On August 7, another domestic AI startup released its own open-source and free commercially available AI macromodel: XVERSE-13B. The company, called Yuanxiang XVERSE, was founded by Yao Xing, former vice president of Tencent and founder of Tencent AI lab.
Since Meta released the open source and free commercial LLaMA 2 series of large models in July, a new wave of "open source" is brewing in the AI large model market.
On August 2, Baidu's AI model platform Wenxin Qianfan, announced that it had access to the full series of LLaMA2 open source models, and the number of large models that can be called by the platform has increased to 33, in addition to the 3 Wenxin models, the other 30 are open source models, including ChatGLM2, RWKV, MPT, Dolly, OpenLLaMA, Falcon, etc. The platform can also be called by the open source models, which can be called by the open source models.
A day after that, AliCloud also announced that it had joined the ranks of open source models. The open source Tongyi Thousand Questions 7 Billion Parameters model, including the generic model Qwen-7B and the dialog model Qwen-7B-Chat, both models are now online in the Magic Hitch community, open source, free and commercially available.
Interestingly, this positive attitude towards open source openness began with Microsoft, the big owner of the closed-source big model ChatGPT. on July 18th, Microsoft announced that it had teamed up with Meta to release an open-source commercially available version of the LLaMA 2 model to provide enterprises with a leveling off product for OpenAI and Google models. openAI OpenAI's monopoly in the AI modeling market seems to be "targeted" by the whole industry, even by its closest partners.
As the world's most recognized large language model, OpenAI's GPT-4 is the only large language model that a large number of users are willing to pay for.
The number one student in the class usually has no incentive to join a study group. Similarly, OpenAI has little reason or motivation to open source.
However, with LLaMA 2 fully open-sourced, more and more developers are jumping into the Meta and various open-source modeling camps. Just like Android fighting iOS with open source, a bunch of big open source AI models, are bypassing the technical barriers of GPT-4 and surrounding OpenAI with open source ecology.
Why open source?
When OpenAI just launched the plug-in feature, there were many people comparing the AI Big Model to the future Windows, iOS, and Android. now, with the release of LLaMA 2, the AI Big Model is not just about the features, but even the market landscape is moving in the direction of an operating system.
Initiated by LMSYS Org, a UC Berkeley-led organization, a ranking competition for Large Language Models (LLMs); the latest version of the ranking as of July 20 counts a total of 40 AI Big Models, and the top five are still Closed-Source Models (Proprietary), which are GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Claude's three models, respectively. However, the latter 34 models, except for Google's PaLM-Chat-Bison-001, are all Open Source models, of which 15 are Non-commercial (Non-commercial).
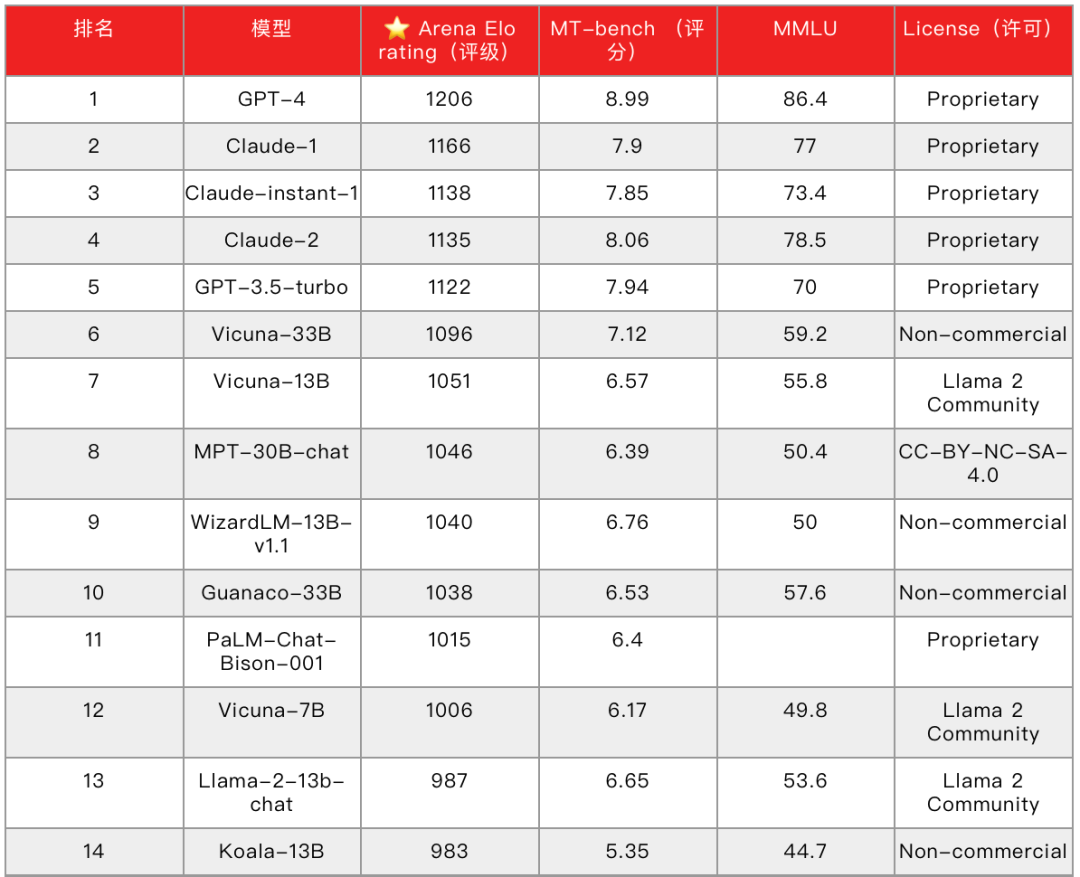
Although on the modeling ability, looking at the entire market, no matter open source closed source model can dare to compete with GPT-4. But the tiger can't stand up to the wolves, can't beat the GPT-4 big models, chose to "change the road to overtake", using open source to seize the application ecosystem, which seems to be somewhat similar to Android against iOS.
"Now, all the open source big models have only one purpose, that is, marketing."
A founder of a domestic open source big model research and development company confessed to Tiger Sense that the main reason for pushing open source big models and open source Android systems now is mainly to grab the market by free. "Many big companies released AI big models, or even just made an app based on an existing model, and started to publicize it with great fanfare. In fact, for the users of the underlying big models, spending more money on advertising is not as good as open-sourcing the models." This is also, the best way for AI companies to prove their strength.
First, open source models are easier to evaluate than closed models. Because the code and datasets of open-source models are publicly available, researchers can directly examine the model's architecture, training data, and training process, leading to more in-depth analysis of the model to understand its strengths and weaknesses.
"There are big AI models that seem to be very capable, but it's not open source and you can only see his output."
Compared to open-source models, closed-source models can only be evaluated by the performance of the model to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the model. This leads to the possibility that the performance of closed-source models may be artificially inflated or their shortcomings hidden. The transparency of open-source models, on the other hand, helps developers gain a deeper understanding of the model and evaluate it more fairly.
For late developers, closed-source models have another problem: they are prone to be questioned about the originality of the technology. A number of big model developers have told HuffPost, "For those models that are not open source, to put it mildly, even if they are shelling out LLaMA, or simply calling the ChatGPT interface in the background, who knows about it?"
When the first wave of domestic AI big models was just released, such skeptical voices were widely circulated on the Internet. For those AI big models that are not open source, it is very difficult to prove their innocence, and in order to prove that they are not calling ChatGPT's API, some companies even move out their reasoning servers and unplug their network cables on the spot to demonstrate.
Open source is undoubtedly one of the best ways for AI models to prove themselves. But the real value of open source is not the ability to self-evidence, but to seize the ecology.
"After LLaMA 2 comes out, it will certainly quickly seize the ecology of OpenAI." A big model developer told Tiger, although the strongest ability of GPT-4 is almost recognized in the industry, but the models after GPT-3 are not open source, and the degree of openness of the API interface of GPT-4 is very low, so there are a lot of limitations on the development of GPT models. As a result, many developers choose open source models such as LLaMA, which not only allow for instruction fine-tuning, but also allow for research on the underlying model.
"LLaMA is definitely more popular among developers than OpenAI."
When LLaMA 2 was first released on July 19, there were more than 5,600 projects on GitHub with keywords including "LLaMA" and more than 4,100 including "GPT-4." Two weeks after its release, LLaMA's growth rate is even faster, with more than 6,200 "LLaMAs" and more than 4,400 "GPT-4s" as of this writing.
On the other hand, open source models can be downloaded locally for private deployment, which facilitates AI training for commercialized companies. The AI applications of such companies need to be trained based on their own business data, and the privately deployed AI models can maximize data security. At the same time, the privatized deployment has more choices of arithmetic, whether it is cloud services, local deployment, or even distributed arithmetic of multiple IDCs, which greatly lowers the cost of model training and inference.
Although ChatGPT has harvested 100 million monthly users in only 2 months, the speed of open source models in the developer ecosystem to seize the minds of users, seems to be faster.
At present, many domestic AI companies have chosen to release open source models. These include, among others, ChatGLM-6B, an open source model released by Smart Spectrum AI, MOSS released by Fudan University, Wudao Skyhawk Aquila released by Zhiyuan Research Institute, and Baichuan Intelligence's Baichuan-7B (13B). Among them, ChatGLM-6B, the open source grand model released by Wisdom Spectrum AI, has more than 4 million downloads globally, and has received 32,000 stars on GitHub, which is 3,000 stars more than LLaMA.
"If we don't make an open source model, then the market will soon be all LLaMA." An executive from an AI company that has already launched an open-source model told HuffPost that open-source is an important step in the development of China's big AI models.
lit. open source with goods
LLaMA 2 is currently open-sourced, with all three of the models in the series: the 7 billion, 13 billion, and 70 billion parameter versions. However, there are rumors going around that "Meta actually has larger parameter versions that have not been released, and the next release may have larger parameter versions that will not necessarily be open source."
It is worth noting that many of the current open source models are not all open source. Wisdom Source Research Institute released Wudao 3.0 model, only open source "Sky Eagle" basic language model; ChatGLM released by Chip AI, only part of a series of open models, the larger 130 billion parameter model is still closed source.
Regardless of whether LLaMA 2 "left a hand" for larger models, but the "free" form will undoubtedly accelerate the formation of Meta in the large model market, and push it to go on Android's "old way! "The free form will undoubtedly accelerate Meta's formation in the large model market and push it down the same path as Android.
Through the open source ecosystem, Android system has accumulated a large number of developers and users in the world. It has greatly checked and balanced the pioneer closed-source system iOS in terms of technology ecology, and has even formed its own monopoly in some markets. Since the beginning of 2018, the European Union has issued a fine of more than 4 billion euros to Google for the monopoly mechanism of the Android system. From this astronomical fine, it can also be seen how lucrative the open source Android system is.
A report by research firm Sensor Tower shows that user spending on Google Play will be about $53 billion in 2022, a figure that will increase to $60 billion in 2023. Another research firm, Statista, released a report that as of January 2022, there were about 140,000 apps in the Google Play store.
At this stage, it is clear that the big open-source AI models do not reach the popularity of cell phones. However, even if AI does become as popular as cell phones, giants such as Meta will not easily let go of companies that have made big money with the help of LLaMA 2.
LLaMA 2 open source agreement, there is such an agreement: if the monthly active users more than 700 million, you must apply for a license to Meta. meta can decide whether to authorize you, and you do not have the right to exercise any rights.
At the same time, the open source model can not only "bring goods" closed-source version, as well as AI large model applications, but also help computing power "bring goods".
The first two vendors to push the AI model, Baidu and Ali, are cloud vendors. The other two cloud vendors, Tencent Cloud and Huawei Cloud, although they do not have LLMs products like Wenxin Yiyin and Tongyi Thousand Questions, they also continue to shout AI big model. The main reason behind this is that the big model of the cloud's "bandwagon effect".
"The announcement of some AI big model aspects of the action, but also the market and customers together to promote. In the past few months, there are too many customers asking for big models." A Tencent cloud business leader told Tiger Sense that the arithmetic queue is the best proof of the ability of the AI big model to bring goods.
The model can not make money, but the arithmetic power must be profitable. Ali open source Tongyi thousand questions, Baidu in the Wenxin Qianfan large model platform to introduce 30 open source models, these two actions are to "free" AI capabilities delivered to the user. Users with open source models, although no longer pay for AI, but as long as their AI runs on the Ali Cloud and Baidu Intelligent Cloud, they have to pay for computing power.
"AI is also going back to the cloud idea of making cloud money." Xin Zhou, general manager of AI and big data platform of Baidu Intelligent Cloud, said that the original intention of the open big model platform is to create value for the customer's business, and the creation of value can enhance the stickiness of old customers and expand more new customers. This is a great help in expanding the scale effect of cloud vendors.