonstrating its influence and market recognition within the ICP ecosystem. It is a standout DeFi project in the ICP ecosystem. With the continuous expansion of the ICP ecosystem, WaterNeuron is consistently innovating and optimizing its liquidity staking products, attracting an increasing number of DeFi users. WaterNeuron is gradually becoming an indispensable project, playing a significant role in enhancing the decentralization and capital efficiency of the ICP network.
Contact: @WaterNeuron
2.1.6 SparkFi
Project Overview: A DeFi protocol for liquid staking of $ICP, utilizing nICP as the underlying asset to unlock composable liquidity for ICP stakers.
X: @sparkfiicp
2.1.7 Bob.Fun
Project Overview: A memcoin launch platform on ICP, formerly an innovative mining protocol based on ICP. Bob.fun has contributed to a significant amount of cycle burning on the ICP network and has also given rise to several successful memecoin projects.
Contact: @bobdotfun
2.1.8 Oisy Wallet
Project Overview: The Oisy Wallet, maintained by the DFINITY Foundation, is the most representative practice of ICP's initiative for "user wallet-free interaction with DApps." It is a browser-based multi-chain crypto wallet operating on the Internet Computer, yet it handles Ethereum ERC-20 tokens, allowing users to send and store cryptocurrencies and connect directly to DApps from the browser. Oisy Wallet users can easily access it across different devices without downloading any plugins or applications. For users keen on decentralization, Oisy Wallet is fully on-chain, with its full-stack application securely deployed on-chain. Moreover, wallet keys are generated and protected on the ICP network using chain key technology, where keys are generated using advanced cryptography and distributed among dedicated ICP nodes. The Oisy Wallet is delivered to browsers via smart contracts rather than being traditionally downloaded as a wallet app from mobile app stores. This once again demonstrates that ICP's advantage is not just user experience but truly achieving decentralization.
X: @oisy
2.2 Social
2.2.1 OpenChat
Projec overview: A renowned decentralized social application founded by Matt Grogan, a former smart contract engineer at DFINITY. It is the world's first community-controlled chat system, fully deployed on the ICP chain. Launched as a DAO in March 2023, it raised 1 million ICP in exchange for 25 million CHAT (25% of the initial supply). It offers a feature set and performance similar to Discord and Slack while providing many crypto-native features, such as allowing users to send messages containing tokens like ICP and BTC to each other. OpenChat currently boasts 25.71k MAU (monthly active users).
X: @OpenChat
2.2.2 DMAIL
Project Overview: This is a platform providing encrypted email services, unified notifications, and targeted marketing. It integrates with multiple chains and dApps to meet the needs of users, developers, and marketers. The platform supports a user self-hosted decentralized mailbox solution deployed across various chains and features a proprietary messaging protocol based on the Web3 identity system. Dmail ensures secure communication via email and notifications, establishing itself as a critical communication link in the Web3 infrastructure. The $DMAIL token was listed on exchanges like OKX at the end of January this year.
X: @DmailoffICPial
2.2.3 Catalyze
Project Overview: Catalyze was established in 2021 with the aim of providing user-friendly tools for community creation and management, event scheduling, and instant value transfer to the Web3 community. In September 2023, the CTZ token was launched on ICP, designed to reward communities on the platform. Looking ahead, Catalyze is committed to attracting key opinion leaders (KOLs) of the new internet and becoming the preferred platform for Web3 learning, community building, events, and seamless token transfers.
X: @catalyze_one
2.2.4 ShareX
Project overview: ShareX's mission is to revolutionize the Web3 sharing economy. This innovative platform aims to enhance the way digital assets are shared and managed, promoting a more interconnected and collaborative Web3 environment. ShareX's vision is to bridge the gaps in the sharing economy and introduce more efficient and decentralized sharing mechanisms. Currently, ShareX has joined the accelerator program jointly organized by ICP and ABCDE.
2.2.5 ICP Racer
Project Overview: ICP Racer is a social mini-program application based on Telegram, integrating the ICP ecosystem with Telegram's ecosystem of 900 million users to promote the mass adoption of ICP. ICP Racer has also joined the Web3Labs accelerator program.
X: @ICPRacer
2.3 DeAI
The AI sector is a key focus area for ICP, currently hosting over 60 AI projects, as shown in the figure below:

Here are selected projects for introduction:
2.3.1 DecideAI
Project Overview: A Web3 company focused on creating AI-based large language models (LLM) announced at the end of August that it had fully deployed its GPT-2 LLM via the ICP blockchain. This development leverages ICP's capabilities to support complex, compute-intensive applications, enabling Web3 developers to build, train, and improve specialized LLMs. In the future, DecideAI will also use ICP's Chain Fusion technology (which allows protocol-level blockchain integration) to expand its AI models to Ethereum and Solana. Following the announcement of full on-chain AI integration at the end of August, DecideAI's native token, DCD, experienced a 100-fold increase in the first week of September, with a current market value of approximately $50 million. It has over 20k users and has grown nearly fourfold in two months.
X: @DecideAI_
2.3.2 ELNA AI
Project Overview: Launched in August 2023, this is a community-driven decentralized platform for creating AI agents. Unlike other AI chatbots, where training data is selected by operators, ELNA allows users to upload their own data to the network and train AI models tailored to their specific topics of interest and applications. Once training is complete, ELNA deploys the AI assistants or agents onto the ICP blockchain. Users can continuously expand their AI's knowledge by adding new data.
X: @ELNA_DeAi
2.3.3 Chosen
Project Overview: Project Chosen is an AI-driven prediction market that was previously the first multi-mode prediction market based on zkSync Era and is now being deployed on the ICP network. The project has undergone audits by PeckShield and DeHacker, ensuring its security and reliability. Chosen enables users to earn rewards and generate sustainable income through activities such as making predictions, social sharing, and voting. Additionally, the integration of AI introduces significant opportunities for innovative features, such as creating prediction events and acting as a counterparty in predictions.
X: @ProjectChosen
2.3.4 MurphAI
Project Overview: Murph AI is an AI Hub built on the ICP (Internet Computer Protocol) ecosystem. By holding ICP tokens or ICP ecosystem tokens, users can access a variety of AI-powered products. Additionally, Murph AI provides essential infrastructure, including computing power and data, to support AI products within the ICP ecosystem, aiming to establish a comprehensive AI technology stack.
X: @murphai_io
2.3.5 NGPU
Project Overview: NGPU is a decentralized AI computing network dedicated to providing cost-effective and reliable GPU resources for various AI applications. Through innovative features such as task-based billing, intelligent resource allocation, and efficient data transmission, NGPU enables permissionless access, low latency, and high reliability in AI-driven services. Additionally, NGPU serves as an AI ecosystem partner of ICP.
X: @ngpu_ai
2.3.6 MemeFun.ai
Project Overview: Memefun.ai is a newly launched and emerging platform positioned as the "Pumpfun" on ICP (Internet Computer Protocol). Its goal is to empower everyone to easily create and launch their own memecoins. MemeFun not only provides creators with a platform to share their ideas and express humor but also offers users a more intuitive and interactive way to engage with Web3 and cryptocurrency culture. Currently, MemeFun is actively expanding its community in the Asia-Pacific region, including Japan and South Korea. What sets it apart is its innovative use of AI as the infrastructure for memecoins, such as employing AI for memecoin creation and community meme generation. This significantly lowers the barriers to issuing memecoins.
As the memecoin trend continues to gain momentum, memecoins on ICP have the potential to evolve into a universal financial and cultural phenomenon.
X: @memefunicp
2.3.7 SpotLabs
Project Overview: SpotLabs is a DeAI platform that provides businesses with a user-friendly interface to manage their security infrastructure. It offers a comprehensive set of tools and an ever-expanding plugin ecosystem, referred to as "Spots." These Spots enable the storage and AI-driven encryption of corporate data, ensuring accessibility to all members of the organization regardless of their technical expertise. SpotLabs achieved first place at the inaugural AI Hackathon held in March this year and was awarded a $10,000 grant from ICP.
2.3.8 Yuku
Project Overview: Established in January 2024, the platform encompasses a wide range of innovative fields, including NFT, Metaverse, Gateway, 3D Avatars, AI, Deflationary Mechanisms, ICP, and Multi-Chain (MultICPhain) technologies. The platform is built around three core modules: NFTs, the Metaverse, and AI Agents. Yuku's Metaverse space stands out with its unique design, allowing users to explore and experience the platform as guests without the need for wallet login or registration. This feature significantly lowers the barrier to entry and enhances the convenience of the user experience.
X: @yukuapp
2.3.9 Onicai
Project Introduction: Onicai is an AI-as-a-Service platform designed to deliver advanced AI solutions for projects within the ICP ecosystem. Its supported AI products include on-chain AI tools such as the conversational AI tool DeVinci and the on-chain language model ICGPT.
X: @onicaiHQ
2.4 CHAIN FUSION
Chain Fusion currently supports 49 protocols and has integrated Ethereum and EVM chains since the Tritium upgrade in May. Its applications include the following:
2.4.1 ckBTC
ICP Integration with Bitcoin Mainnet: Internet Computer (ICP) has become a Bitcoin Layer 2 solution without relying on cross-chain bridge mechanisms. The ICP network operates a Bitcoin light node and integrates threshold Schnorr signatures, enabling ICP smart contracts to sign Bitcoin network transactions directly at the protocol level. This includes functionalities such as inscribing ordinals, engraving runes, and trading Ordinals NFTs. Chain-Key Bitcoin (ckBTC), launched in April 2023, is a native token on the ICP chain that mirrors Bitcoin and represents an innovative DeFi solution. ckBTC enables fast, low-cost, cryptographically secure, and fully on-chain Bitcoin transactions, bringing true decentralization to DeFi and blockchain ecosystems. It is backed 1:1 by real Bitcoin and issued or redeemed through containerized smart contracts that anyone can verify. Every step of converting BTC to ckBTC and vice versa is decentralized, eliminating centralized custodians, cross-chain bridges, or traditional cloud providers as potential attack vectors. Users can mint ckBTC by sending real BTC to the smart contract or redeem ckBTC for BTC sent directly to their Bitcoin wallets.
2.4.2 ckETH
ICP Integration with Ethereum Mainnet: Beyond Bitcoin, Ethereum also benefits from Chain Fusion through the release of the EVM RPC Canister and the introduction of Chain-Key Ethereum (ckETH). ckETH serves as a twin token for ETH on the ICP network.
2.4.3 ckSol
ICP Integration with Solana Network: Similar to Ethereum, Solana integration is expected by late 2024.
2.4.4 BifiPal
Project Overview: BifiPal aims to transform Bitcoin’s financial landscape by leveraging ICP technology to enable bridge-free cross-chain transfers of BTC onto ICP while offering comprehensive financial protocols. Its goal is to address liquidity challenges and low returns associated with Bitcoin while creating a robust financial system for BTC and gradually introducing traditional financial services into the Bitcoin network.
X : @BifiPal
2.4.5 TAP Protocol
Project Overview: TAP is a Bitcoin Ordinals protocol supporting OrdFi (Ordinal Finance) by facilitating discovery and tracking of Ordinals. It introduces the TAP token standard, emphasizing simplicity and accessibility, with its key feature being "tapping," which streamlines transaction verification within the protocol. TAP includes mechanisms like Token-Send for efficient large-scale transfers, Token-Trade for text-based inscription transactions, and Token-Auth for third-party issuance of signed redeemable inscriptions.
The TAP protocol can be embedded into other chains, enabling secure communication with Bitcoin Layer 1 (L1). It supports interoperability with chains like Ethereum, ICP, XRP, and Aptos. By leveraging TAP's decentralized and secure capabilities alongside ICP’s programmable transaction signing, it brings true L1 programmability to Bitcoin.
X: @tap_protocol
2.4.6 BitSmiley
Project Overview: BitSmiley is a native DeFi project on Bitcoin that introduces innovative designs at both application and protocol levels. It pioneers the Fintegra framework, comprising three core components: a decentralized over-collateralized stablecoin protocol, a native trustless lending protocol, and an on-chain derivatives protocol.
The project will initially launch bitUSD, an over-collateralized stablecoin on the Bitcoin blockchain designed to address the lack of stable price-pegged tools in the ecosystem. Users can generate bitUSD by over-collateralizing BTC, allowing participation in all BTC blockchain DeFi protocols. Each bitUSD is backed by over-collateralized BTC and maintained through robust liquidation and repayment systems to ensure stability and asset security.
On November 6th, BitSmiley officially launched its $SMILE token after raising $10 million in funding across two rounds this year.
X: @bitsmiley_labs
2.4.7 Bioniq
Project Overview: Bioniq is a marketplace for Bitcoin Ordinals that leverages Internet Computer technology to save time and costs by bundling assets efficiently. The platform launched on its mainnet in November 2023 and has received investment from Polychain.
X: @bioniqMarket
2.4.8 Other Innovative Projects
Other projects utilizing Chain Fusion’s seamless functionalities include Helix Markets and Omnity, among others. This advanced technology continues to attract more developers and assets to the ICP ecosystem.
2.5 Initiatives for Building the ICP Ecosystem
The Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) ecosystem currently hosts nearly 300 decentralized applications (dApps). ICP continues to invest in ecosystem-building activities, demonstrating its commitment and determination to steadily expand its influence. Below are some of the key initiatives:
-
Collaboration with the United Nations to Deepen Engagement in Southeast Asia
ICP has established a long-term and stable partnership with the United Nations. For instance, in July this year, they jointly launched the "Universal Trust Credential" (UTC) initiative, leveraging blockchain technology to address financing challenges faced by small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The project began in Cambodia and aims to expand to 10 countries in the future. This collaboration not only provides technological credibility to ICP but also significantly enhances its influence in the Southeast Asian market. Through such practical projects, ICP further solidifies its role in empowering socio-economic development through blockchain technology.
-
Establishment of an AI Development Center
As mentioned earlier, with the rapid evolution of the digital landscape, countries worldwide are exploring the potential of blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and cybersecurity. AI has become a key focus area for ICP. Demonstrating both vision and action, DFINITY founder Dominic Williams visited Argentina in October 2024 to participate in a tech forum week, where he outlined plans to leverage ICP's transformative capabilities and foster collaborations with Argentina and Latin America's emerging tech sectors. Additionally, ICP partnered with local universities to organize bootcamps and hackathons, providing hands-on training for students and developers on new technologies. These efforts not only enhance the skills of Latin American developers but also showcase ICP's potential as a hub for technological innovation.
-
Global Hubs
ICP Hubs are centers established to increase global awareness of ICP while fostering ecosystem development in areas such as ICP-related development, collaboration, training, and Web3 program support. Currently, these hubs are located across regions including India, Latin America, Italy, Indonesia, Thailand, Turkey, North America, and East Africa.
-
Accelerator Programs:A Growth Platform for Entrepreneurs
In March this year, ICP partnered with Web3Labs to launch the "ICP X Web3Labs Accelerator," offering selected projects a comprehensive startup package that includes a $50,000 grant, technical training, market expansion support, and resource connections. This all-encompassing support not only helps projects within the ecosystem scale rapidly but also attracts more developers to join the ICP community. Additionally, ICP collaborates with other renowned partners in Asia such as ABCDE and Outlier Ventures to run accelerator programs—underscoring its emphasis on the Asian market.
-
Strategic Collaboration on Enterprise Wallets
In late October, ICP Hub Korea signed a strategic partnership agreement with IoTrust. IoTrust’s Wepin Wallet focuses on simplicity and ease of use—allowing enterprises with zero blockchain experience to integrate wallets into their applications quickly using simple SDKs and APIs. Through this partnership, Wepin will further promote its services within the ICP ecosystem while offering users innovative Web3 experiences. This collaboration not only enhances technical tools within the ecosystem but also strengthens ICP's practical value in enterprise services.
-
SNS Launchpad
The Service Nervous System (SNS) is a launchpad infrastructure introduced by the DFINITY Foundation in December 2022 for projects within the ICP ecosystem. It enables projects to issue tokens and deploy decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) with a single click, allowing any ICP holder to participate in token purchases.
To launch on SNS successfully, projects must complete two critical steps:
-
The project's whitepaper and tokenomics must receive majority approval from stakers on the Network Nervous System (NNS), known as neurons.
-
After token sales conclude, the total amount of ICP raised must meet or exceed the minimum threshold set by the project itself.
Once successfully launched on SNS, projects can transition into DAOs. For example, OpenChat completed its decentralized sale via SNS and became a DAO. Since then, numerous proposals have been submitted and voted on—ranging from website upgrades and smart contract enhancements to marketing campaigns, treasury fund allocation, and ecosystem group management.
According to official data, 30 projects have successfully launched as DAOs through SNS so far.
-

Here, it is important to distinguish between NNS and SNS mentioned earlier. Both NNS and SNS serve as the core governance infrastructure of the ICP network. The former (NNS) is responsible for governing the entire ICP network as a DAO, while the latter (SNS) is a "one-click" launchpad specifically designed to support ecosystem dApps. SNS facilitates advancements in areas such as open governance, tokenization, and transparency. It represents a continuation of innovation by ICP, building on the success of NNS.
3. Summary of Highlights
Within the vast Web3 ecosystem, few projects demonstrate the same commitment to foundational innovation and full-chain integration as DFINITY. In its publication "Internet Computer Mainnet and a 20-Year Roadmap", DFINITY outlines an ambitious 20-year development plan. This roadmap is not about "killing Ethereum" or becoming the number one player in crypto and blockchain but rather achieving the following milestones:
● 5 years (2026): Attracting more Web2 entrepreneurs and development teams to build products on the Internet Computer (ICP) network, making fundraising and DAO governance more accessible.
● 10 years (2031): Becoming an "open internet" for the tech industry, embodying the true essence of Web3.
● 20 years (2041): Evolving into an "open internet" larger than Web2, integrating seamlessly into everyday life.
Three years after its mainnet launch, DFINITY continues to make strides in key technological areas, steadily advancing toward its grand vision. Below are our key insights into ICP:
1. Robust Foundational Technology
● ICP's technical capabilities may not be directly reflected in its token price, but its transaction processing speed (TPS) is six times that of Solana, operating at "internet speed" with virtually unlimited scalability.
● Unlike many overhyped Web3 projects, DFINITY adopts a pragmatic approach, focusing on refining core technologies to steadily realize the vision of an "Internet Computer."
● While ICP's price faced market manipulation upon launch—beyond DFINITY's control—the project's mission has consistently been about delivering on technological promises.
2. Unmatched Cost Efficiency in Storage
● Storing 1GB of data on Ethereum for a year costs approximately $240 million, while Solana charges $840,000. In contrast, ICP achieves this for just $5 using stablecoin-denominated Cycles, avoiding cost fluctuations tied to token volatility. This makes ICP the most cost-effective blockchain storage solution.
3. Innovative NNS Governance Mechanism
● ICP's "Neuron" governance ties voting rights and rewards to staking amounts and durations. Approximately 60% of users have opted for an eight-year dissolve period, reflecting long-term confidence in ICP.
● More importantly, the Network Nervous System (NNS) governance system supports broader ambitions such as third-generation DAOs and "open internet services." Founder Dominic Williams envisions a future where DAOs replace traditional companies due to their advantages in automation, transparency, and direct rule enforcement.
4. Pioneering Decentralized AI
● The release of Cyclotron in July significantly enhanced ICP's computational power—nearly tenfold—approaching native CPU performance levels.
● This makes ICP the only blockchain capable of running smart contracts that fully execute tasks like on-chain facial recognition. For instance, DecideAI announced in August that it had fully deployed its GPT-2 large language model (LLM) on ICP—a first step toward running large AI models entirely on-chain.
5. 100% On-Chain Storage and Computation
● Beyond static data storage akin to Filecoin or Arweave, ICP uniquely enables dynamic data processing entirely on-chain. This includes large-scale computations such as training AI models—a groundbreaking capability in blockchain development.
6. "Chain Fusion" Technology
● Just as the internet connects disparate networks, blockchain needs a unifying force to bridge ecosystems—and Chain Fusion fulfills this role.
● For example, smart contracts on ICP can execute transactions based on events occurring on Ethereum or Bitcoin networks, opening new possibilities for decentralized finance (DeFi). Additionally, Chain Fusion integrates AI capabilities from ICP into other blockchains.
● Looking ahead, Chain Fusion aims to enhance seamless integration across blockchains while improving transaction speed, security, and user experience.
7. User-Friendly Account Abstraction and Privacy
● ICP offers a user account model resembling Web2 simplicity: users register once without needing wallets and can log into any application within the ecosystem via fingerprint or facial recognition.
● Furthermore, each application interaction generates a unique external ID for the same account, ensuring user privacy.
8. Network Security
● The ICP network comprises thousands of nodes globally, with over half operating 24/7 as active nodes forming part of the NNS to safeguard network security.
● Each decentralized application (dApp) relies on subnet architecture for security—subnets can consist of either fixed or randomly assigned node groups.
● Balancing scalability and decentralization within blockchain's "trilemma," ICP offers unparalleled flexibility for project teams.
9. Developer-Friendly Support System
● DFINITY provides a supportive environment for Web3 developers through initiatives like ICP Hub and accelerator programs alongside community resources and technical assistance. This encourages bold innovation and diverse application development.
As speculative narratives around financial investments wane, markets are returning to fundamentals—focusing on infrastructure services for the internet's foundation. The ultimate vision for ICP is to host all global software systems—a trajectory increasingly aligned with AI advancements. To achieve this vision, decentralizing AI becomes essential. By integrating AI capabilities into its roadmap—including successfully running AI models with millions of parameters on-chain—ICP has taken its first significant step toward this goal. While this path may initially seem challenging, it promises to become broader and smoother over time. Will DFINITY—or the Internet Computer network—draw closer to its 20-year roadmap? Only time will tell—but the future holds immense potential.
4.References
1.https://defillama.com/chain/ICP
3.https://sentient.foundation/introduction
5.https://medium.com/dfinity/announcing-internet-computer-mainnet-and-a-20-year-roadmap-790e56cbe04a